Navigating DORA Compliance: Software Development Requirements for Financial Services Companies
Note: This blog was updated May 1, 2025
Regulatory compliance is a common and critical part of today’s rapidly evolving financial services landscape. One new regulation that EU financial institutions must adhere to is the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA), enacted to enhance the operational resilience of digital financial services. The BCI Supply Chain Resilience Report 2024 highlighted that 80% of organizations experienced supply chain disruptions, marking a significant increase from the previous year. This shows the lingering impact of Information and Communications Technology (ICT) resilience issues on operational continuity.
DORA compliance entered into application as of January 17, 2025. ICT encompasses a wide array of technological tools and resources employed for communication, content creation, information dissemination, storage, and management. This comprehensive term includes electronic devices, networking components, and software applications that facilitate diverse forms of digital communication and information handling.
In terms of the financial services sector, DORA applies to insurance companies, investment firms, banks, fintech, and ICT vendors, who must understand and adhere to DORA requirements to ensure operational resilience and avoid substantial fines. This blog post discusses the essential software development requirements financial companies should meet to assist in complying with DORA.
What is DORA?
DORA is a regulation enacted by the European Union to enhance the digital operational resilience of financial institutions, to ensure that financial entities can withstand and recover from all types of technology-related disruptions and threats.
The goal of DORA is to enhance operational resilience across the financial sector, even in cases of severe operational disruptions. The regulation emphasizes the need for financial institutions to establish robust capabilities for:
- Protection: Safeguarding against technology-related incidents
- Containment: Limiting the impact of disruptions
- Detection: Identifying incidents promptly
- Recovery: Restoring services efficiently
- Repair: Fixing any damage caused by an incident
Who Needs to Comply with DORA?
DORA applies to a wide range of financial organizations operating in the EU. Over 22,000 entities are estimated to be impacted by DORA, making compliance essential for regulatory adherence and business continuity.
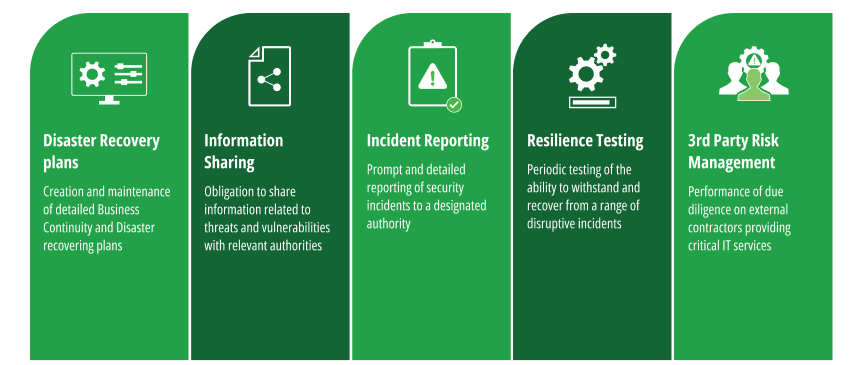
The 5 Key Software Development Requirements
DORA compliance covers many areas. Let’s take a closer look at how the wider guidelines specifically affect software development operations and processes. To bring this from theory into practice, we present each of the five core pillars and suggest what steps to take to ensure compliance from a software development perspective.
- Governance and Robust ICT Risk Management Framework
Financial companies must identify and assess potential vulnerabilities within their software systems while Implementing mitigation strategies to reduce the impact of identified risks - Information & Intelligence Sharing
This refers to the exchange of cyber threat intelligence among organizations to build collective resilience against cyber threats and enhance the sector’s overall preparedness and response capabilities. - Incident Reporting and Response
To comply with procedures for timely incident detection and response, DevOps must implement logging and monitoring solutions that detect anomalies and prevent potential security incidents. In addition, DevSecOps has to establish a clear incident response plan that outlines steps for containment, eradication, recovery, and post-incident analysis. - Digital Operational Resilience Testing and Assessments
Continuous testing is vital to maintain the resilience of financial software systems. This should include penetration testing, vulnerability assessments, and disaster and business recovery planning. - Third-Party Risk Management
Financial companies often rely on third-party providers for software and technology-related services. To comply with DORA, it’s essential to perform due diligence on their suppliers’ security practices, stipulate contractual adherence to security and resilience standards, and monitor third-party security practices.
