How to Optimize DevSecOps Workflows Using JFrog
Embedding security within the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is no longer just a best practice; it’s a full-on necessity. DevSecOps extends the DevOps model by making security a shared responsibility from the earliest stages of development. Today’s enterprises require this kind of integrated approach to streamline workflows from development to deployment.
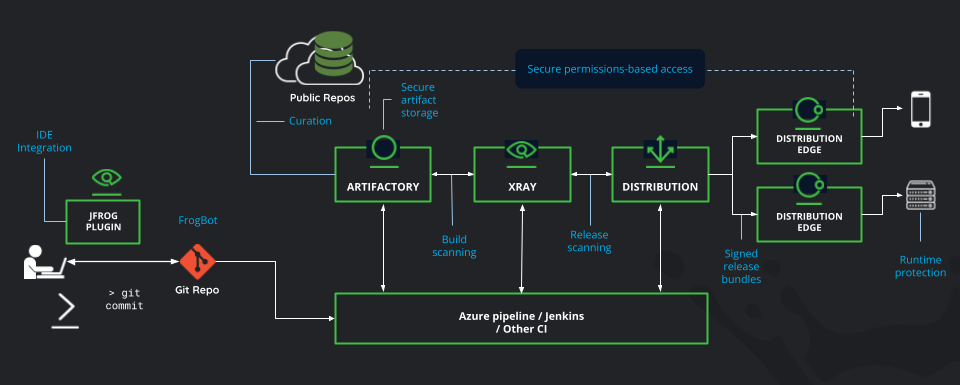
The JFrog Platform enables this model by seamlessly integrating security, compliance, and automation throughout the entire software supply chain. In this blog, we’ll show you how JFrog’s unified toolset, including Artifactory, Xray, Distribution, and more, enhances DevSecOps workflows by ensuring security, visibility, and control from code commit to production deployment.
End-to-End DevSecOps with the JFrog Platform
JFrog provides a comprehensive suite of tools that enhance collaboration while ensuring security and efficiency throughout the software development pipeline. Here’s how it works, in a nutshell:
- This integration begins at the coding phase, where developers can use the JFrog extension within their Integrated Development Environment (IDE) to connect seamlessly with Git repositories. As code changes are committed, JFrog’s FrogBot scans each merge request for vulnerabilities, helping maintain code quality without disrupting developers’ focus.
- Once code is pushed to a Git repository, it triggers CI/CD pipelines (such as Azure Pipelines or Jenkins) to automate the build process. Here, JFrog Artifactory plays a crucial role as a universal repository manager, providing secure storage for artifacts. These artifacts then undergo thorough scanning via JFrog Xray, which identifies vulnerabilities and license compliance issues, ensuring that only safe and compliant code progresses through the pipeline.
- Following successful scans, JFrog Distribution takes charge, ensuring that the right artifacts are delivered to the appropriate environments. This facilitates efficient deployment and runtime protection across various locations.
In the following sections, we’ll explore each phase of this journey in detail, highlighting how JFrog’s integration across the software development pipeline ensures cohesion and efficiency at every step, from development to distribution. The diagram below demonstrates how JFrog components integrate across the software development pipeline to enforce security and automate governance at every stage.
The JFrog Platform across the SDLC
1. IDE Integration – Shift-Left with JFrog Xray
While security may not be developers’ top priority, the reality is that security starts at the developer’s workstation. To make this responsibility as easy as possible to fulfill, JFrog provides IDE extensions (e.g., IntelliJ IDEA, Visual Studio, Eclipse) that integrate directly with Xray, enabling real-time scanning of dependencies and source code for vulnerabilities.
Key Capabilities:
- Software Composition Analysis (SCA) with contextual insights
- Secrets detection and token validation
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC) scanning
- Static Application Security Testing (SAST)
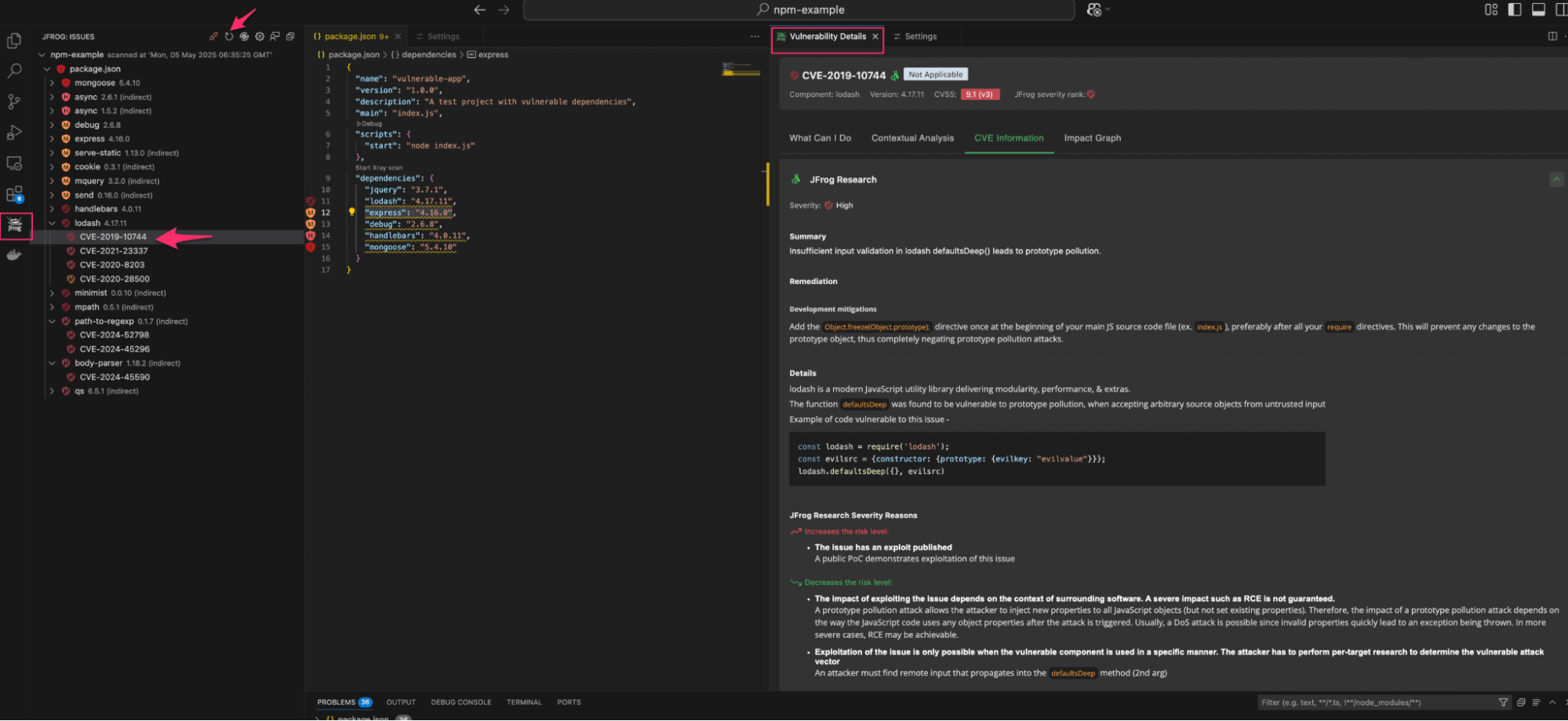
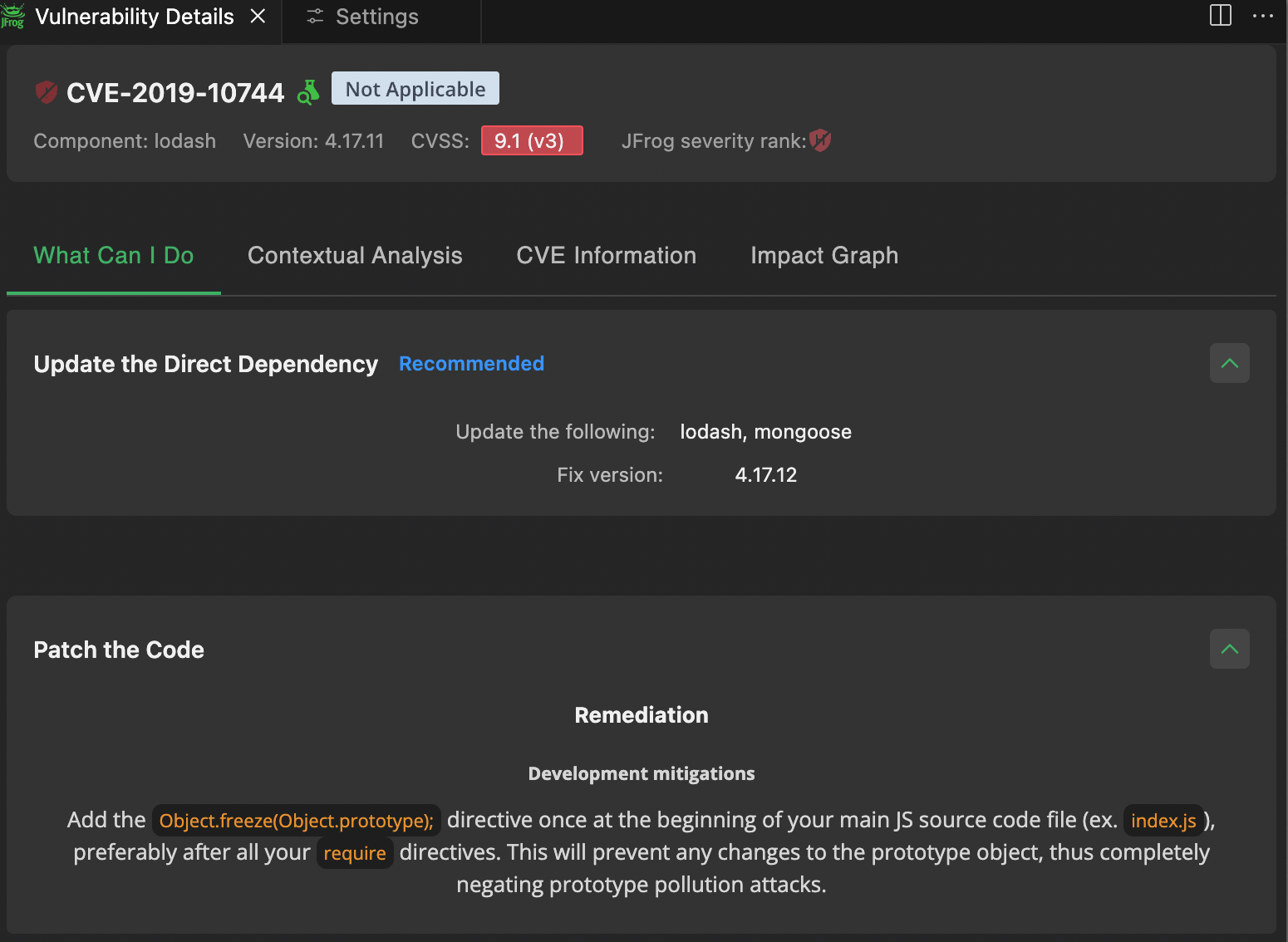
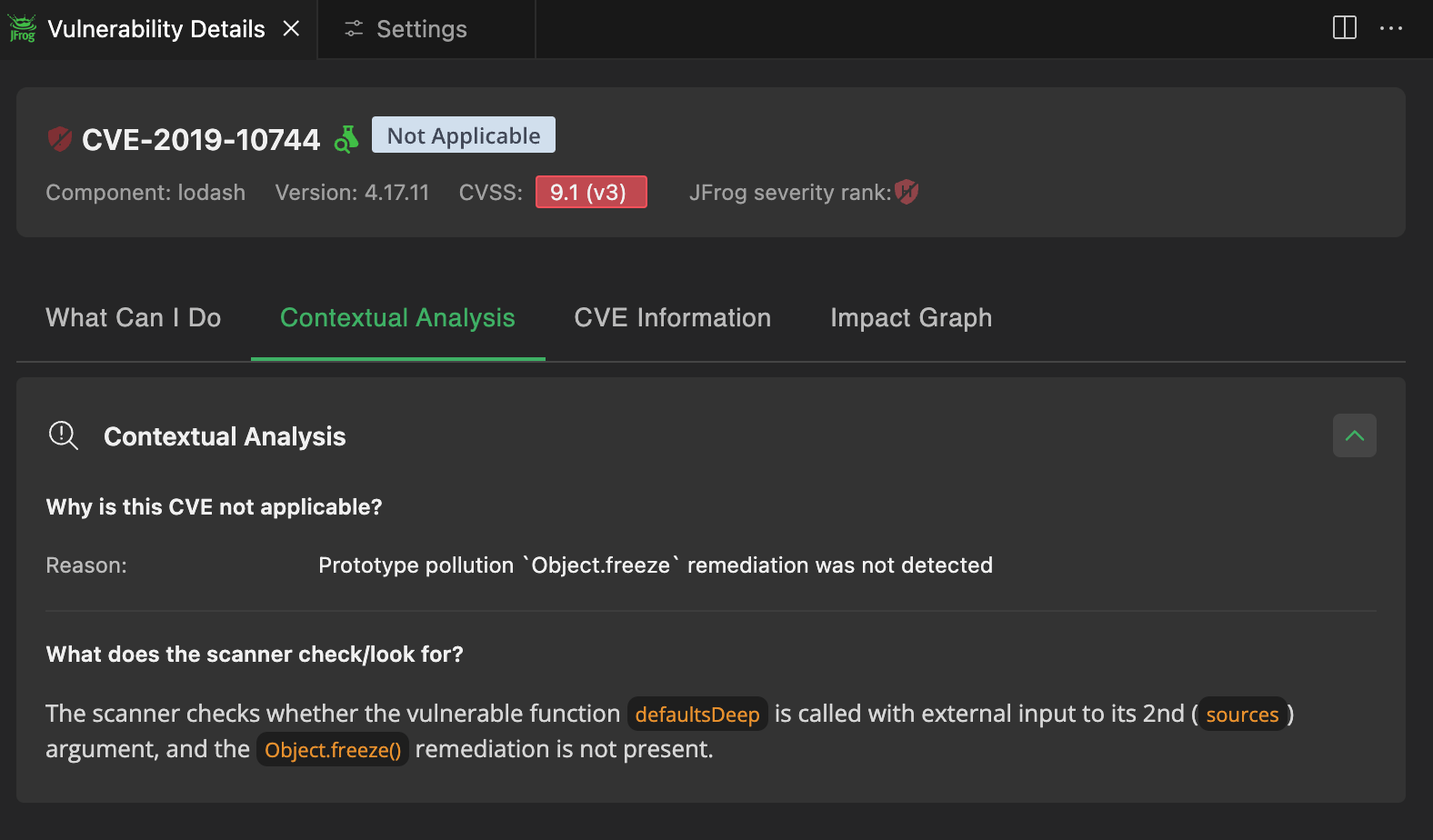
As developers write code, Xray flags known CVEs and provides actionable remediation guidance preventing insecure code from entering the codebase.
