Definition
Operational Risk Management (ORM) refers to the practices and processes for identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks associated with a company’s daily operations. These risks can include many factors, such as failures in internal processes, system breakdowns, human errors, and even external events that may disrupt business continuity.
The Importance of Operational Risk Management
Modern businesses face a multitude of risks that can disrupt operations, impact reputation, and jeopardize financial stability. Operational Risk Management (ORM) encompasses a range of strategic initiatives aimed at helping organizations navigate today’s inevitable uncertainties and thrive in a competitive environment. Understanding what constitutes operational risk is the first step toward effectively managing it.
Effective operational risk management means not only responding to present issues as well as preempting potential disruptions to maintain steady operations. By proactively addressing risks, organizations can avoid costly downtime and minimize financial losses. Furthermore, in an era where trust is paramount, a robust ORM framework can safeguard an organization’s reputation and customer loyalty, thereby helping to maintain a competitive edge. Without proper risk management, companies could face severe consequences, including legal liabilities, fines, and damage to their brand.
Other impacts of operational risk
The potential business impacts of operational risk are multifaceted. For example, a data breach or cyberattack can lead to regulatory penalties, financial losses, and the degradation of customer trust. In another case, improper management of risks in the supply chain could cause delays, substantial costs, and issues with the delivery of products or services.
Beyond the obvious repercussions, operational risks can have a cascading effect. For instance, a minor issue in one area of the business might quickly escalate into a full-blown crisis affecting the entire organization. By implementing a comprehensive ORM strategy, businesses can become more resilient, foster a culture of risk awareness, and protect operational continuity – even when the unexpected happens.
Key Components of Operational Risk Management
As we now understand, navigating operational risks in today’s digital landscape is a multifaceted undertaking. It encompasses several key elements that — together — help ensure the seamless functioning of an organization. Here are some of the key components of ORM:
Detection and Evaluation of Potential Operational Risks
- Understanding Risks
-
- The first phase of this process is the detection and evaluation of potential operational risks. Although it might seem straightforward, this complex process requires a thorough comprehension of the organization’s internal mechanisms and systems, as well as any external dependencies.
- Crafting a Risk Profile
-
- By systematically identifying risks, enterprises can craft a detailed risk profile. This profile is the foundation of effective risk management.
Implementation of Strategies and Controls
- Minimizing Risks by Developing Tailored Policies
-
- Once risks are identified, the next critical step involves implementing strategies and controls to minimize them. This involves developing and enforcing policies and processes customized to specific risks, such as:
- Data security measures
- Disaster recovery plans
- Backup systems
- Once risks are identified, the next critical step involves implementing strategies and controls to minimize them. This involves developing and enforcing policies and processes customized to specific risks, such as:
- Leveraging Technology
-
- Organizations can harness technological innovations like automation and Artificial Intelligence (AI) to reduce the likelihood of risks emerging and lessen their impact when they do.
Continuous Monitoring and Reporting
- Ongoing Assessments
-
- Continuous monitoring and reporting are essential components of managing operational risks. Regular monitoring ensures that the risk management framework remains relevant and effective in the face of evolving risks.
- Evaluating Performance
-
- This involves ongoing assessments, audits, and reviews to evaluate the performance of risk mitigation strategies.
- Fostering Transparency
-
- Providing stakeholders with timely and accurate information about the organization’s risk status enables proactive decision-making and nurtures a culture of transparency and risk awareness throughout the organization.
The key components of risk detection, mitigation strategies, and continuous monitoring and reporting constitute the basis of a strong risk management framework. By integrating these components, enterprises can safeguard their operations, financial stability, and reputation in the face of operational risks.
Operational Risk Management Best Practices
Implementing and maintaining an effective operational risk management (ORM) system within an organization requires a multi-faceted approach that combines strategic planning, a strong risk culture, and the integration of advanced technologies. Here are a few best practices to consider as you design and implement your ORM strategy:
- Foster a culture of risk awareness – This means ensuring that every employee, from frontline workers to executive leaders, understands their role in identifying, assessing, and mitigating operational risks. By making risk awareness a part of daily operations and decision-making, organizations can greatly enhance their resilience and preparedness to handle unexpected challenges.
- Strong governance and oversight mechanisms – Establishing clear policies, procedures, and accountability helps organizations ensure that their risk management activities are consistent and aligned with strategic objectives. Regular audits and reviews can identify areas for improvement and ensure that the ORM framework is functioning as intended.
