Migrate NGINX from “stable” Helm Charts Repo with ChartCenter
UPDATE: As of May 1, 2021 – ChartCenter central repository has been sunset and all features deprecated. For more information on the sunsetting of the centers read the Centers deprecation blog post
For the last four years, anyone wanting to deploy the Ingress NGINX Controller for Kubernetes would find its official Helm chart nginx-ingress in the stable repository maintained by the Helm project.
Those days are over. And not just for NGINX, the most popular Ingress Controller used as a reverse proxy and load balancer, but for all open-source K8s apps.
With the advent of Helm 3, the Helm project is deprecating the stable repositories. As of November 2019, no new charts were to be accepted to stable as chart owners transition to individual repos. That transition period is now over — stable repos have been delisted from Helm Hub, and will be officially obsolete this coming November.
What does this mean for installers and maintainers of NGINX deployments? To start, The NGINX project now maintains a new ingress-nginx Helm chart in the GitHub repositories for Kubernetes. Anyone installing or updating a deployment of NGINX Ingress Controller should now use the chart from this repo.
Even though the new chart currently deploys the same version of the NGINX app, it isn’t identical to the chart in stable. This requires some adjustment when updating an NGINX installation in place with the new chart.
Let’s take a look at what’s involved, and also how JFrog ChartCenter can help you transition.
A Central Helm Repository
The stable set of Helm charts meant that official charts for many popular Kubernetes apps could always be found in a central repository. You would simply add the stable repo to the Helm client:
$ helm repo add stable https://kubernetes-charts.storage.googleapis.com/
From this single stable repository, you could confidently deploy nginx-ingress using the latest author-approved Helm chart.
As the stable repository is nearly obsolete, it is no longer available as a one stop source for known-good Helm charts. NGINX now instructs you to add ingress-nginx individually to the Helm client:
$ helm repo add ingress-nginx https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx
Without a central repository, you need to perform a separate helm repo add every time you need to maintain a different K8s app.
Is there a better way?
Ingress NGINX Controller in ChartCenter
JFrog ChartCenter is a free Helm chart central repository that was built to help the Helm community find immutable, secure, and reliable charts and have a single source of truth to proxy all the charts from one location. It can be used as one central Helm repository from the Helm client, so you do not have to add many public Helm repositories, but use just one instead.