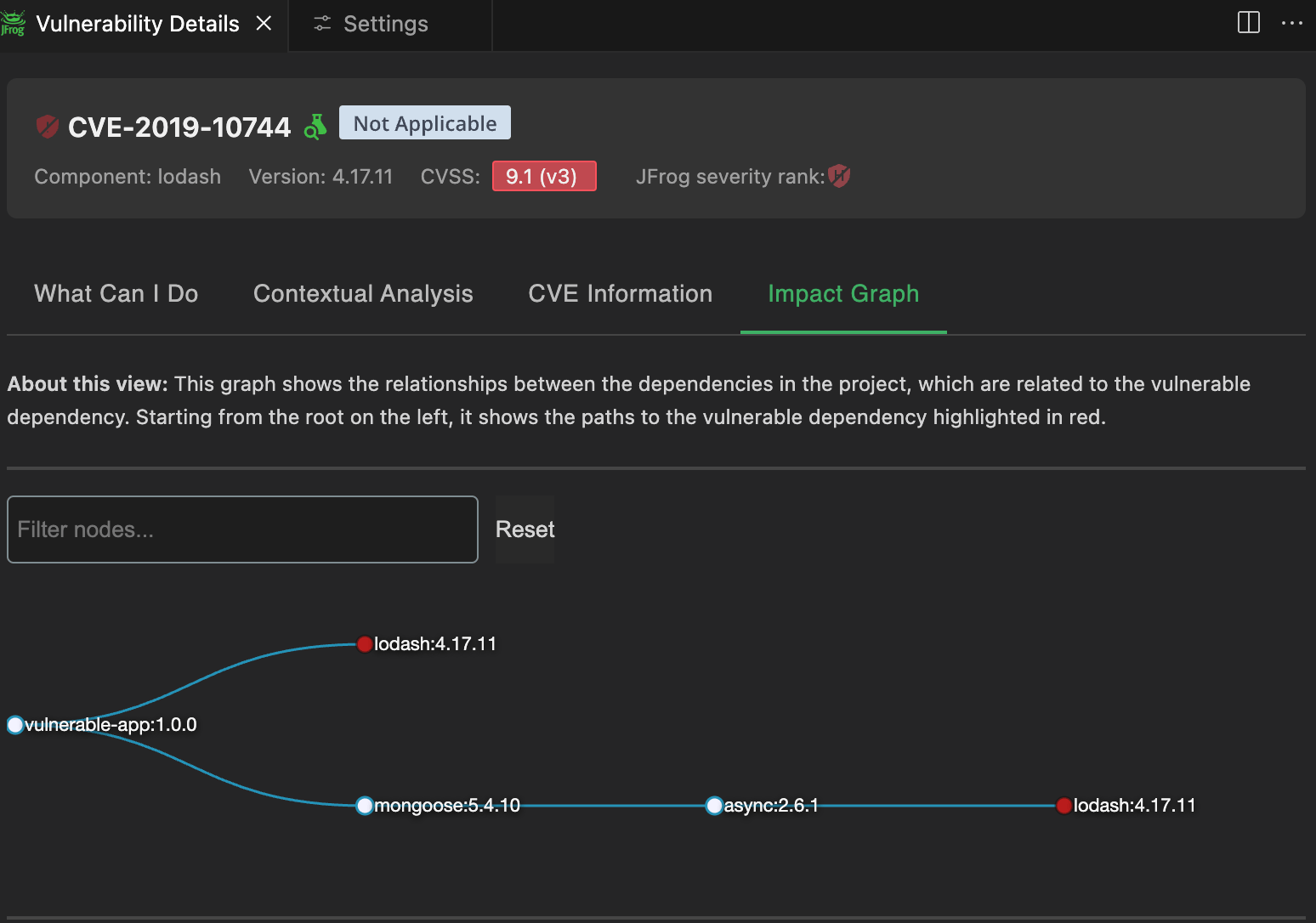
The screenshots below demonstrate how Xray’s integration within the IDE alerts developers to vulnerabilities in real time as they write code. In this example, a vulnerability is detected in one of the lodash dependencies used in the project. The right-hand panel provides detailed CVE information along with recommended remediation actions, empowering developers to address security issues proactively before the code is even committed.
Visual Studio IDE showcasing detailed vulnerability information
2. Secure Before You Build with JFrog Curation
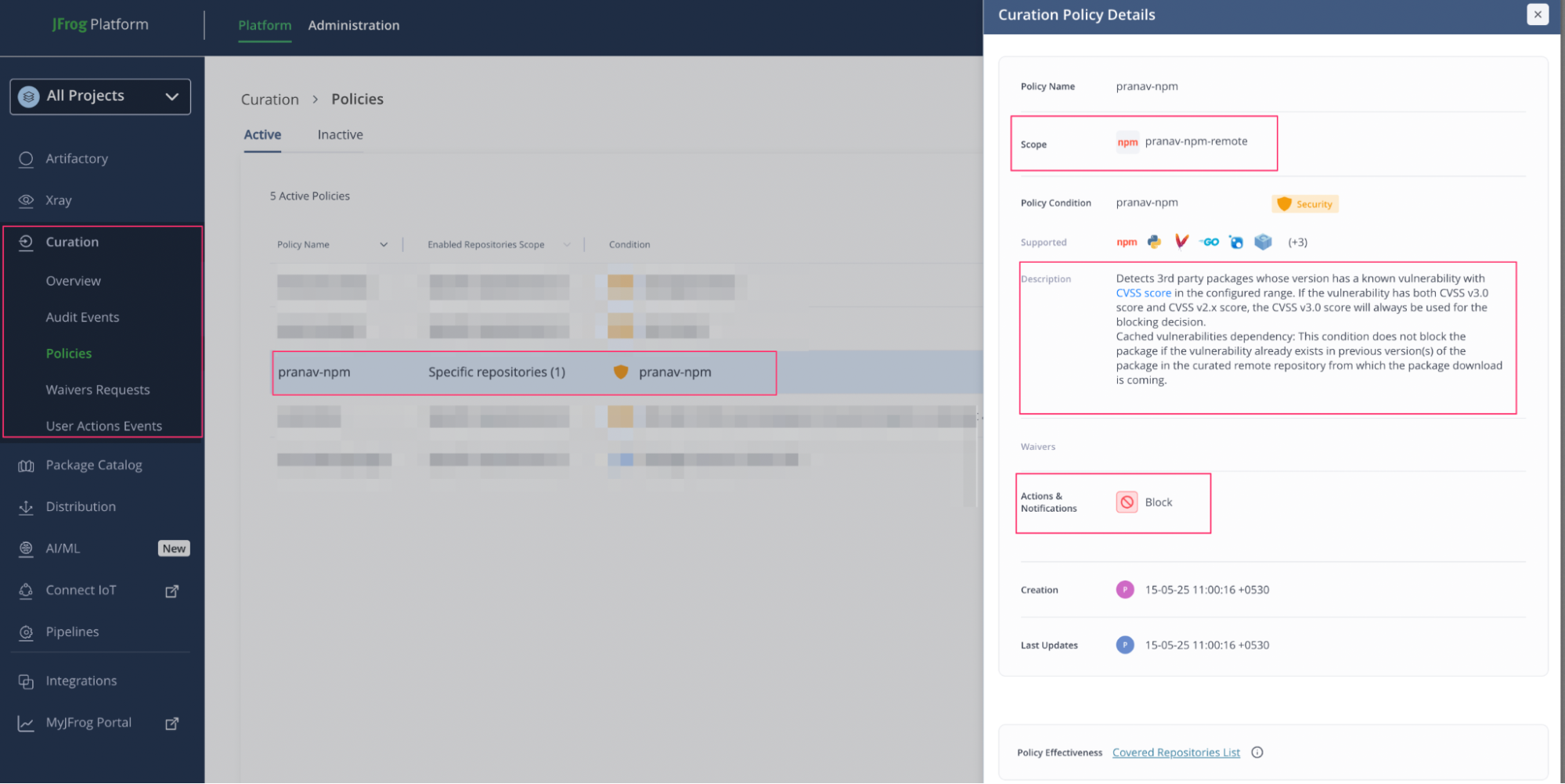
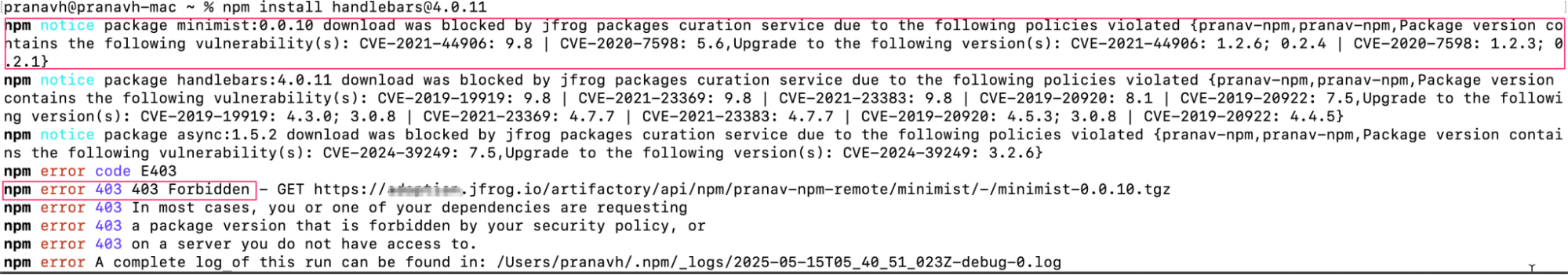
JFrog Curation enables organizations to block components with known security or license issues before they’re downloaded.