- Leverage automation – Advanced tools like risk analytics, predictive modeling, and automated monitoring systems can provide real-time insights into potential risks. This enables more proactive and responsive risk management. Artificial intelligence and machine learning can also help find patterns and trends that might not be noticed otherwise, further helping organizations predict and reduce risks.
- Continuous education – Regular workshops, seminars, and virtual learning modules can help build competency in this area so that employees are equipped with up-to-date techniques for handling operational risks. Encouraging open communication and feedback can also help refine your ORM framework, by applying real-world insights and experiences to the continuous improvement of policies and procedures.
These best practices can help organizations improve their operational risk management strategy, making them more resilient and better prepared to handle the complexities and uncertainties of today’s world.
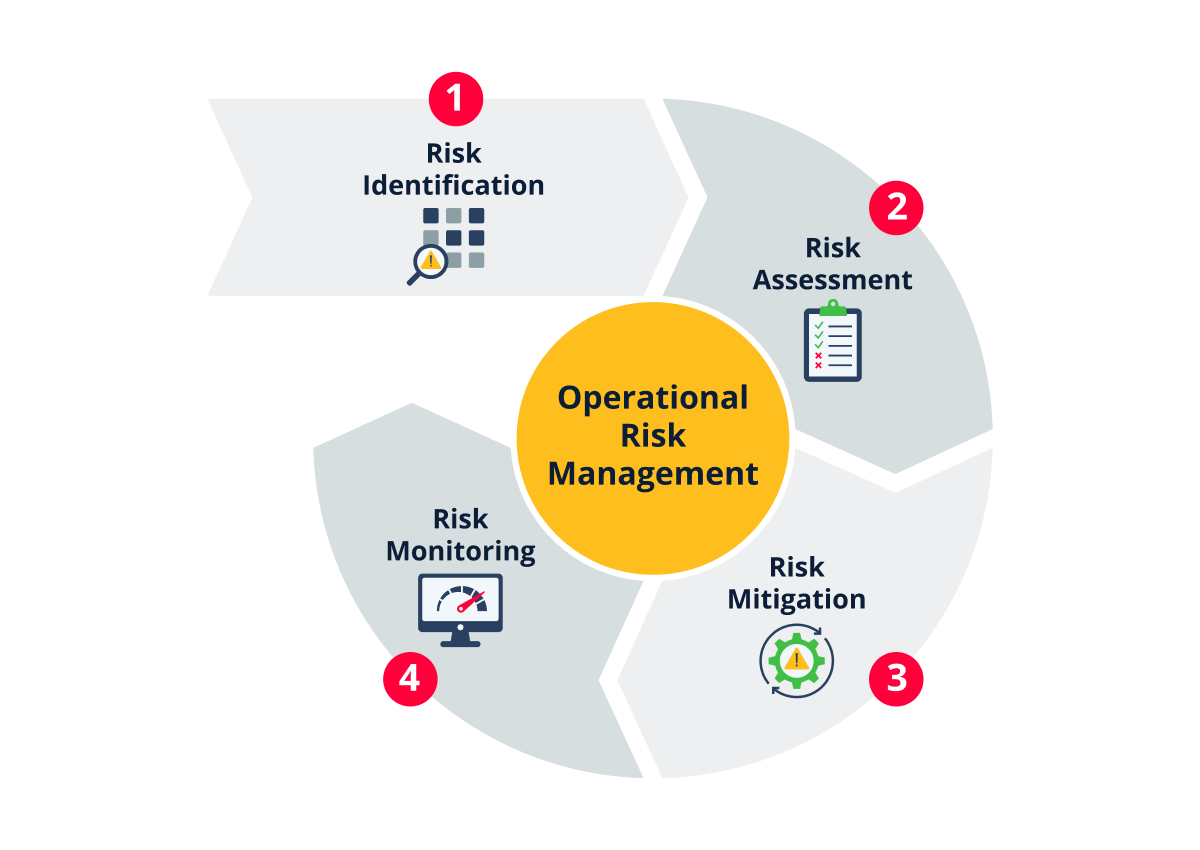
Operational Risk Management Framework
Implementing a robust operational risk management (ORM) framework is essential for any organization aiming to identify, assess, and mitigate risks stemming from daily operations. The framework serves as a structured approach to integrate ORM seamlessly with the overall risk management strategy.
At its core, the ORM framework involves several key steps:
Step 1: Risk identification
Effective risk management begins with identifying potential risks that could hinder an organization from achieving its objectives. This step involves a comprehensive understanding of what the organization aims to accomplish.
