Definition
A private Cargo registry serves as a centralized, controlled repository for Rust Cargo crate packages, offering enhanced security and reliability for software development. It allows organizations to host their own crates internally, separate from public registries.
Overview
A private Cargo registry is a self-hosted or privately managed repository for Rust programming language packages, known as “crates.” Its primary purpose is to provide a controlled environment for storing, managing, and distributing internal or proprietary Rust code, as well as caching external cargo crate dependencies. This allows for greater control over the software supply chain, ensuring that cargo crate assets are securely and efficiently managed.
Advantages of Using a Local Registry
Using a local registry offers several key advantages for development teams:
- Provides enhanced security by keeping proprietary code within the organization’s infrastructure.
- Allows for tighter control over which cargo crate versions are used, mitigating risks from public registry issues.
- Improves build speeds by caching frequently accessed dependencies, reducing reliance on external network access and ensuring consistent build environments.
How a Private Cargo Registry Differs from a Public Registry
A private Cargo registry fundamentally differs from a public registry like crates.io in its scope and control. Public registries are open-source platforms accessible to anyone, hosting a vast collection of cargo crate packages for general use. In contrast, a private Cargo registry is typically hosted internally within an organization, providing exclusive control over package access, versioning, and security policies. This distinction is critical for managing proprietary code, sensitive dependencies, and ensuring compliance with internal security standards.
Use Cases for Docker from a Private Cargo Registry
Private Cargo registries are particularly useful in scenarios involving Docker and container images, where consistent and secure access to cargo crate dependencies is crucial. Organizations can use a private registry to store custom-built Rust applications and their dependencies, which are then integrated into Docker images. This ensures that builds are reproducible and that applications deployed as Docker containers always pull trusted and verified cargo crate versions, enhancing the security and reliability of the deployment pipeline.
How to Run a Private Cargo Registry – Infrastructure Options
Organizations have several options for establishing a private Cargo registry, each offering different levels of control, complexity, and integration with existing development workflows. The choice of infrastructure often depends on factors such as the scale of development, security requirements, and existing DevOps tooling.
Install crates.io Locally
One method for creating a private Cargo registry is to install crates.io locally. This involves mirroring the public crates.io registry on internal infrastructure. This approach can provide fast access to public crates and reduce external dependencies. However, it also requires significant storage and maintenance to keep the local copy synchronized with the upstream public registry, demanding a robust package management strategy.
Use a Git Repository as a Private Cargo Registry
A common and relatively simple method for a Rust private Cargo registry is utilizing a Git repository. Developers can publish crates to a private Git repository, and Cargo can be configured to fetch dependencies directly from it. This method offers straightforward version control and integrates well with existing Git-based workflows, making it a flexible solution for smaller teams or projects with less stringent requirements for a local registry.
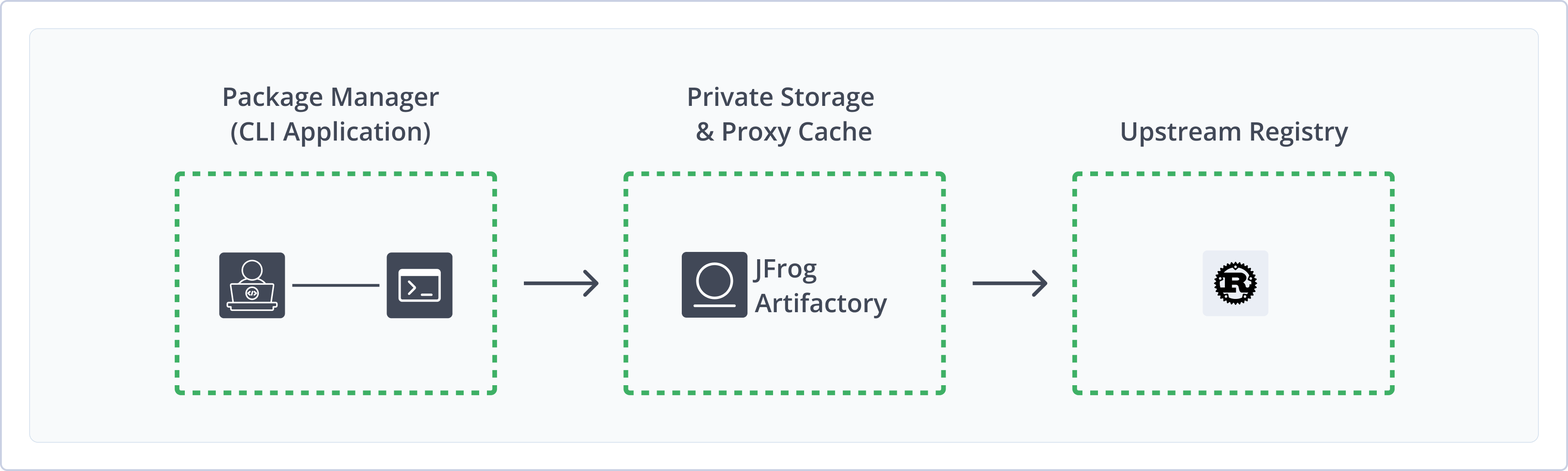
Use JFrog Artifactory as a Private Cargo Registry
Using JFrog Artifactory as a private Cargo registry provides a robust, enterprise-grade solution for managing Rust packages. Artifactory, as a universal binary repository manager, supports Cargo alongside other package types, offering advanced features like high availability, replication, fine-grained access control, and comprehensive security scanning. This approach centralizes all software artifacts, including cargo crate packages, within a single platform, streamlining package management and enhancing the overall software supply chain security.
Setting up a Private Cargo Registry
Setting up a private Cargo registry involves making strategic decisions about the hosting environment and implementing a series of technical steps to ensure its functionality and security. Proper configuration is key to a reliable and efficient private registry.