In this example, a policy blocks any npm package with a CVSS score between 7-10. Attempts to download non-compliant packages are blocked, enforcing security before development even begins.
Curation policy setup in the JFrog Platform
Download unsuccessful due to enforced Curation policy
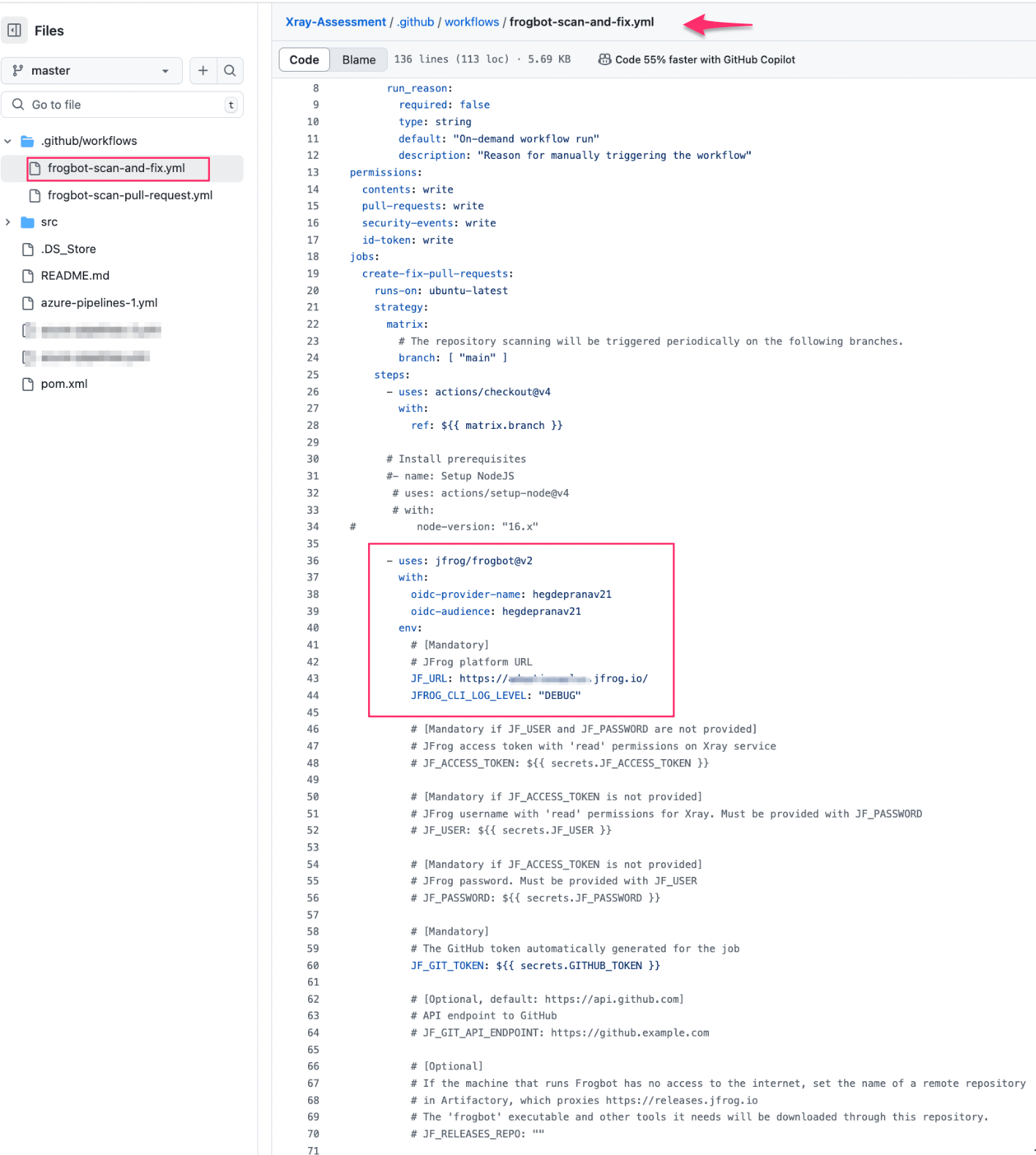
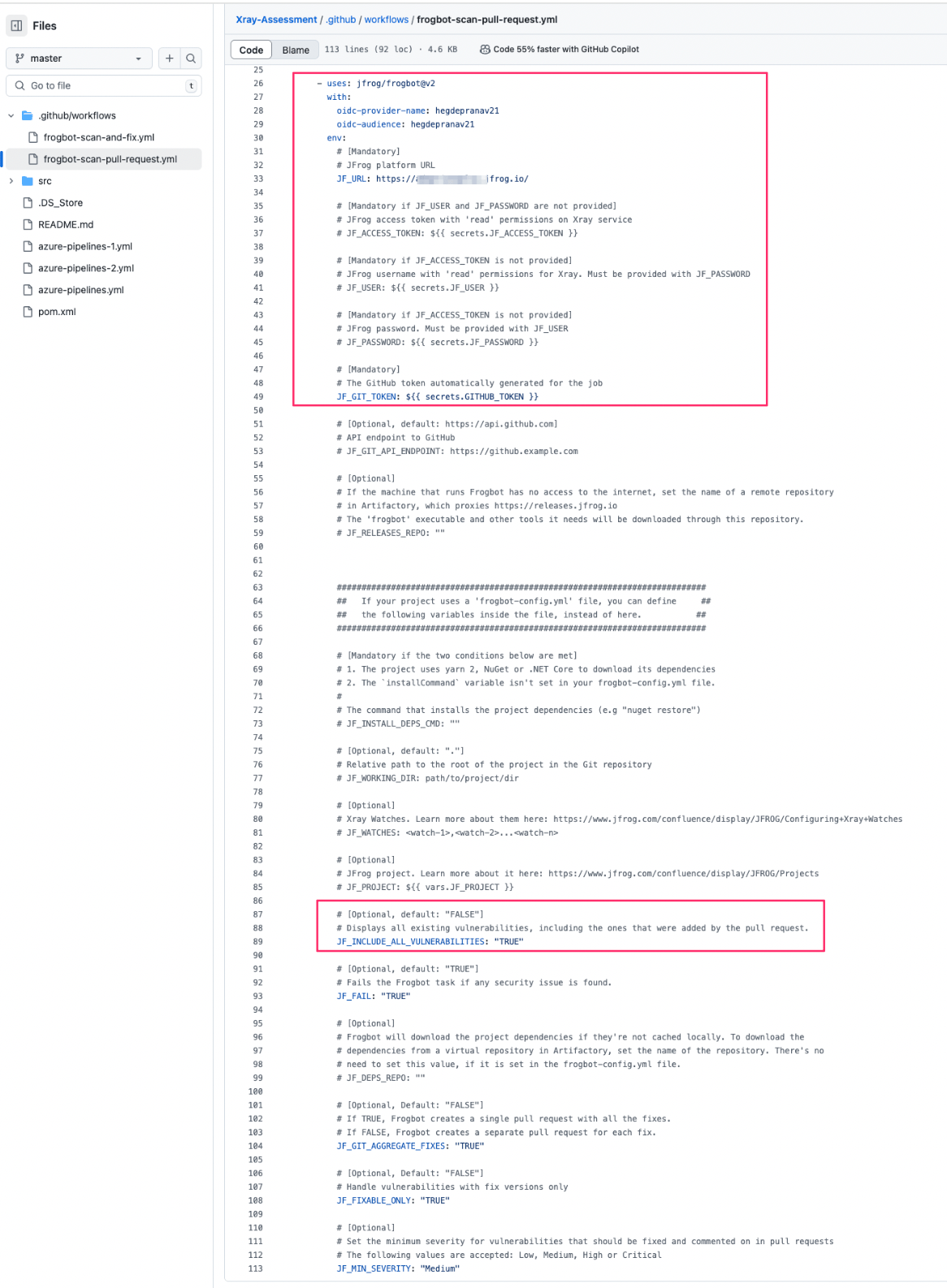
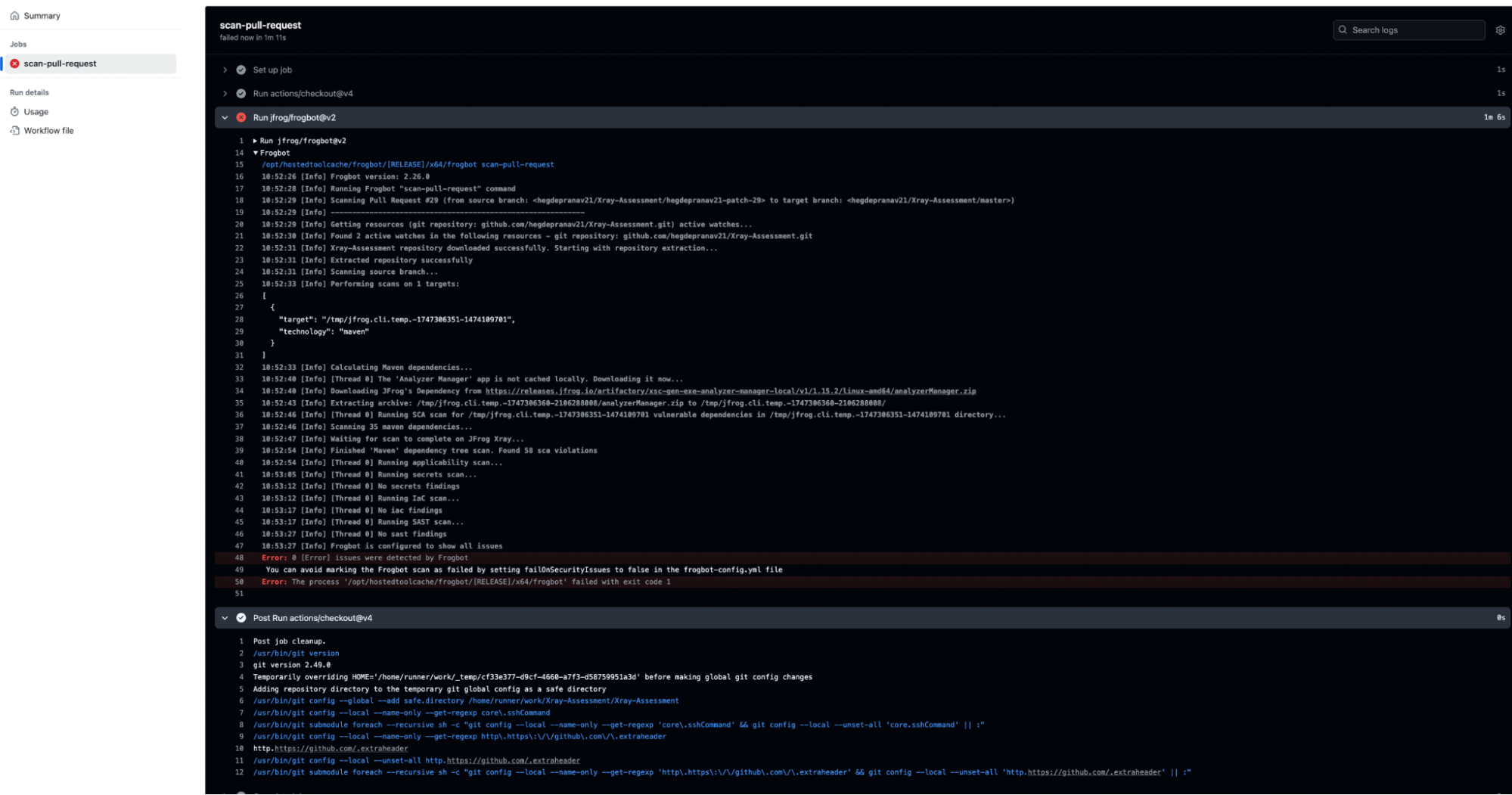
3. Code Commit and Git Repo Analysis – JFrog Frogbot
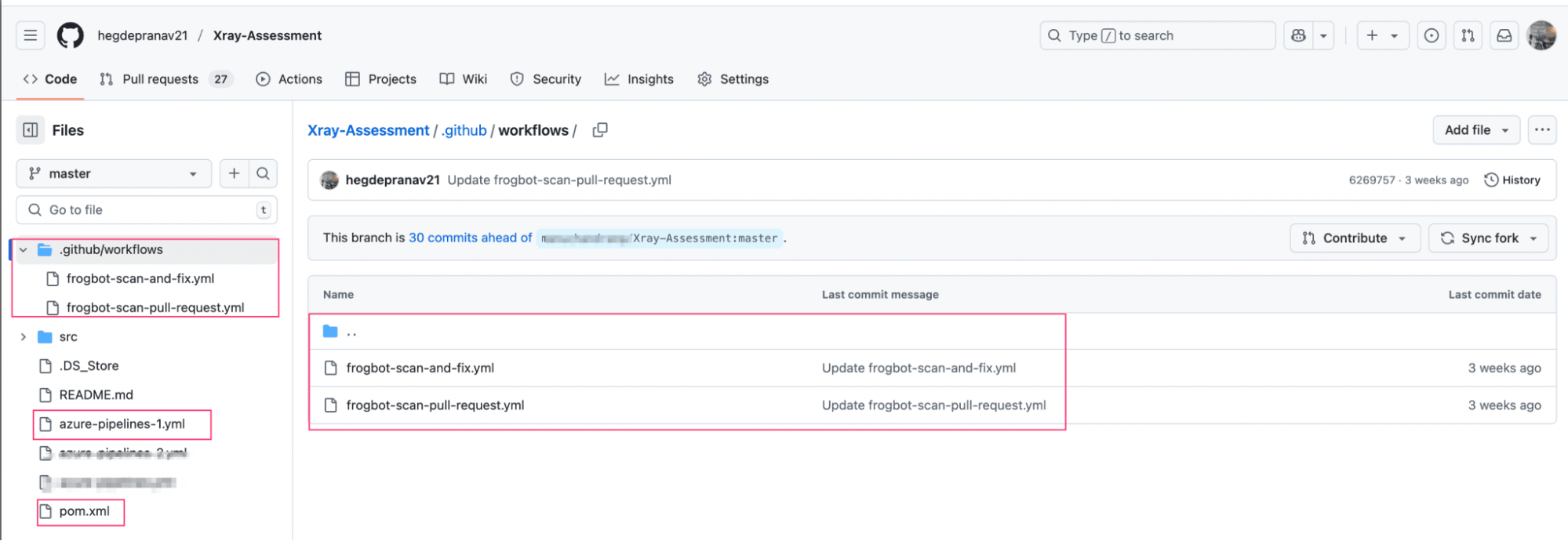
Once code is committed, JFrog Frogbot scans Git repositories for newly introduced vulnerabilities. This serves as a second layer of protection, ensuring any risks introduced post-IDE are detected and mitigated before progressing further in the pipeline.