Through ChartCenter, over 30,000 versioned Helm charts are available, and many popular app charts — including for the NGINX Ingress Controller — are featured on its home page so you can conveniently locate them.
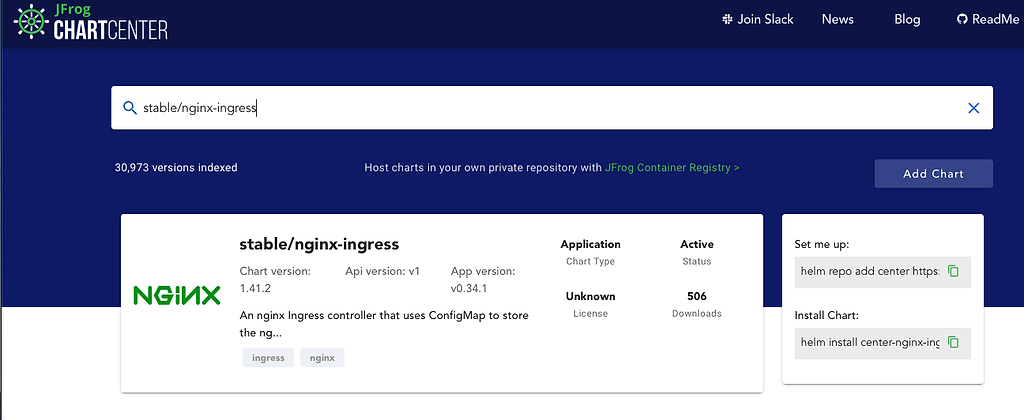
Through ChartCenter’s search, we can find the stable helm chart nginx-ingress:
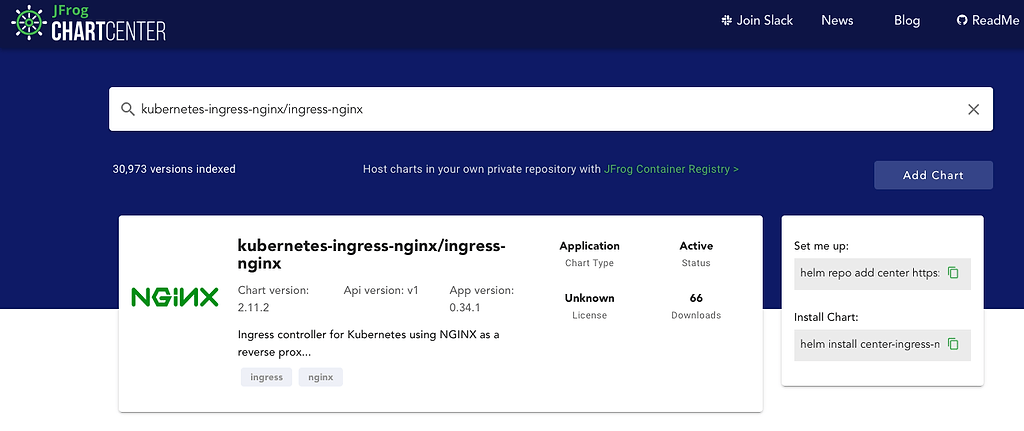
We can also locate the current chart ingress-nginx in ChartCenter:
Using ChartCenter
Once we add ChartCenter to our Helm client, we can use it as a central repository for all our Helm charts, including both the NGINX repositories we will be using in our demonstration.
Step 1: Add ChartCenter as your Helm repository
Set your Helm client to use the ChartCenter repository as your single central location to consume charts from:
$ helm repo add center https://repo.chartcenter.io
$ helm repo update
Step 2: Using ChartCenter as a repository
Now let’s check for the nginx-ingress and ingress-nginx charts from the helm client:
$ helm search repo center/stable/nginx-ingress
NAME CHART VERSION APP VERSION DESCRIPTION
center/stable/nginx-ingress 1.41.2 v0.34.1 An nginx Ingress controller that uses ConfigMap...
$ helm search repo center/kubernetes-ingress-nginx/ingress-nginx
NAME CHART VERSION APP VERSION DESCRIPTION
center/kubernetes-ingress-nginx/ingress-nginx 2.11.2 0.34.1 Ingress controller for Kubernetes using NGINX a...
Nice, we see the same version of the charts as we did in ChartCenter UI.
And here, you’re able to see how much easier it is to use one central Helm repository for charts from different Helm repositories.
Installing nginx-ingress Helm chart
To test the upgrade first we need to install a nginx-ingress chart. I’m going to use a small shell script nginx-ingress.sh which creates an override values file, and then installs nginx-ingress.
The nginx-ingress.sh has a chart name and version, and a static IP for the Load Balancer:
#!/bin/bash
CHART_NAME="center/stable/nginx-ingress"
CHART_VERSION="1.41.2"
RELEASE=nginx-ingress
NAMESPACE=nginx-ingress
VALUES_FILE=nginx-ingress.yaml
LB_STATIC_IP=35.197.192.35
generateValues() {
cat << EOF > "${VALUES_FILE}"
# Override values for nginx-ingress
controller:
## Use host ports 80 and 443
daemonset:
useHostPort: true
kind: DaemonSet
service:
## Set static IP for LoadBalancer
loadBalancerIP: ${LB_STATIC_IP}
externalTrafficPolicy: Local
stats:
enabled: true
metrics:
enabled: true
EOF
}
generateValues
kubectl create ns nginx-ingress || true
echo
helm upgrade --install ${RELEASE} -n ${NAMESPACE} ${CHART_NAME} --version ${CHART_VERSION} -f ${VALUES_FILE}
echo
kubectl -n ${NAMESPACE} get all
Let’s run nginx-ingress.sh to install nginx-ingress:
$ ./nginx-ingress.sh
namespace/nginx-ingress created
Release "nginx-ingress" does not exist. Installing it now.
NAME: nginx-ingress
LAST DEPLOYED: Mon Aug 10 17:27:13 2020
NAMESPACE: nginx-ingress
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
NOTES:
The nginx-ingress controller has been installed.