Risk identification methods might include:
- Process Analysis: Look at how the company functions in different areas, like production, IT, human resources, and customer service to help you spot problems and weaknesses.
- Loss Data Analysis: Examine historical loss data within the organization to identify trends and areas of concern. These may include:
- Financial losses
- Data breaches
- Compliance violations
- Incidents disrupting operations
- Risk Workshops and Interviews: Hold workshops and engage employees at different levels to gather insights on past incidents, perceived future risks, and areas for optimization.
- External Event Analysis: Take external factors into account. These could be things like regulatory changes, industry trends, geopolitical events, or any other event or change that could affect operations.
- Scenario Analysis: Come up with hypothetical situations to find potential risks and their effects. This helps you gauge how prepared the organization is for these kinds of events.
Step 2: Risk assessment
This involves analyzing the likelihood and potential impact of various risks. By understanding the severity and probability of each identified risk, organizations can prioritize their mitigation efforts effectively.
Step 3: Risk mitigation
This focuses on developing and implementing strategies to reduce the likelihood and/or impact of risks. Mitigation strategies can range from policy changes and training programs to technological upgrades and process improvements. Effective mitigation requires accountability and collaboration across departments and levels within the organization.
Step 4: Risk monitoring
Operational risks are dynamic and ever-evolving, requiring ongoing vigilance. Continuous monitoring allows organizations to track the effectiveness of their risk mitigation strategies and make adjustments as needed. Regularly reviewing the ORM framework also helps keep it in line with an organization’s broader risk management goals.
Benefits of Implementing Operational Risk Management
Adopting a holistic approach to operational risk management offers multiple strategic benefits for organizations aiming to effectively navigate the complexities of modern business.
Enhanced Decision-Making
By systematically identifying and evaluating risks, organizations can gain a clearer view of potential challenges and opportunities, enabling them to make more informed and strategic decisions. This forward-looking approach not only mitigates risks but also enhances overall performance by positioning companies to capitalize on emerging trends and market shifts.
Compliance and Regulatory Alignment
In today’s heavily regulated business landscape, compliance isn’t just a necessity – it’s a competitive differentiator. Risk management frameworks give organizations the essential tools and protocols to ensure that all operations align with current laws and industry standards. Not only does compliance reduce the risk of regulatory fines and legal liabilities, it also strengthens an organization’s credibility in the eyes of customers, partners, and stakeholders.
Financial Stability and Loss Prevention
By recognizing and addressing risks associated with day-to-day operations, organizations can significantly reduce financial repercussions associated with dilemmas such as downtime, data breaches, and supply chain disruptions. Especially in times of economic uncertainty, having a robust risk management strategy enables businesses to weather challenges and sustain growth.
Reputation Management and Stakeholder Trust
A company’s reputation can be severely damaged by operational failures and crises. By implementing an effective risk management framework, organizations can ensure they’re well-equipped to handle unexpected obstacles. A proactive stance not only protects the organization’s reputation but also builds customer and stakeholder trust, contributing to long-term success and stability.
Operational Risk Management in the Digital Age
The digital age has undoubtedly delivered unprecedented opportunities for businesses, but it’s also introduced a new set of challenges that necessitate a comprehensive operational risk management strategy. As organizations increasingly rely on digital technologies to streamline operations, drive innovation, and enhance customer experiences, they also become vulnerable to an ever-expanding list of digital risks – all of which can have catastrophic consequences if not properly managed.
This is precisely why cybersecurity and data protection have emerged as critical components of operational risk management. The interconnected nature of digital systems means that a breach in one area can quickly spread to affect other areas of the business, potentially causing widespread disruptions and financial losses. Companies need to implement robust cybersecurity measures, including thorough encryption, frequent security audits, and employee training to help minimize these risks. Equally important is data protection, as the mismanagement of sensitive information can lead to severe legal and reputational damages.
Traditional operational risk management strategies must also evolve to keep pace with today’s rapid advancements in technology. This involves adopting advanced risk assessment tools that can analyze data in real time, identifying potential threats before they materialize. AI/ML can play a significant role in enabling businesses to anticipate and mitigate risks more effectively.
The digital age demands that businesses take on a multi-faceted approach to operational risk management. Companies can’t solely focus on the technical aspects of risk mitigation but also on building a resilient organizational culture. This includes fostering cybersecurity awareness and transparent communication, and encouraging employees to report potential risks in a proactive approach to risk management.
By integrating these elements, as well as the ORM framework and best practices outlined above, organizations can build a comprehensive risk management strategy that is as robust as it is adaptable, ensuring business continuity and setting the stage for long-term success.