The following images demonstrate the implementation of Frogbot within a GitHub Actions workflow:
Frogbot configuration view in GitHub
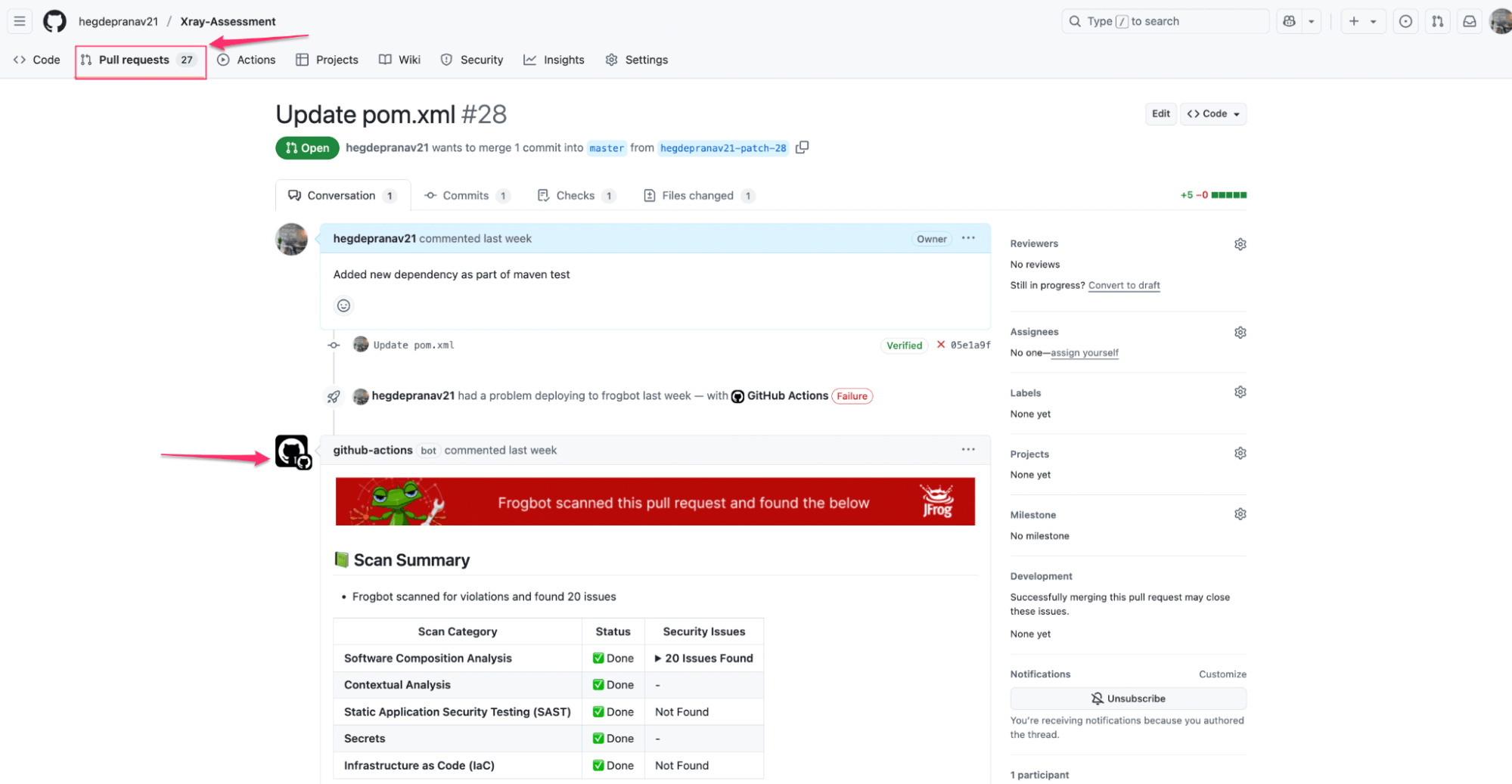
4. Pull Request Validation with Frogbot
When a pull request is opened, Frogbot automatically scans the changes and opens remediation PRs if issues are detected, proactively suggesting upgraded dependencies.
This enforces security within the review process and provides developers with real-time feedback directly in the Git platform.
Pull request validation in action using Frogbot
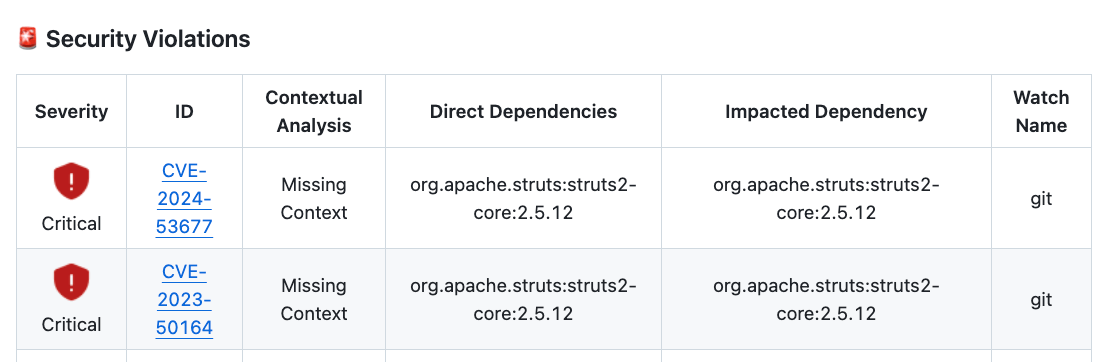
Frogbot-generated scan summary
Once the Frogbot scan is completed, you can review the Frogbot scan results under the pull request section of your Github, as shown below:
Frogbot-generated scan summary
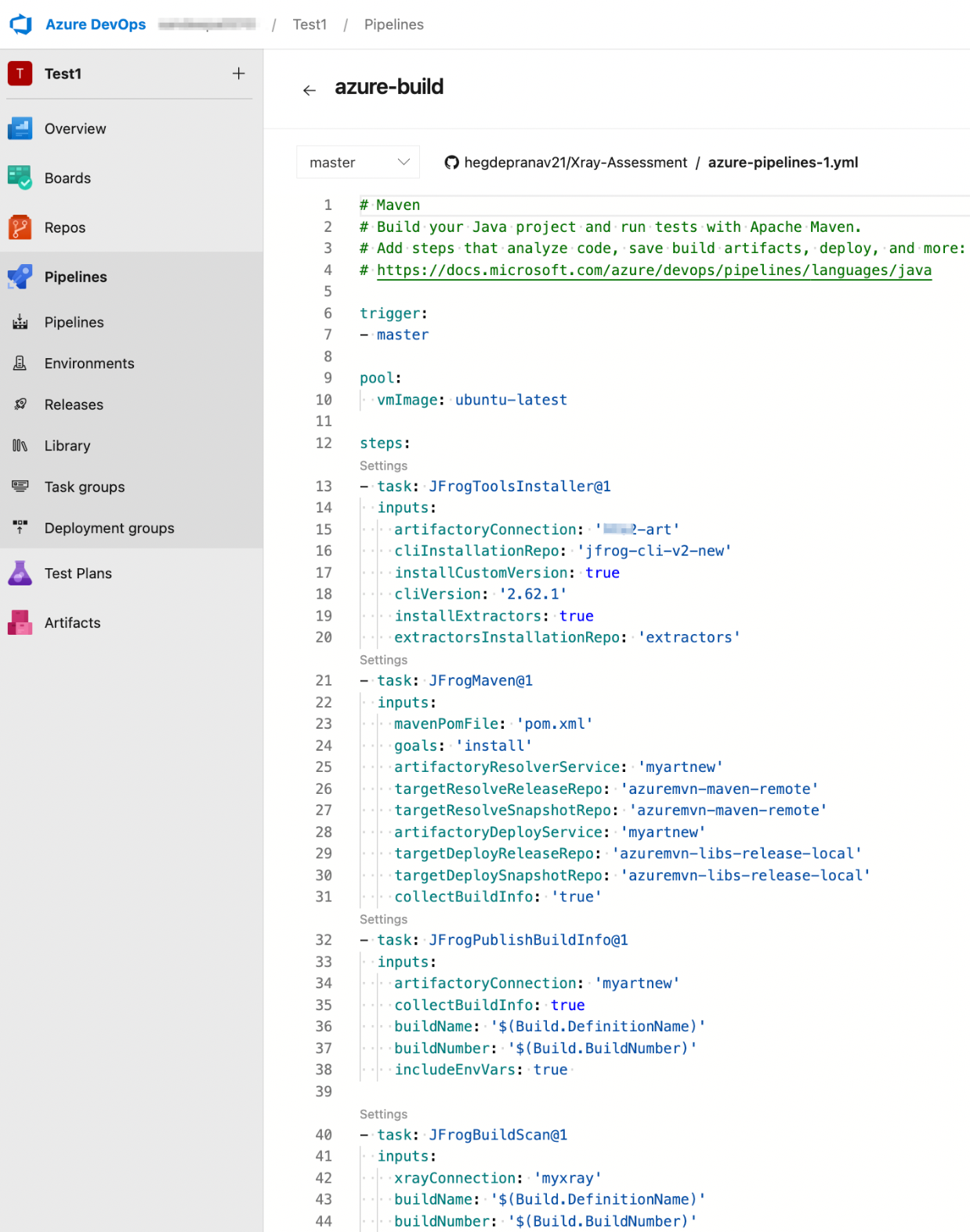
5. CI Pipeline Integration – Build and Scan
Upon PR approval, the Azure DevOps pipeline triggers:
- Artifact creation
- Build Info generation
- Xray scanning of the build outputs
Build Info provides traceability, while Xray ensures that vulnerabilities are caught before artifacts are stored in repositories.