It may take a few minutes for the LoadBalancer IP to be available.
You can watch the status by running 'kubectl --namespace nginx-ingress get services -o wide -w nginx-ingress-controller'
An example Ingress that makes use of the controller:
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
name: example
namespace: foo
spec:
rules:
- host: www.example.com
http:
paths:
- backend:
serviceName: exampleService
servicePort: 80
path: /
# This section is only required if TLS is to be enabled for the Ingress
tls:
- hosts:
- www.example.com
secretName: example-tls
If TLS is enabled for the Ingress, a Secret containing the certificate and key must also be provided:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: example-tls
namespace: foo
data:
tls.crt:
tls.key:
type: kubernetes.io/tls
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/nginx-ingress-controller-rrsl9 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 1s
pod/nginx-ingress-default-backend-5b967cf596-wrrfl 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 1s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/nginx-ingress-controller LoadBalancer 10.242.2.213 80:30643/TCP,443:31622/TCP 2s
service/nginx-ingress-controller-metrics ClusterIP 10.242.10.112 9913/TCP 2s
service/nginx-ingress-default-backend ClusterIP 10.242.11.172 80/TCP 2s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE NODE SELECTOR AGE
daemonset.apps/nginx-ingress-controller 1 1 0 1 0 3s
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/nginx-ingress-default-backend 0/1 1 0 2s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/nginx-ingress-default-backend-5b967cf596 1 1 0 2s
And let’s check for pods and service:
$ kubectl -n nginx-ingress get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-ingress-controller-rrsl9 1/1 Running 0 78s
nginx-ingress-default-backend-5b967cf596-wrrfl 1/1 Running 0 78s
$ kubectl -n nginx-ingress get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
nginx-ingress-controller LoadBalancer 10.242.2.213 35.197.192.35 80:30643/TCP,443:31622/TCP 89s
nginx-ingress-controller-metrics ClusterIP 10.242.10.112 9913/TCP 89s
nginx-ingress-default-backend ClusterIP 10.242.11.172 80/TCP 89s
Nice, NGINX Ingress Controller pod is up, and it’s service got assigned external IP by the Load Balancer.
Ok, we got the nginx-ingress chart successfully installed, let’s move on to upgrading it.
Upgrading to ingress-nginx Helm chart
Let’s try to upgrade NGINX Ingress Controller using the more current chart..
Again we are going to use a shell script this time with the different name ingress-nginx.sh.
The ingress-nginx.sh has a different chart name and version, and the same Helm release name and the same static IP for the Load Balancer.
#!/bin/bash
CHART_NAME="center/kubernetes-ingress-nginx/ingress-nginx"
CHART_VERSION="2.11.1"
RELEASE=nginx-ingress
NAMESPACE=nginx-ingress
VALUES_FILE=ingress-nginx.yaml
LB_STATIC_IP=35.197.192.35
generateValues() {
cat << EOF > "${VALUES_FILE}"
# Override values for ingress-nginx
controller:
## Use host ports 80 and 443
hostPort:
enabled: true
kind: DaemonSet
service:
## Set static IP for LoadBalancer
loadBalancerIP: ${LB_STATIC_IP}
externalTrafficPolicy: Local
stats:
enabled: true
metrics:
enabled: true
admissionWebhooks:
enabled: false
defaultBackend:
enabled: true
EOF
}
generateValues
echo
helm upgrade --install ${RELEASE} -n ${NAMESPACE} ${CHART_NAME} --version ${CHART_VERSION} -f ${VALUES_FILE}
echo
kubectl -n ${NAMESPACE} get all
The ingress-nginx.sh has some differences from nginx-ingress.sh:
controller:
## Use host ports 80 and 443
daemonset:
useHostPort: true
as some values got changed to:
controller:
## Use host ports 80 and 443
hostPort:
enabled: true
kind: DaemonSet
and some extra ones were added:
admissionWebhooks:
enabled: false
defaultBackend:
enabled: true
In this upgrade scenario we are not using admissionWebhooks so we disable it, and we enable defaultBackend as in nginx-ingress chart it is enabled by default. And of course you can tweak the values as suits your needs.
Let’s run ingress-nginx.sh to upgrade nginx-ingress:
Release "nginx-ingress" has been upgraded. Happy Helming!
