Definition
An agentic repository is an intelligent system that applies the principles of agentic AI to the software development lifecycle. By integrating autonomous AI agents, it moves beyond the static function of storing binaries and artifacts to become an active, decision-making component of the software supply chain. This innovation fundamentally changes how developers interact with their artifact repositories, allowing for automated, dynamic, and context-aware operations.
Summary
- An agentic repository is a new type of software repository that uses AI agents to automate and optimize the software delivery process.
- Unlike a traditional, passive repository, an agentic one is an active, intelligent system that can reason about its goals, make decisions, and execute complex workflows on its own.
- It significantly improves collaboration, code quality, and deployment speed by autonomously handling repetitive and time-consuming tasks.
- While offering powerful benefits, it also introduces new security challenges that require robust governance and trust frameworks to manage.
- JFrog Fly is a pioneering example of an agentic repository, transforming the software artifact repository into a proactive, intelligent engine for modern software development.
How Does an Agentic Repository Work?
An agentic repository uses AI agents to execute dynamic, goal-oriented workflows rather than static, predefined instructions. An AI agent is a system that can perceive its environment, reason about its goals, and take actions to achieve them. In the context of a repository, these agents can be tasked with complex objectives like “update all dependencies for the latest security patches” or “prepare a semantic release for production.” The agent then breaks down the goal into smaller, manageable steps, such as identifying dependencies, fetching updates from a remote repository, testing the new versions, and updating the metadata. This multi-step, iterative process allows for real-time adaptation and problem-solving, which is a significant advancement over traditional automation.
Key Components of an Agentic Repository
An agentic repository is built on a foundation of core components that enable its autonomous and intelligent functions. Each component plays a critical role in facilitating the dynamic behaviors of AI agents, transforming a traditional repository into an active participant in the software lifecycle.
AI Agents
AI agents are the central intelligence units of the system, capable of acting autonomously to achieve specific goals. Unlike simple scripts, AI agents can use reasoning and planning to break down complex tasks and adapt their behavior based on real-time data and feedback. In a repository, agents might be specialized for tasks like security scanning, license compliance, or release management.
AI Agent Frameworks
An agentic framework provides the foundational structure for building and managing intelligent, autonomous systems. These frameworks provide the tools and protocols for agents to communicate, coordinate, and orchestrate complex tasks. They simplify the development of sophisticated multi-agent systems by providing a blueprint for agent interaction and workflow execution.
Agentic Workflows
An agentic workflow is a series of interconnected, dynamically executed steps that an agent or group of agents performs to achieve a specific goal. Rather than following rigid rules, these workflows are adaptive and can self-correct based on outcomes. This enables them to handle complex, unpredictable scenarios that would cause a traditional, rule-based automation script to fail. The workflow is not a static script but a dynamic plan created and executed by the agents themselves.
Agentic Workflows vs. Traditional Automation
The primary difference between agentic workflows and traditional automation lies in their adaptability and intelligence. Traditional automation, such as a CI/CD pipeline, follows a fixed, pre-programmed sequence of steps. If a step fails or an unexpected event occurs, the workflow typically stops or requires manual intervention. Agentic workflows, on the other hand, are dynamic and goal-driven. An AI agent can reason about a failure, make a new plan, and attempt to self-correct without human oversight. This capacity for autonomous action allows agentic workflows to handle complex, non-linear problems and adapt to changes in the environment.
| Feature | Agentic Workflows | Traditional Automation |
|---|---|---|
| Execution | Dynamic, goal-driven, and adaptive | Static, rule-based, and deterministic |
| Decision-Making | Autonomous, based on reasoning and planning | Pre-defined, based on static rules |
| Adaptability | High; can self-correct and handle unexpected events | Low; typically requires human intervention on failure |
| Use Case | Complex, multi-step tasks like semantic release management or automated dependency updates | Repetitive, well-defined tasks like building a project or running a simple test suite |
Benefits of Using Agentic Repositories
Agentic repositories provide a number of advantages by using autonomous AI agents to manage complex and dynamic software tasks. These benefits lead to a more efficient, collaborative, and secure software development lifecycle.
Enhances collaboration among development teams
By automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks, agentic repositories allow developers to concentrate on more strategic and creative work. According to DORA research, the use of AI in software development improves overall productivity and job satisfaction among technology professionals. Agentic systems also facilitate better cross-functional teamwork by providing a shared, intelligent platform where different specialized AI agents can collaborate to solve complex problems, such as a release management agent working with a security agent to ensure a build is both functional and secure. Teams responsible for various aspects of the software development lifecycle can work better together within this unified platform.