Choosing the Right Infrastructure for your Private Cargo Registry
Selecting the appropriate infrastructure for your private Cargo registry depends on your organization’s specific needs, including scalability, security, and ease of maintenance. Options range from self-hosting on a dedicated server using a Git repository or crates.io locally to leveraging a comprehensive software artifact repository like Artifactory. Cloud-based solutions also offer flexibility and managed services, reducing operational overhead.
Step-by-step Guide to Installing and Configuring a Private Cargo Registry
Installing and configuring a private Cargo registry involves several steps tailored to the chosen infrastructure. For a Git-based registry, this includes initializing a bare Git repository, configuring Cargo to use it as a registry, and managing access permissions. For solutions like Artifactory, the process typically involves setting up a new Cargo repository within the platform’s UI, configuring proxy settings for external dependencies, and defining user access policies. Regardless of the method, proper repository setup and network configuration are essential for smooth operation.
Best Practices for Securing and Managing Access to Your Private Cargo Registry
Securing and managing access to your private Cargo registry is paramount to protect your intellectual property and maintain software supply chain integrity. Best practices include implementing robust authentication mechanisms, such as API keys or token-based authentication, and enforcing strict access control policies (local registry). Regularly auditing access logs and integrating the registry with existing identity management systems can further enhance security. Additionally, encrypting data at rest and in transit, and performing regular vulnerability scanning of stored cargo crate packages, are vital for preventing unauthorized access and mitigating risks.
Integrating with Existing Workflows
Integrating a private Cargo registry into existing development and deployment workflows is crucial for maximizing its benefits, ensuring seamless operations, and maintaining developer productivity. A well-integrated registry becomes a natural extension of the development pipeline, providing a consistent, secure source for all Rust dependencies.
Steps for Seamless Integration
Integrating a private Cargo registry seamlessly into your development process involves several key steps:
Update Local Cargo Configuration:
- Developers must configure their local Cargo settings (typically the
.cargo/config.tomlfile) to prioritize the private registry for internal crates. - The configuration must also ensure a fallback to public registries (like
crates.io) for external dependencies that aren’t mirrored internally. - This ensures that crate resolution is efficient and consistent across all development environments.
Implement Proper Authentication:
- Set up secure authentication methods (such as API tokens or SSH keys, depending on the registry type) to ensure only authorized developers and CI/CD systems can access and publish packages.
Configure CI/CD Pipelines:
- Update your Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines (e.g., Jenkins, GitLab CI, GitHub Actions) to use the private registry for fetching dependencies during the build process.
- Ensure the pipeline environment has the necessary authentication credentials.
Document the New Workflow:
- Create clear and comprehensive documentation detailing how to configure local setups, how to publish new internal crates, and how the CI/CD system handles dependencies.
Provide Developer Training:
- Conduct training or information sessions for developers to ensure a smooth transition and rapid adoption of the new dependency management workflow.
Automating Package Publishing and Consumption
Automating the publishing and consumption of packages from your private Cargo registry is essential for a truly efficient DevOps workflow. This involves integrating the registry with your CI/CD pipelines, enabling automatic publishing of new cargo crate versions upon successful builds and tests. On the consumption side, CI/CD pipelines and developer environments can be configured to automatically pull dependencies from the private registry, ensuring that builds are always using the most up-to-date and approved internal cargo crate packages, while also leveraging caching for external ones. This automation reduces manual overhead, minimizes errors, and accelerates the release cycle.
Compatible Tools and Platforms for Working with a Private Cargo Registry
A private Cargo registry can integrate with various tools and platforms commonly used in modern DevOps and software development environments.
- CI/CD platforms like Jenkins or GitLab CI, which can automate the publishing and consumption of Cargo crate packages.
- Container platforms such as Docker and Kubernetes also benefit from a private registry by ensuring secure and consistent access to Rust private cargo registry dependencies within containerized applications.
- Binary repository manager solutions like JFrog Artifactory offer native support, providing comprehensive management capabilities beyond basic storage.
JFrog Artifactory as a Private Cargo Registry
A private Cargo registry is crucial for secure, efficient Rust development, offering advantages like enhanced control over dependencies, improved build times through local registry caching, and compliance with internal security policies. By implementing a private registry, organizations gain granular control over their software supply chain, mitigating risks associated with public repositories and ensuring the integrity of their Rust cargo crate assets. This investment streamlines development workflows, making software delivery faster and more reliable.
Key Features of JFrog for Private Cargo
The JFrog Platform offers a robust solution for managing private Cargo registry needs, integrating seamlessly with your existing DevOps and DevSecOps practices. This comprehensive approach empowers your teams to deliver trusted software with speed and confidence.
Key features and benefits of using JFrog for your private Cargo registry include:
- Universal Package Management: JFrog Artifactory serves as a central hub for all binaries, including Rust cargo crate packages, consolidating management across your technology stack.
- Sophisticated Security Scanning: Integrates with JFrog Xray for Software Composition Analysis (SCA), providing advanced security scanning to detect vulnerabilities in your dependencies.
- Fine-Grained Access Control: Allows you to set precise permissions, ensuring secure access and integrity for your private packages.
- Full Traceability: Provides complete visibility and an audit trail for all your crate assets, supporting compliance and supply chain security.
- Centralized Asset Integrity: By centralizing your Cargo crate assets, JFrog helps you maintain the integrity of your software supply chain.
Ready to enhance your Cargo crate management and secure your software supply chain? Start your free trial of the JFrog Platform today to experience streamlined package management, robust security scanning, and full control over your private Cargo registry. You can also schedule a demo with a JFrog expert to see how our solutions can be tailored to your specific needs.