The example below illustrates the CI pipeline script in use:
Build script configured in Azure Pipeline
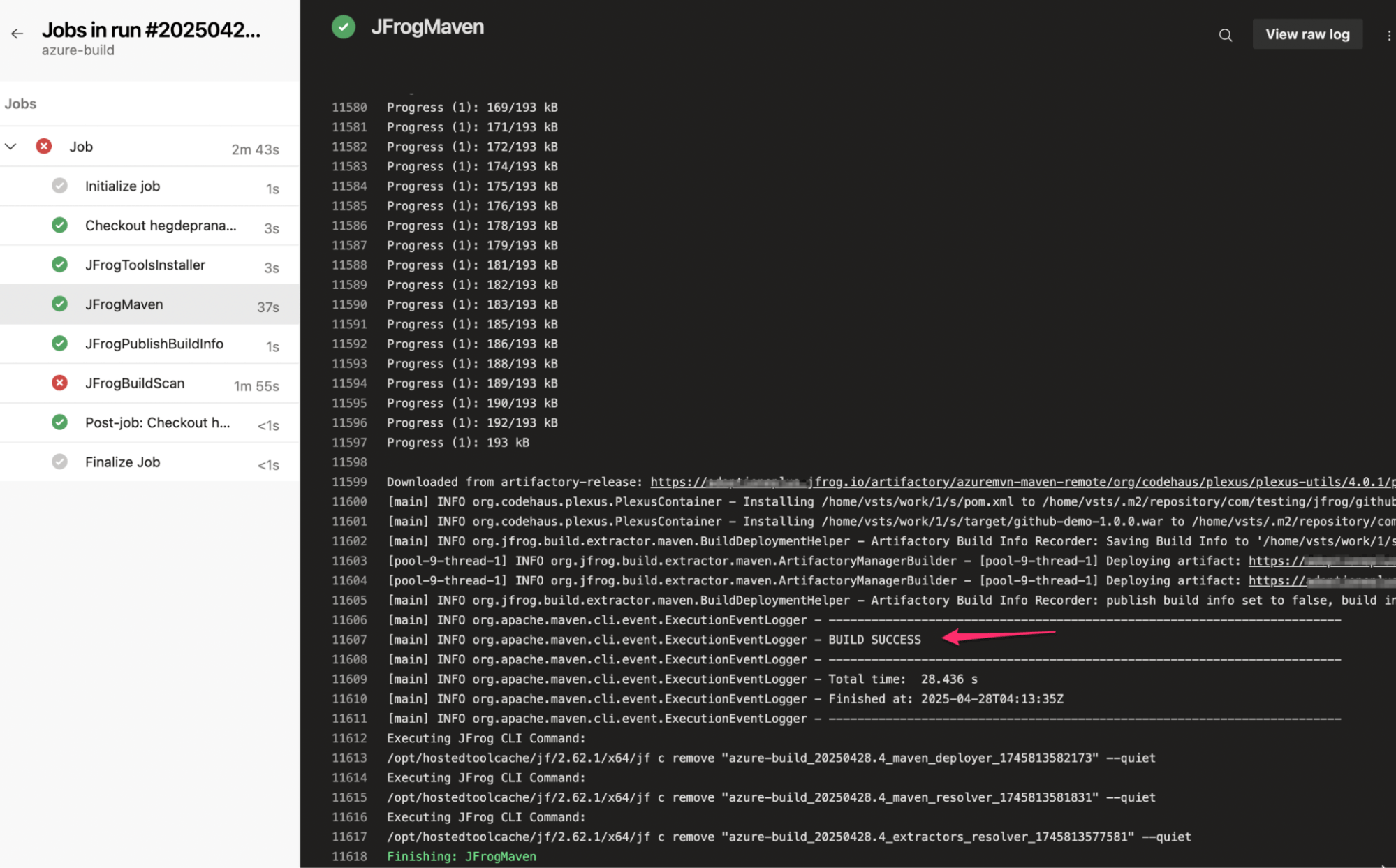
Stage responsible for generating build information:
Build output from Azure Pipeline
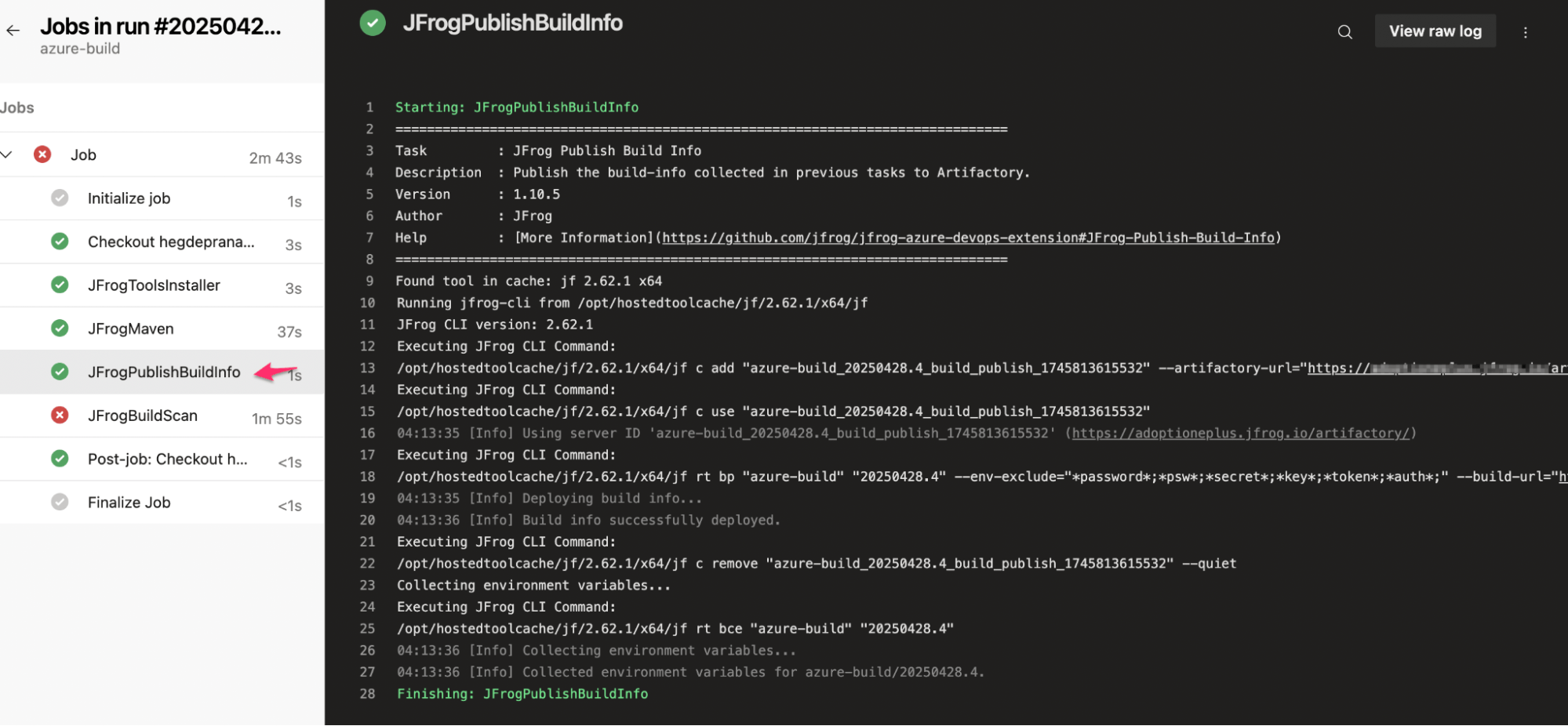
Stage where build information is published to JFrog Artifactory:
Build output from Azure Pipeline
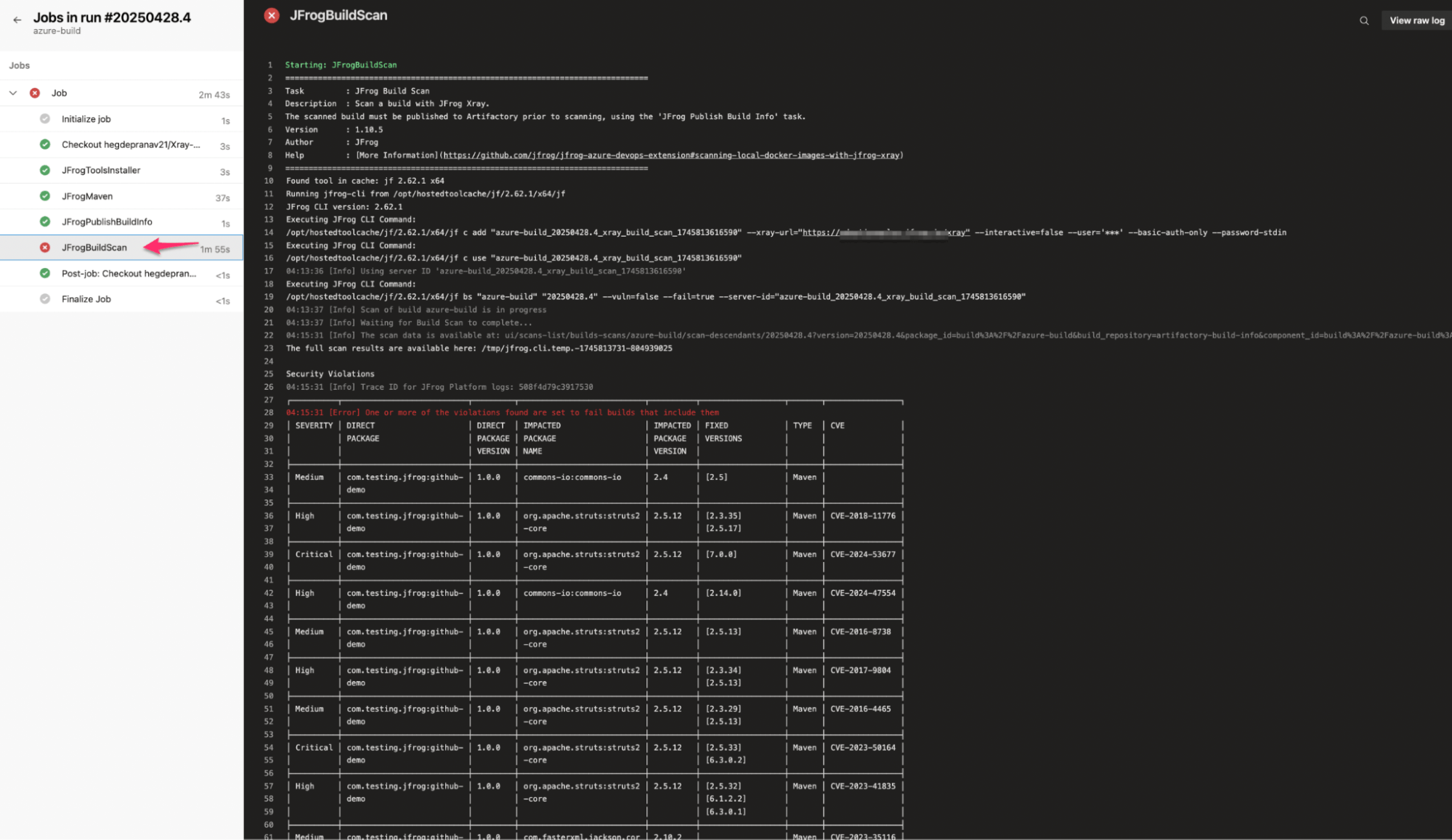
Stage where JFrog Xray scans the build info and flags any detected vulnerabilities:
Build output from Azure Pipeline
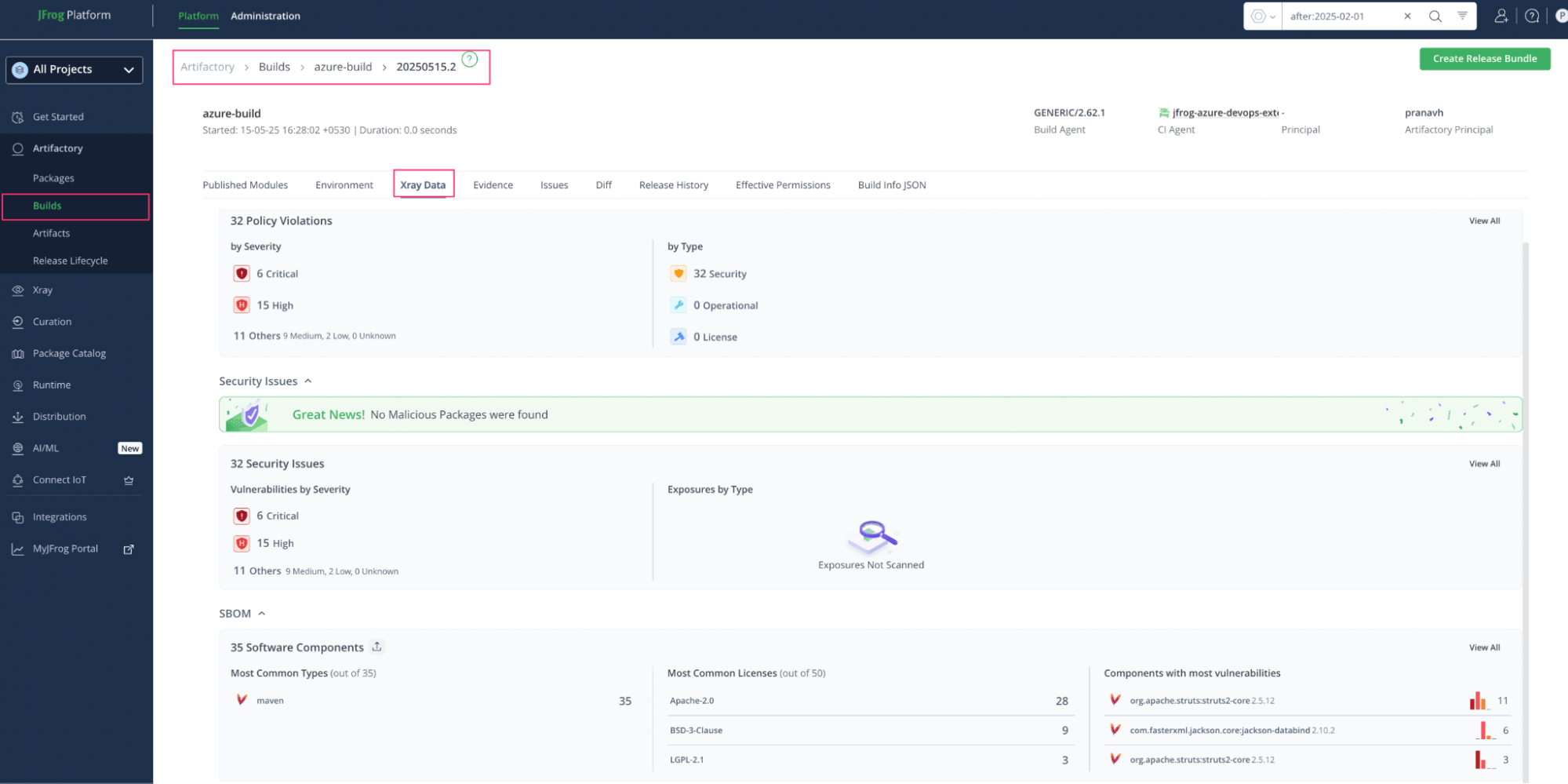