Improves code quality and deployment speed
Agentic repositories directly contribute to higher code quality by continuously enforcing coding standards and performing automated security scans. They can run tests, debug code, and even make corrections without human intervention, which helps catch issues earlier in the development process. This automated approach, combined with the ability to manage complex tasks like semantic releases, significantly accelerates the deployment speed and allows for faster, more frequent software updates.
Facilitates integration with AI-driven tools
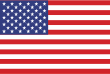
Agentic repositories are built to work seamlessly with a wide array of AI-driven tools and frameworks. They can use protocols like Model Context Protocol (MCP) to communicate with other AI platforms, ensuring that agents can access relevant data sources and tools, such as security scanners and package managers, to execute complex workflows. This integration capability allows organizations to create a cohesive ecosystem of intelligent tools that enhance every stage of the software delivery process.
Security, Governance, and Trust in Agentic Repositories
The autonomous nature of agentic repositories introduces new security and governance challenges that require careful management. Given that AI agents can execute code and make decisions, ensuring their actions are secure, auditable, and compliant with organizational policies is paramount.
Addressing Security Challenges
Because agentic repositories can autonomously interact with the software supply chain, they create new Application Security (AppSec) considerations. A key challenge is safeguarding against prompt injection attacks, where a malicious actor provides a natural language prompt that manipulates an agent’s behavior. Another concern is the potential for agents to introduce vulnerabilities or non-compliant dependencies without proper oversight. To mitigate these risks, agentic repositories must implement robust security features like:
- Zero-trust architectures: Ensuring all agent actions are verified and authenticated, regardless of their origin.
- Explainable AI (XAI): Providing clear, human-readable explanations for every decision an agent makes, enabling auditing and debugging.
- Automated guardrails: Enforcing strict policies that prevent agents from performing unauthorized actions, such as introducing known vulnerabilities or accessing sensitive data without permission.
The Role of Governance and Trust
Governance frameworks for agentic repositories extend beyond technical controls to include policies that define the scope and authority of AI agents. Establishing trust requires transparency and accountability. Organizations must create clear frameworks that define an agent’s autonomy levels, data usage rights, and decision-making responsibilities. In doing so, they can ensure that as AI agents become more deeply integrated into a company’s operations, the organization can confidently manage risk and maintain control. The goal is to treat governance not as a hurdle but as a fundamental enabler that builds stakeholder trust and allows for the safe and scalable adoption of agentic AI.
How Agentic Repositories Improve Security, Governance, and Trust
While agentic AI comes along with a set of security and governance considerations, it must also be noted that the proper utilization of agentic repositories can serve to enhance an organization’s security posture and compliance as well.
Security: By using intelligent automation, agentic repositories provide a proactive approach to security and compliance. They can continuously monitor and analyze the software supply chain for vulnerabilities and policy violations, providing a new level of diligence that surpasses manual checks. This is accomplished by integrating security scanning tools directly into the agentic workflows, ensuring that every artifact is vetted before it is used.
Governance: The ability of agents to provide clear, auditable explanations for their actions through Explainable AI is also crucial, as it builds transparency and trust, allowing teams to verify decisions and maintain compliance with governance policies.
Implementing an Agentic Repository in Your Workflow
Transitioning to an agentic repository is a strategic move that involves more than just a new tool. The process begins with integrating the new technology into existing CI/CD environments. Unlike traditional repositories, which are primarily storage systems, an agentic repository is deeply integrated into the development workflow, often operating within a larger DevOps or DevSecOps pipeline.
The implementation of an agentic repository requires a shift in mindset from treating the repository as a passive storage unit to an active, intelligent partner in the software delivery process.
Future Trends in Agentic Repositories
As the field of AI continues to evolve, the future of agentic repositories is moving toward greater autonomy, collaboration, and integration.
- Multi-Agent Collaboration: We will see more sophisticated systems where multiple specialized AI agents work together to solve complex problems, such as a release management agent collaborating with a security agent to ensure a build is both functional and secure.
- Explainable AI: The demand for transparency and trust will drive the development of more advanced XAI capabilities, making it easier for developers to understand an agent’s reasoning and actions.
- Hyper-personalization: Agentic repositories will adapt workflows and optimize processes for individual developers and teams, creating a more personalized and efficient experience.
- Edge-Based AI: For low-latency and high-privacy use cases, agentic capabilities will increasingly be deployed on-premises or at the network edge, enabling real-time decision-making without reliance on cloud-based systems.