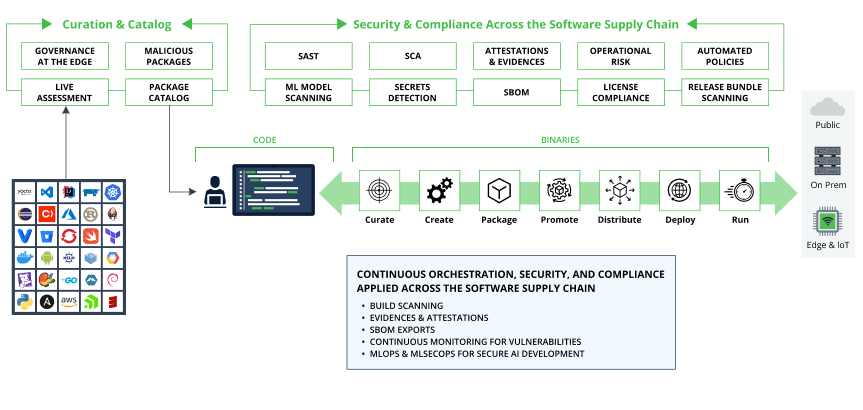
Coding for DORA: Putting it into Practice
Adhering to other regulations like the Cybersecurity Resilience Act (CRA) in the EU and NIST SP 800-218 Secure Software Development Framework (SSDF), and the U.S. EO 14028 Cybersecurity Executive Order requires security, risk, and compliance practices to be followed in a similar way to DORA. So, how do you translate these DORA pillars into concrete software development practices? Here are some key takeaways on how to do that:
- Secure by Design: Integrate security considerations throughout the SDLC. This could involve threat modeling, secure coding practices, vulnerability scanning, code reviews, static code analysis, secure package curation, and dependency resolution.
- DevSecOps: Break down silos between development, security, and operations teams, while fostering a collaborative environment where security is everyone’s responsibility and you achieve continuous scanning of your software across your supply chain.
- Automate for Efficiency: Utilize automation tools for vulnerability scanning, security testing, package curation, and incident response. This frees up developer time and streamlines the process
- Logging and Monitoring: Implement robust logging and monitoring practices within your applications. This allows for early detection of anomalies and potential security incidents. In addition, teams should look at managing security risks throughout their SDLC to maintain a single system of record.
Penalties for Noncompliance
Financial institutions failing to achieve DORA compliance may face strict penalties of up to one percent of their average daily worldwide turnover for each day of noncompliance.
How JFrog can help EU Financial Institutions comply
JFrog’s security solutions including JFrog Xray, JFrog Advanced Security, and JFrog Curation can help financial services companies comply with DORA software development regulations. JFrog’s security solutions offer financial institutions a holistic suite of software supply chain security and compliance tools, essential for DORA compliance. Compliance is one of the most challenging aspects of doing business for Financial institutions as they adhere to strict regulatory frameworks like OCC, GDPR, PCI DSS, SOX, and NIST which mandate secure and compliant software development practices, data privacy, and corporate governance. The JFrog Software Supply Chain Platform serves as the foundation for these security and compliance practices and is used by the majority of large financial institutions across the world.
The JFrog Platform ensures continuous identification, prioritization, tracking, monitoring, management, and suggestions for remediation of potential vulnerabilities across the software development lifecycle. The solution leverages automated configurable policies, which can be tailored to assist in compliance with DORA or other regulations-specific requirements.
For example, curating vulnerability-free, non-malicious, and non-operationally risky open-source libraries, and packages can help with DORA’s security fundamentals and risk reduction intent. JFrog’s holistic software supply chain approach to security and compliance puts it in a prime position for helping financial institutions with their DORA compliance and can be applied to future financial services or other industry security and compliance regulations in the future.
A Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) is an essential tool for understanding the components included in your production release. JFrog’s automated SBOM generation feature provides release managers, QA, and security teams with a detailed inventory of what is slated for production including any identified security vulnerabilities and license compliance issues. JFrog’s SBOM exports support industry-standard formats such as SPDX and CycloneDX (CDX) and support the recently introduced VEX format.
The JFrog Platform helps break down the silos that can build up between development, security, and operations teams. JFrog can facilitate a collaborative DevSecOps environment where everyone is on the same page and security is top of mind.
Conclusion
Complying with DORA is not just about meeting regulatory requirements; it’s about fostering a resilient and secure digital environment for financial operations. DORA emphasizes the operational resilience of financial institutions to ICT disruptions and requires financial institutions to establish and maintain ICT risk management frameworks and regularly test their resilience.
By embedding robust risk management, secure software development practices, and continuous testing into the software development lifecycle, financial companies can ensure they are well-prepared to tackle the challenges of the digital age. Staying informed and proactive is key to maintaining operational resilience and safeguarding the integrity of financial services. DORA is not just about ticking boxes; it’s about building a resilient foundation for the stability of the entire financial services system. Remember, secure code is the key to a secure financial future!
Book a demo or take a product tour to see for yourself how JFrog can help make your software development operations DORA-ready while preparing for emerging standards coming down the road.
Disclaimer: The content provided in this article is for general information purposes only and does not constitute legal advice. The content may not reflect current legal developments, is not guaranteed to be correct, complete, or address your situation, and should not be relied upon.