6. Artifact Deployment – Centralized with Artifactory
Validated artifacts are deployed to JFrog Artifactory, the central repository for binaries. With Xray watches and policies enabled, Artifactory continuously scans new and updated builds for compliance and vulnerabilities.
This enables continuous governance and fast feedback loops.
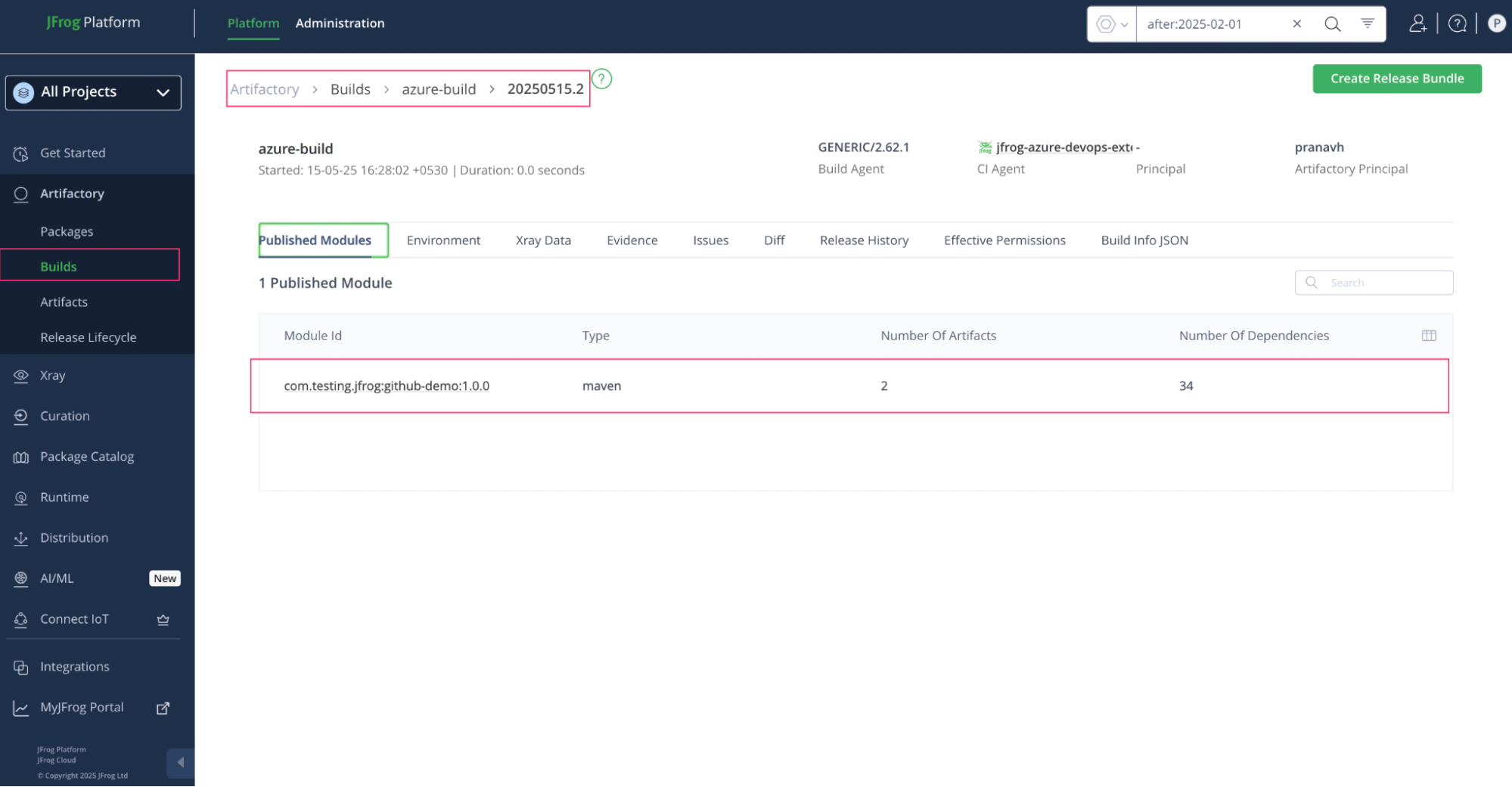
Build info details from Artifactory
Xray data from build info section
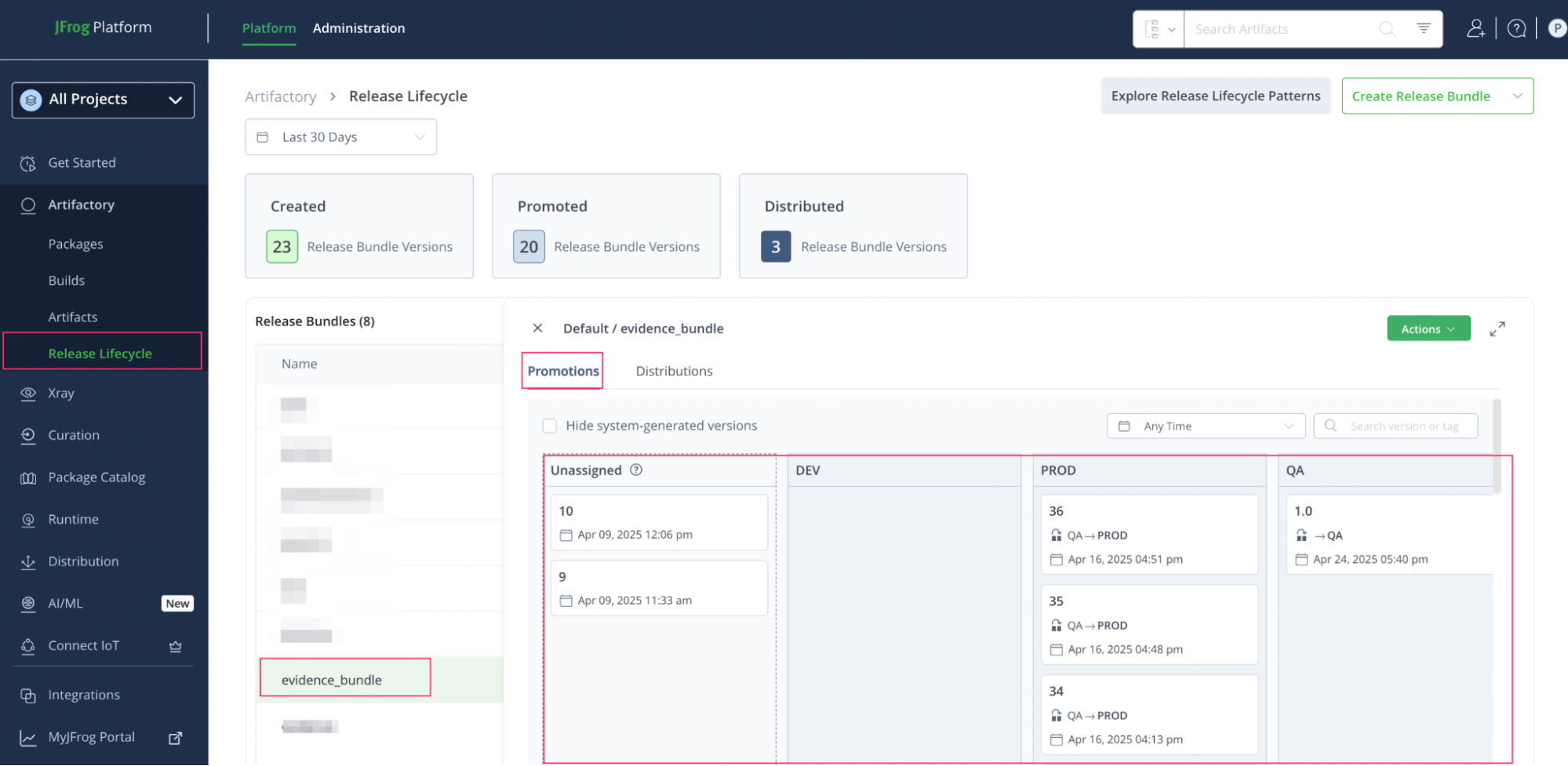
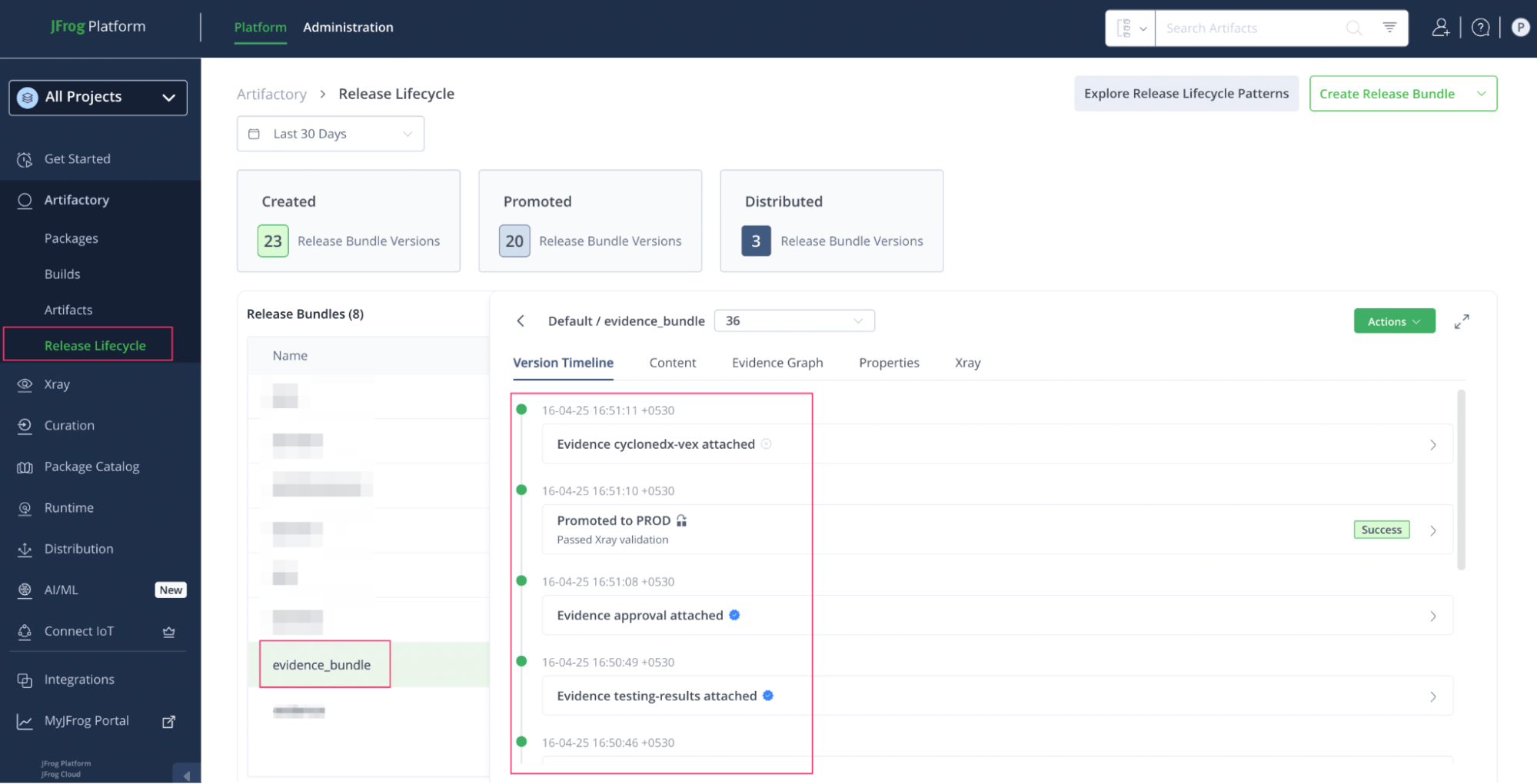