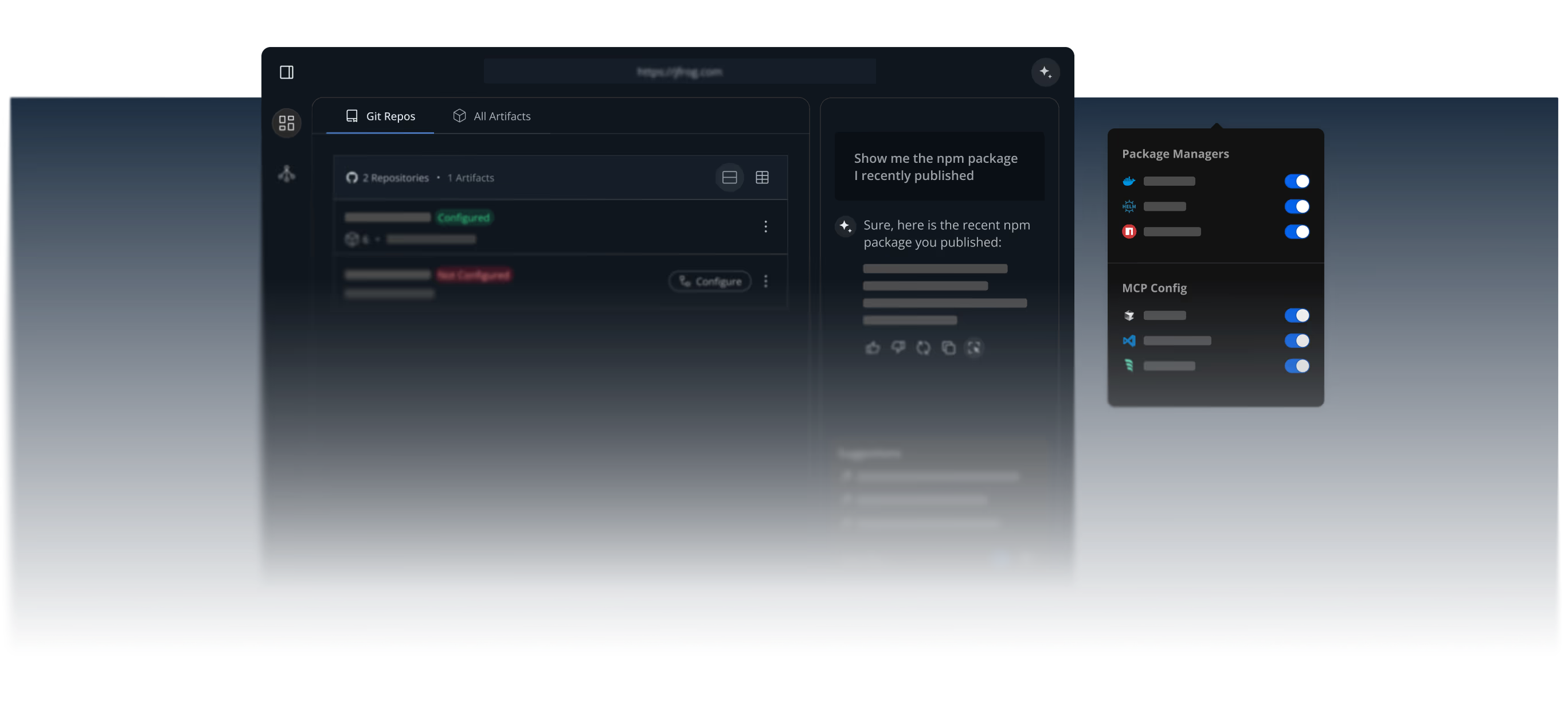
JFrog Fly: The World’s First Agentic Repository
The JFrog Platform is built on a foundation of repository management and software supply chain solutions, providing a single system of record for all software packages. With the introduction of JFrog Fly, JFrog is taking the next step in this evolution.
JFrog Fly introduces the world’s first agentic repository. It is a zero-config, AI-native system designed to support modern agentic workflows for development teams. By leveraging AI agents, JFrog Fly automates complex software delivery tasks, allowing developers to focus on innovation and accelerate the pace of software releases. The technology is designed to integrate with existing development environments and tools, offering a zero-hassle, AI-driven experience that brings automation and scale to AI-native software delivery. JFrog Fly is designed to be the future of the software artifact repository, transforming it into a proactive, intelligent engine for modern software development.
To learn how the JFrog Platform helps you manage your software artifacts, automate your CI/CD workflows, and secure your software supply chain, book a demo or start a free trial at your convenience.