NAME: nginx-ingress
LAST DEPLOYED: Mon Aug 10 18:00:31 2020
NAMESPACE: nginx-ingress
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 2
TEST SUITE: None
NOTES:
The ingress-nginx controller has been installed.
It may take a few minutes for the LoadBalancer IP to be available.
You can watch the status by running 'kubectl --namespace nginx-ingress get services -o wide -w nginx-ingress-ingress-nginx-controller'
An example Ingress that makes use of the controller:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
name: example
namespace: foo
spec:
rules:
- host: www.example.com
http:
paths:
- backend:
serviceName: exampleService
servicePort: 80
path: /
# This section is only required if TLS is to be enabled for the Ingress
tls:
- hosts:
- www.example.com
secretName: example-tls
If TLS is enabled for the Ingress, a Secret containing the certificate and key must also be provided:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: example-tls
namespace: foo
data:
tls.crt:
tls.key:
type: kubernetes.io/tls
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/nginx-ingress-controller-rrsl9 1/1 Terminating 0 33m
pod/nginx-ingress-default-backend-5b967cf596-wrrfl 0/1 Terminating 0 33m
pod/nginx-ingress-ingress-nginx-controller-f9ztr 0/1 Pending 0 5s
pod/nginx-ingress-ingress-nginx-defaultbackend-845f7cfd46-56grw 1/1 Running 0 5s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/nginx-ingress-controller LoadBalancer 10.242.2.213 35.197.192.35 80:30643/TCP,443:31622/TCP 33m
service/nginx-ingress-ingress-nginx-controller LoadBalancer 10.242.13.184 80:30601/TCP,443:30644/TCP 6s
service/nginx-ingress-ingress-nginx-controller-metrics ClusterIP 10.242.12.190 9913/TCP 6s
service/nginx-ingress-ingress-nginx-defaultbackend ClusterIP 10.242.11.112 80/TCP 5s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE NODE SELECTOR AGE
daemonset.apps/nginx-ingress-ingress-nginx-controller 1 1 0 1 0 6s
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/nginx-ingress-ingress-nginx-defaultbackend 1/1 1 1 6s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/nginx-ingress-ingress-nginx-defaultbackend-845f7cfd46 1 1 1 6s
Now let’s check the pods and service:
$ kubectl -n nginx-ingress get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-ingress-ingress-nginx-controller-f9ztr 0/1 Running 0 34s
nginx-ingress-ingress-nginx-defaultbackend-845f7cfd46-56grw 1/1 Running 0 34s
$ kubectl -n nginx-ingress get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
nginx-ingress-controller LoadBalancer 10.242.2.213 35.197.192.35 80:30643/TCP,443:31622/TCP 34m
nginx-ingress-ingress-nginx-controller LoadBalancer 10.242.13.184 80:30601/TCP,443:30644/TCP 40s
nginx-ingress-ingress-nginx-controller-metrics ClusterIP 10.242.12.190 9913/TCP 40s
nginx-ingress-ingress-nginx-defaultbackend ClusterIP 10.242.11.112 80/TCP 39s
You see there the pods are getting updated and we see two services, one old one new.
Let’s run kubectl -n nginx-ingress get svc again:
$ kubectl -n nginx-ingress get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
nginx-ingress-ingress-nginx-controller LoadBalancer 10.242.13.184 35.197.192.35 80:30601/TCP,443:30644/TCP 3m26s
nginx-ingress-ingress-nginx-controller-metrics ClusterIP 10.242.12.190 9913/TCP 3m26s
nginx-ingress-ingress-nginx-defaultbackend ClusterIP 10.242.11.112 80/TCP 3m25s
Voila, the old service was deleted and the new one created just by running helm upgrade and not using any other magic with kubectl. Of course replacing the service some downtime is expected as the new load balancer needs to be created for the new service.
Thanks, and Good Luck
Pretty easy, right? Big thanks to the NGINX Ingress Controller chart’s maintainers for such a seamless upgrade between two different charts!
With good fortune, the transition to individual chart repos for your other K8s apps will be equally smooth. Using ChartCenter as your central Helm chart repository can help get those updates going.
Happy Ingressing