How to Detect and Eliminate Shadow AI in 5 Steps
The pressure to integrate AI is immense. Your developers need to move fast, and they’re finding ways to get the job done. But this rush for innovation often happens outside of established governance, creating a sprawling, invisible risk known as Shadow AI.
To secure your organization, you must first understand what Shadow AI actually is.
It’s not just a developer downloading a file to their laptop. Shadow AI is the totality of unmanaged AI assets within your supply chain. This includes three distinct but equally dangerous components:
- External API Calls: Hardcoded API keys and data leakage risks from calls to third-party services within your code.
- Open-Source Models: Vulnerabilities such as supply-chain poisoning from models downloaded from public repositories.
- Custom Models: Proprietary, in-house models that lack a security scan or an auditable lineage.
If you don’t detect and govern all types of AI resources, you expose your organization to data leakage, malicious injection, and license violations. Here are five actionable steps to bring them under control using JFrog AI Catalog.
Step 1: Scan Your Existing Repositories
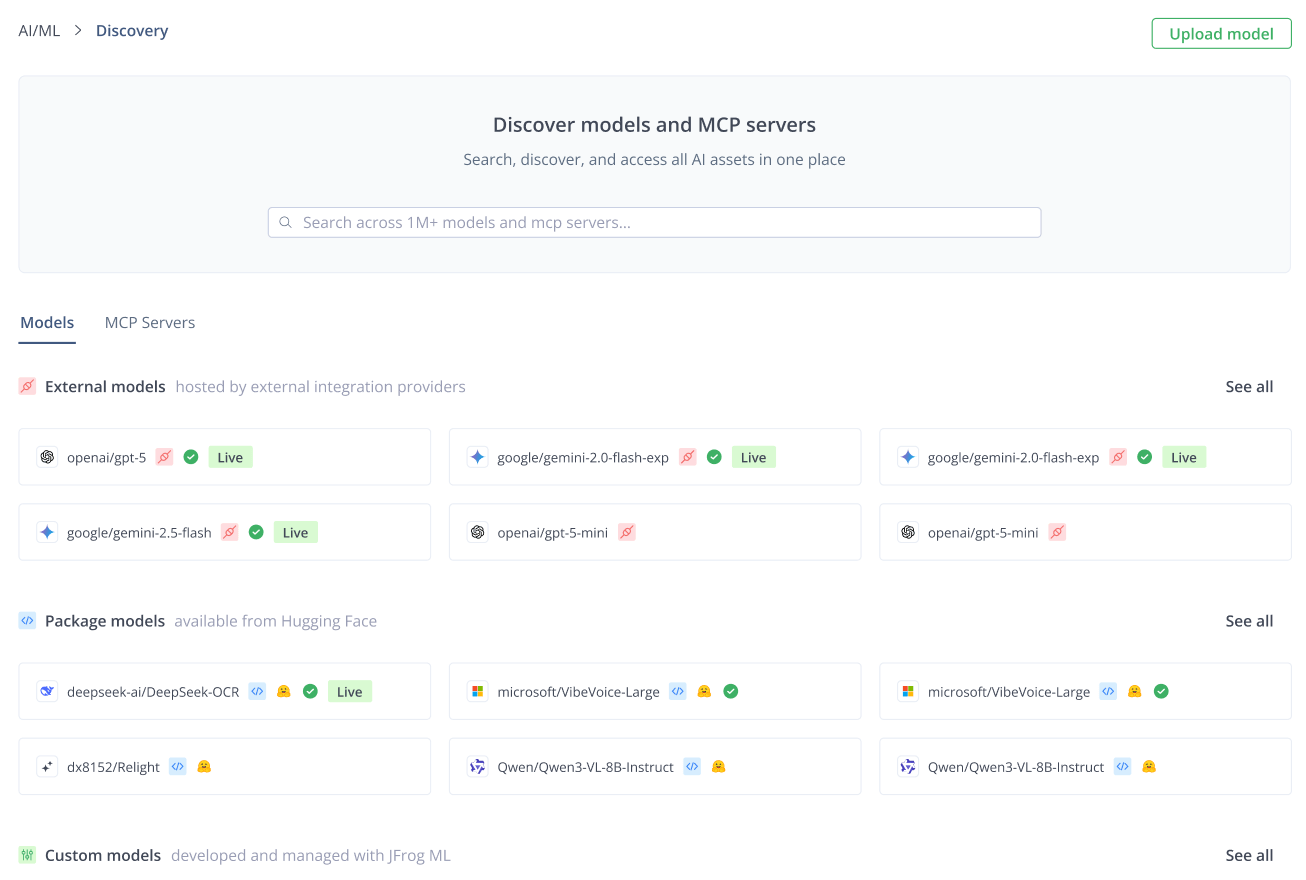
The first step in taming Shadow AI is to stop guessing and start auditing. You need a single mechanism to scan every artifact, build, and source code repository within your system to detect AI usage. Whether it lives in a binary file or an API call.