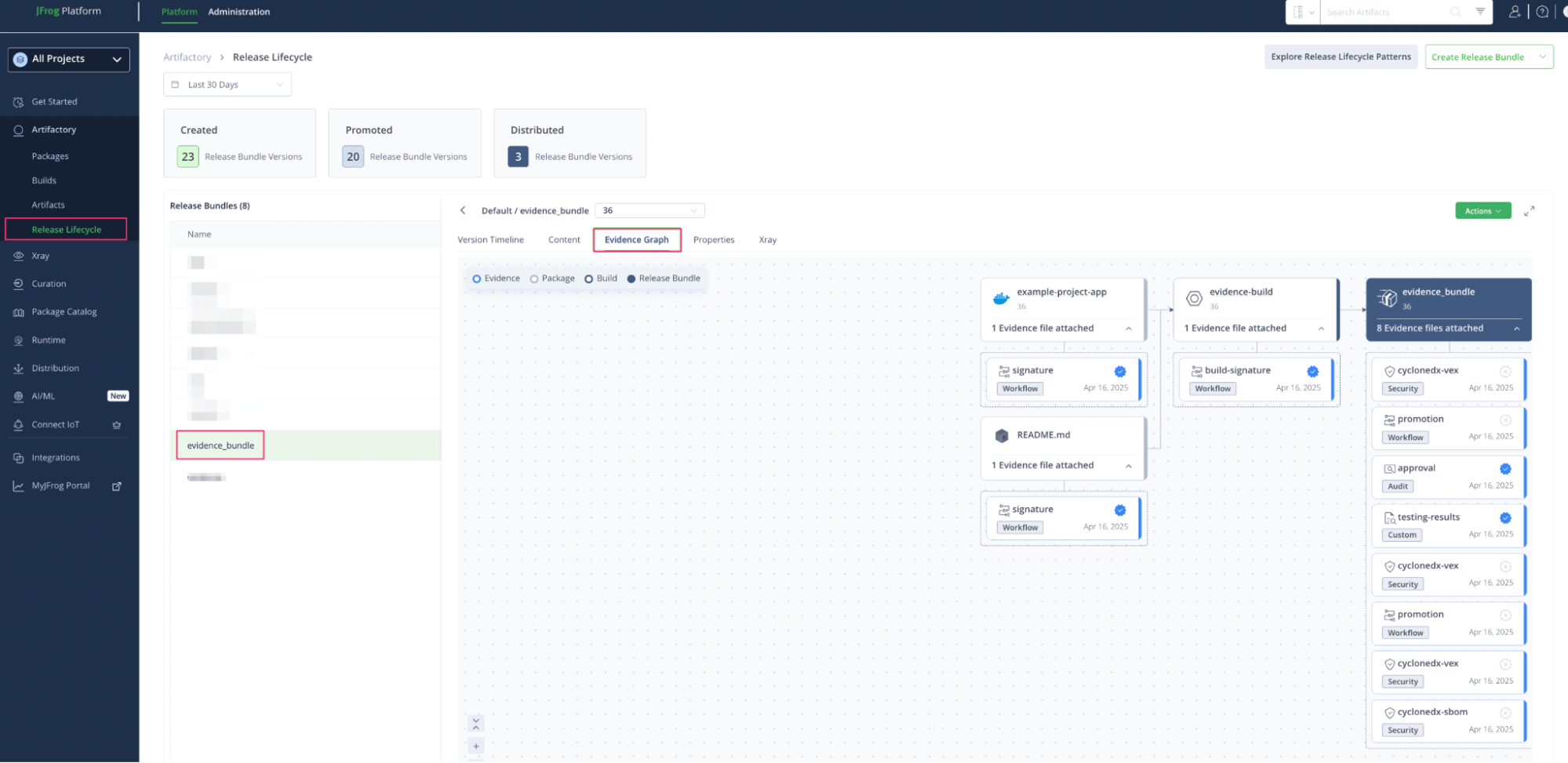
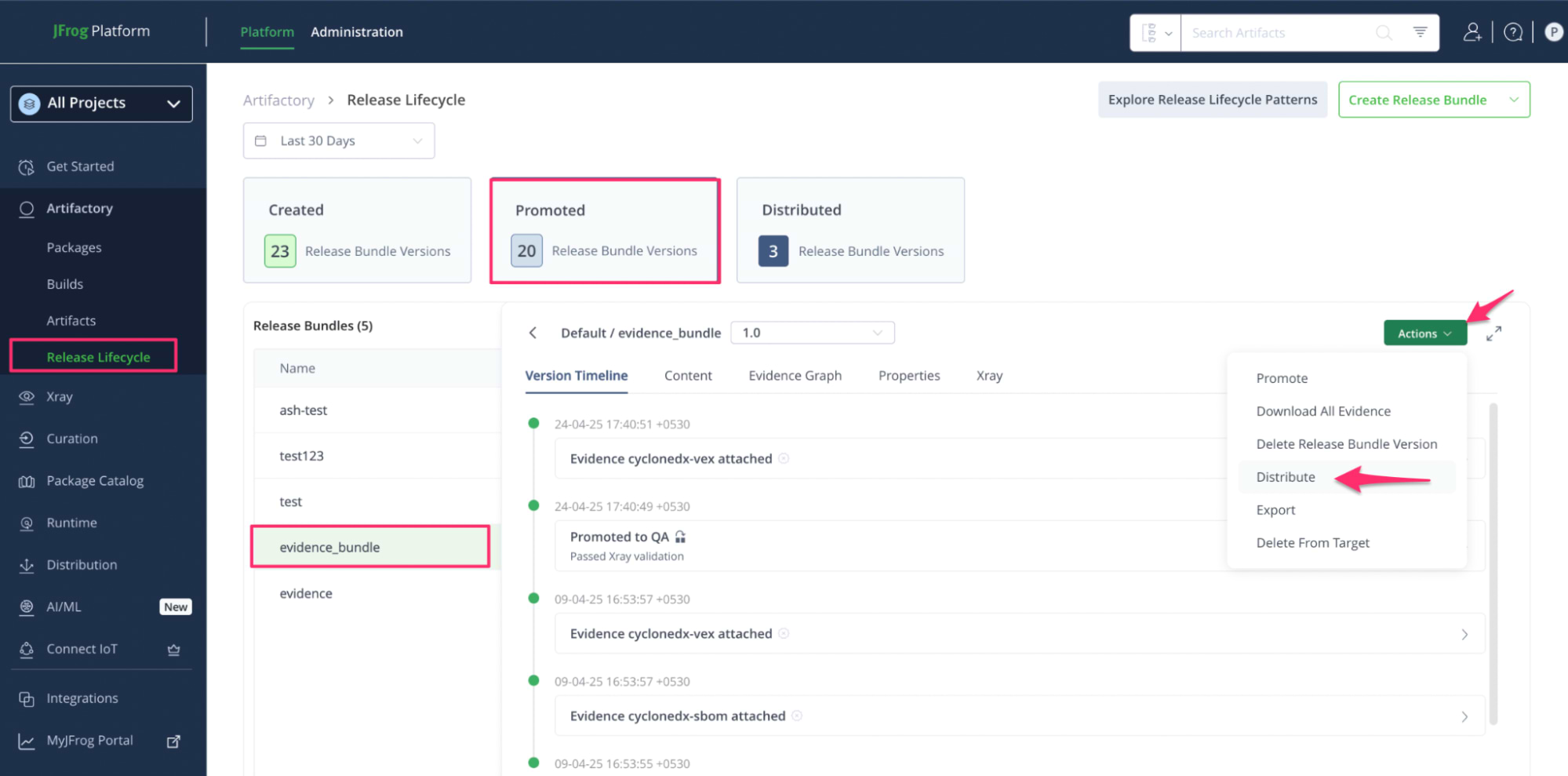
7. Release Lifecycle Management – Promote with Confidence
Artifacts are bundled into signed Release Bundles and promoted across environments (DEV → QA → PROD). Each promotion includes metadata, Xray scan results, and test evidence.
JFrog Evidence Collection records every step taken to prepare the release, offering an audit-ready trail of compliance and security checks. In regulated environments, this documentation becomes invaluable for approvals and audits.