This process leverages JFrog’s underlying security components to find unmanaged AI assets across the entire platform:
- JFrog Xray scans your repositories and artifacts (such as Docker images or Maven packages) to identify every custom or open-source model, package, dataset, or associated dependency.
- JFrog Advanced Security performs source code analysis to detect signatures of calls to external AI APIs (e.g., OpenAI, Gemini, or Anthropic).
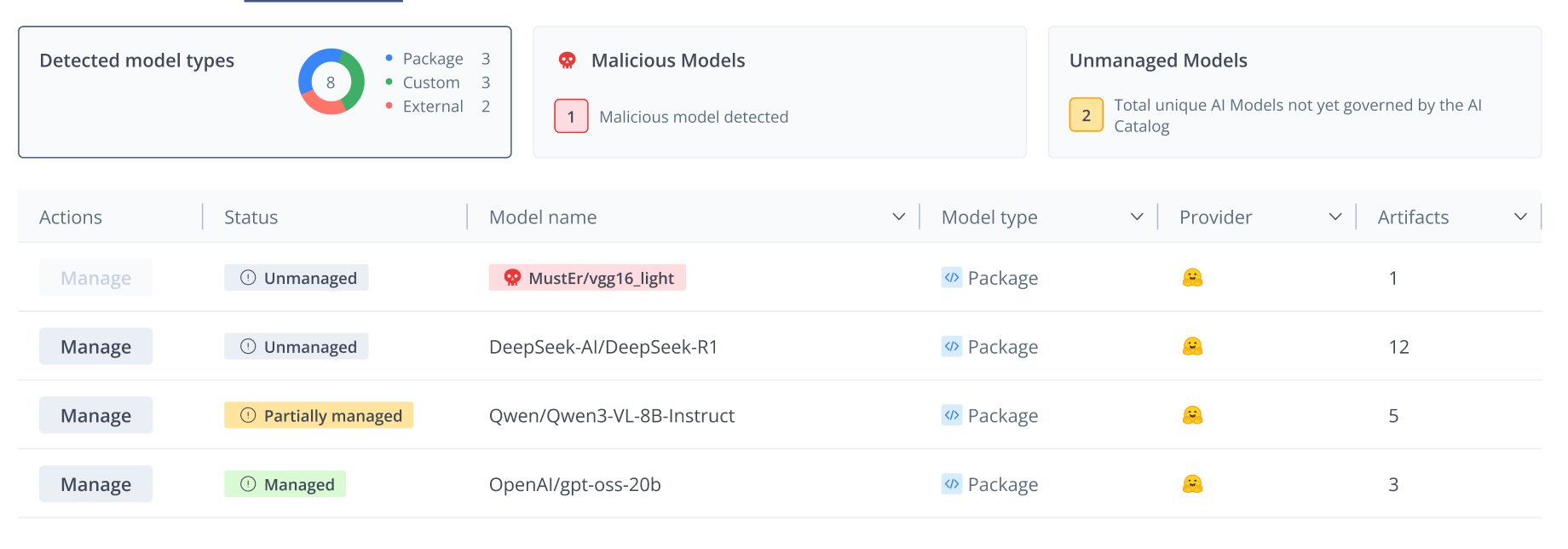
Once the scan is complete, the Detected Models dashboard in the AI Catalog becomes your centralized source of truth, showing every instance of AI usage, whether managed or not, across your repositories and builds.
Step 2: Review the “Shadow” Inventory
Now that you have full visibility, you must prioritize. The Detected Models dashboard automatically sorts and categorizes findings, so you can focus on the highest-risk assets first.
Prioritize your review using these three criteria:
- Malicious Models First: Always address models flagged by Xray as malicious or high-risk immediately. These are your burning fires.
- Frequency of Use: Sort models by how often they appear across your builds. Widespread use indicates a heavy dependency and a larger operational risk that you must address quickly.
- Governance Status: The system marks assets as Unmanaged, Managed, or Partially Managed.
This detailed inventory forces a shift from reactive to proactive governance; you move beyond simply identifying Shadow AI to understanding its actual business impact.
Step 3: Assess the Risk
Before you decide to “Allow” or “Block” a model, you must quantify the risk. This requires a deep dive into both the security and compliance implications of the unmanaged asset.
1. Security Risk:
Open-source models, especially from hubs like Hugging Face, are targets for supply chain attacks like namespace hijacking. Malicious actors can upload “poisoned” models that execute code upon download, leading to reverse shell injections and system compromise.
2. Compliance Risk:
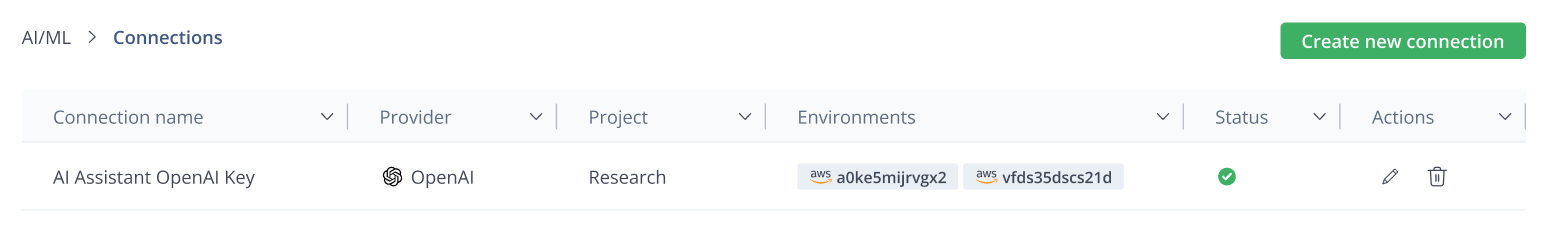
Unmanaged assets also pose severe legal risks. On the licensing front, inadvertently using a model with a non-commercial license in a commercial product violates IP law. Furthermore, hardcoded API calls to services like OpenAI create a data leakage risk, where sensitive prompts and proprietary data may leave your controlled environment and be processed by third-party systems.
To counter these threats, the AI Catalog uses JFrog Xray and Advanced Security to build a clear security and compliance view for each model. The platform scans the artifacts that contain these models for vulnerabilities in dependencies, and flags malicious or high-risk packages so you can act quickly. Simultaneously, it verifies license compliance and detects API signatures in your code. By aggregating this security and legal data into a single view, you gain the auditable record necessary to make a definitive governance decision.
Step 4: Policy Enforcement
With risk quantified, you move from passive observation to active control. Your objective is simple: ensure teams use only compliant, approved AI assets and block everything else.