Evidence including Xray scans, test results, and approvals are attached to the bundles for audit readiness
8. Secure Distribution – Global and Tamper-Proof
Release Bundles are securely distributed to production environments using JFrog Distribution. This guarantees:
- Immutable, tamper-proof delivery
- Audit-traceable deployment
- Geographic replication across edge nodes
Release bundle creation and distribution process
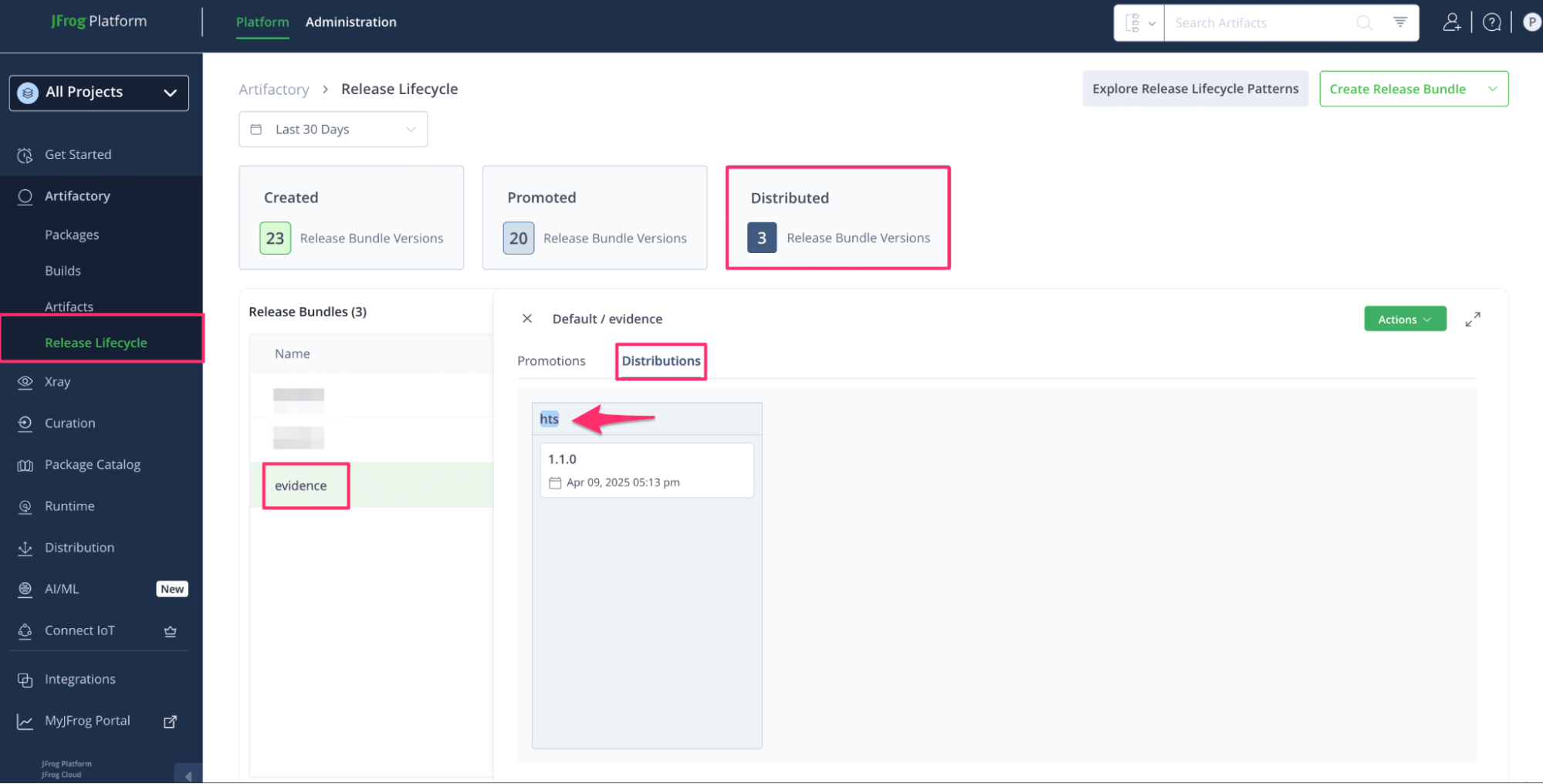
After successful release bundle distribution, you can verify the edge node and version details in the Distributions section. In this case, ‘hts’ is the edge node and the distributed version is 1.1.0.
New release bundle created and pushed to target nodes
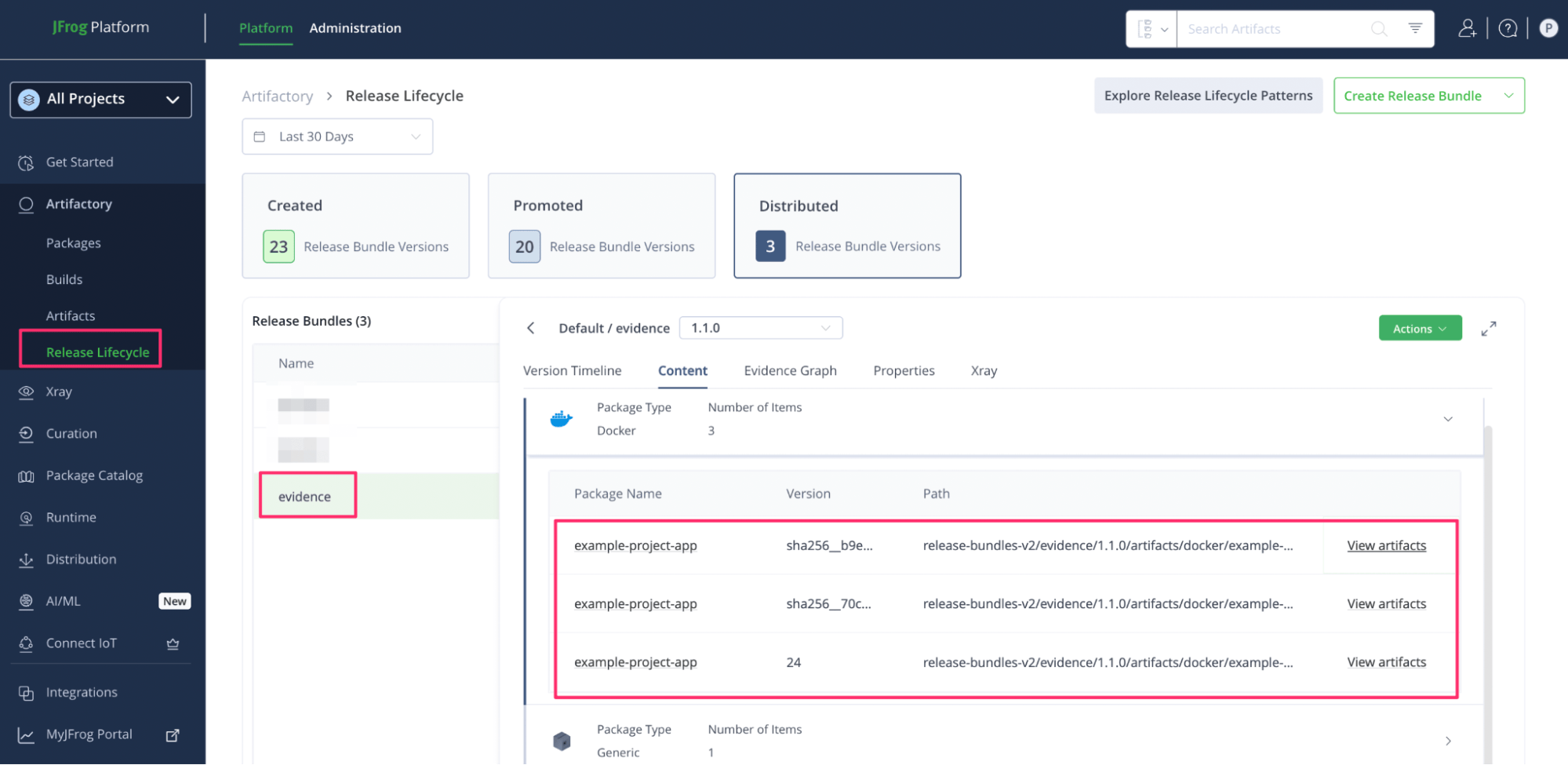
The following details outline the packages included in version 1.1.0. In this case, the package name is example-project-app.
Newly distributed release bundle and its content
9. Edge Node Delivery – Performance and Runtime Protection
Release Bundles are cached at JFrog Edge Nodes, bringing artifacts closer to runtime environments. This reduces latency, supports air-gapped deployment models, and ensures the authenticity of deployed packages.
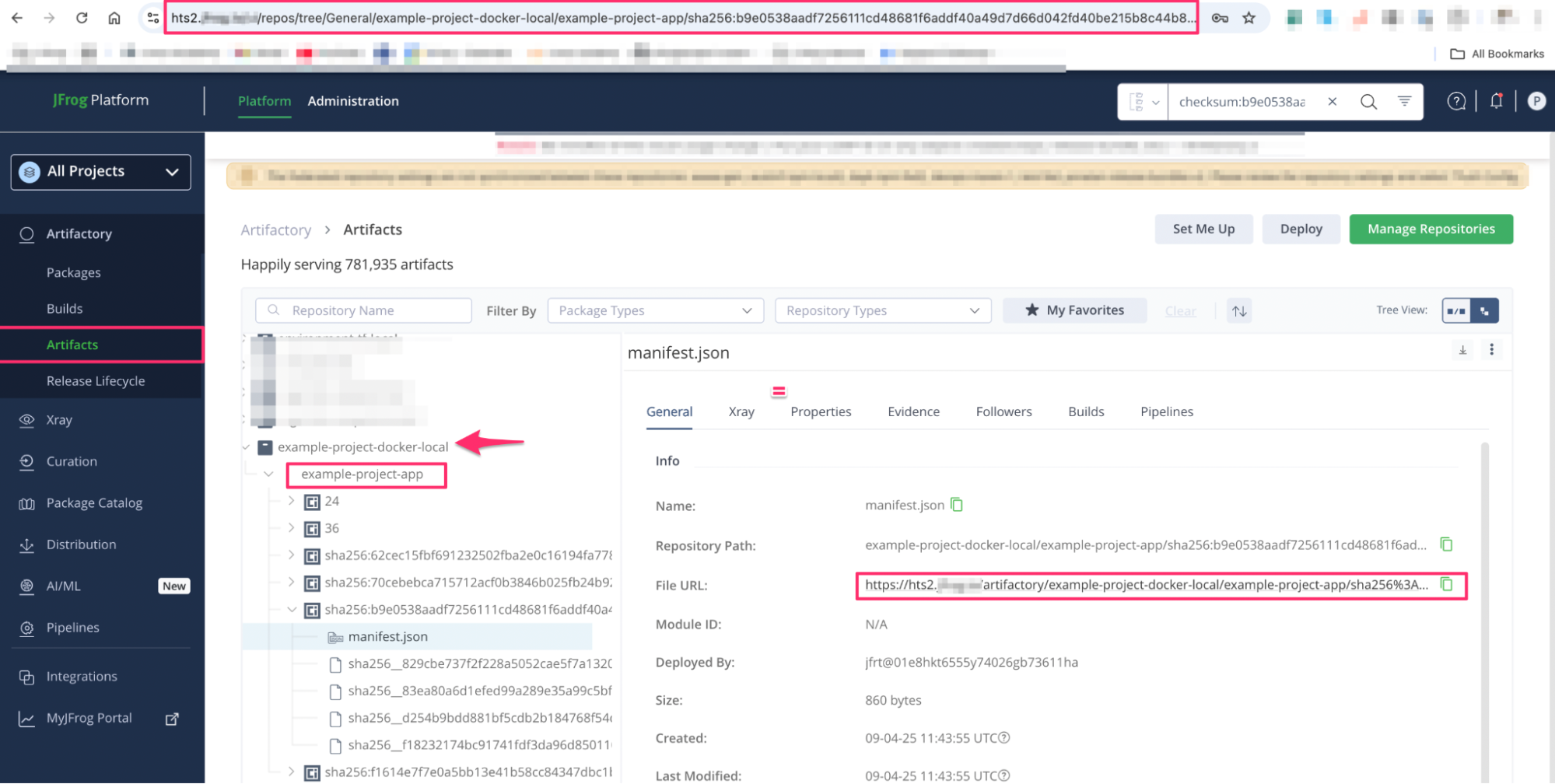
In the following screenshot, you can observe that the packages from release bundle version 1.1.0, specifically example-project-app, have been deployed to the Edge node.
New released version and the package details from the edge node
Conclusion
To help organizations meet ever-evolving industry standards, the JFrog Platform offers a modern DevSecOps blueprint combining robust binary management, continuous security, and enterprise-grade automation.
By adopting JFrog across the SDLC, organizations benefit from:
- Shift-left security from development through deployment
- Automated compliance and vulnerability scanning
- Tamper-proof distribution and runtime protection
- A complete, audit-ready trace of software releases
Whether you’re operating under strict regulatory standards or scaling delivery pipelines across teams, the JFrog Platform empowers you to innovate fast without compromising on security or trust.
To see it in action, take a platform tour or start a free trial.