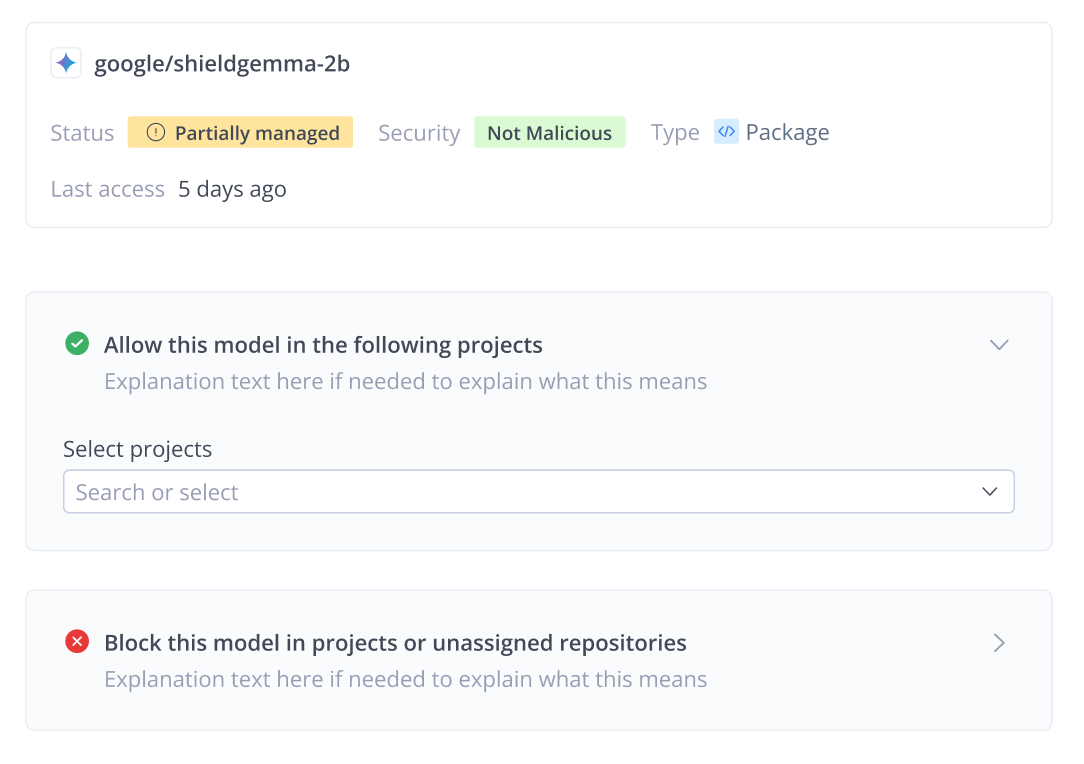
If an asset is high-risk, malicious, or violates policy, you can block it immediately.
- Block from Cache: When you mark a model as “Blocked,” the system automatically creates a Curation policy. In one action, it removes all cached instances of that model across remote repositories and prevents future downloads.
- Xray Block Policy: For local repositories, applying an Xray Download Block policy ensures the model cannot be used in governed projects.
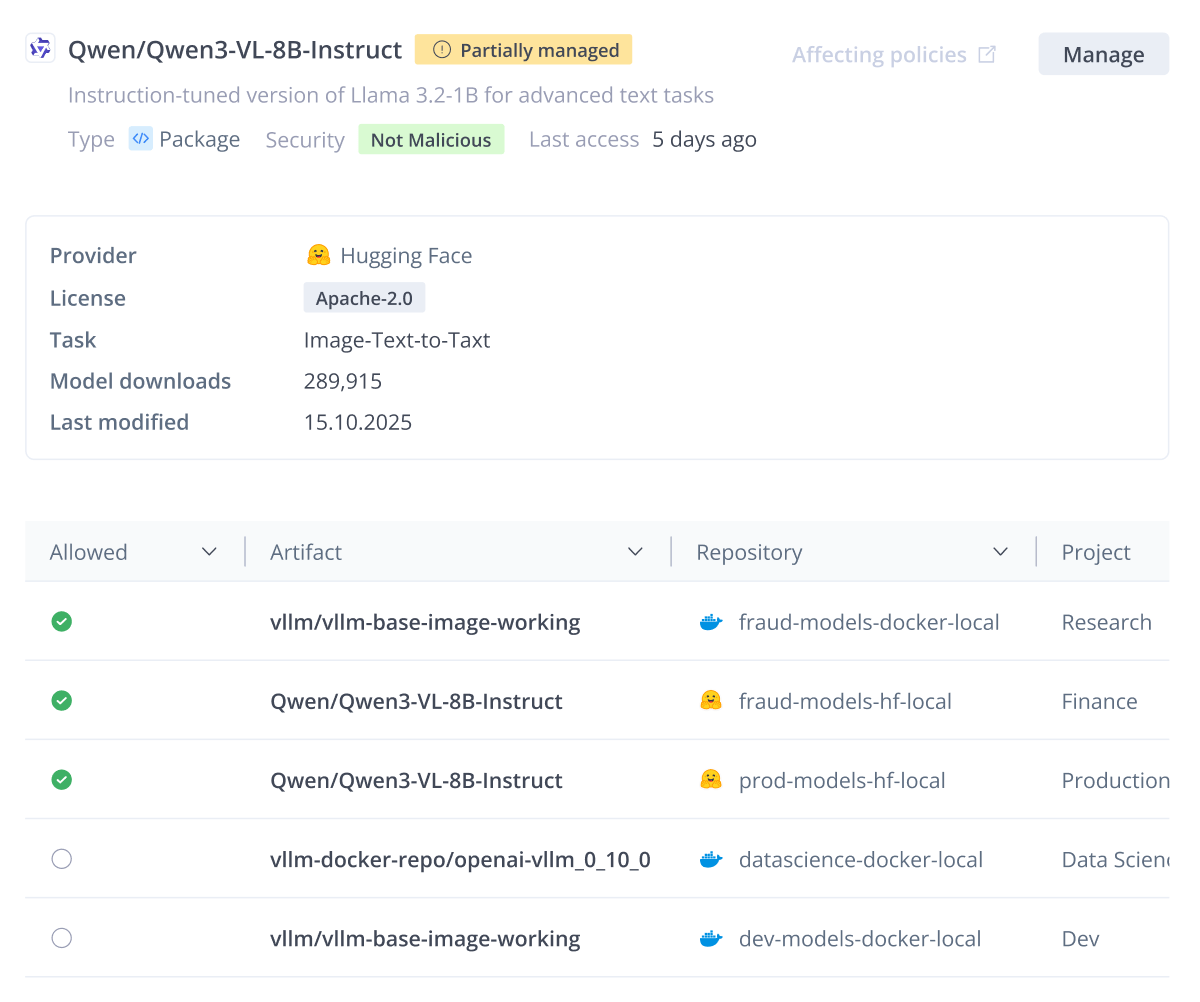
You will often encounter models with a Partially Managed status. This indicates a state of inconsistency: the model is allowed in only one project, but it’s still detected in the repositories of other projects where a governance decision hasn’t been made yet.
Instead of blocking these models and potentially breaking valid workflows, use the Allow action to extend governance to the unmanaged instances. This unifies the model’s status, ensuring it’s consistently monitored and secured across all teams that use it.
Managing the Existing Usage
Some models are already in use across multiple teams, making an immediate, hard block disruptive. For these, the Partially Managed status is key:
- This status indicates the model is allowed in one project but remains unmanaged in another, often due to shared repositories.
- The solution is to use the Allow action to bring the remaining unmanaged projects under the governance of the AI Catalog, ensuring a smooth transition to a fully managed state without causing unnecessary failure states for developers.
Step 5: Create the “Golden Path”
The final step is to shift your developer experience from a “wild west” of unsanctioned models to a “golden path” of safe innovation.
If you block an AI asset, you must provide a trusted alternative. The AI Catalog enables this by creating a centralized self-service hub:
- Trusted Discovery: Developers browse the Registry for approved internal, open-source, and commercial services. They know instantly that any asset they choose is secure and compliant.
- Credential Abstraction: The AI Gateway solves the “API Key” problem. It abstracts away credential management, so developers never handle raw API keys. They simply connect to the governed service.
By turning your governance dashboard into a single control plane, you transform your AI strategy from uncontrolled chaos to trusted, risk-adjusted velocity.
Take Control of Your AI
Shadow AI is an unavoidable reality in a fast-paced development world, but it doesn’t have to be an unmanageable risk. By recognizing that AI assets are now integral parts of your supply chain, you can apply your existing expertise in artifact management, security, and policy enforcement to this new domain.
The AI Catalog delivers the visibility to detect every unmanaged asset and the control plane to govern them, ensuring you can adopt AI securely and at scale.
Ready to eliminate Shadow AI and gain control of your AI workflows? Meet our experts and run the scan today.