Managing Security Entities with JFrog Access
The Unsung Hero of Your Binaries’ Security
JFrog Access is the sentinel that manages authentication and authorization for all JFrog services. Packaged and installed together with JFrog Artifactory, Access keeps your binaries secure by making sure that only authorized users can access them. And then, those that do access your binaries, can only do what their permissions allow. Since Access has no UI of its own, it is operated under the hood by Artifactory and as such, is the unsung hero of security for your binaries.
Making the Connection
For Access to do what it does for a JFrog service, it needs to be connected to it. In the case of Artifactory, Access is installed together under the same Tomcat, and Artifactory communicates with it via an internal REST API. In the case of JFrog Xray and JFrog Mission Control, the connection is made when you set an Artifactory as the authentication provider. And for JFrog Distribution, the connection is through Mission Control’s authentication provider.
The Basics: Users, Groups and Permissions
Whether you’re creating users and groups directly within Artifactory, or pulling them in from external authentication servers like LDAP, SAML or Crowd, Access is the service that actually enforces the relationships between the users and groups and the permissions they are assigned. For example, when a user tries to login to one of the services, it is actually JFrog Access (and not the service) that ensures that user is properly registered. Or, when a user tries to access or do something to an artifact, it is Access that checks that user’s permissions, whether granted explicitly, or indirectly through membership in a group, and makes sure that user is allowed to do perform that action.
Now It Starts Getting Cool: Access Tokens
Access tokens are an alternative means of authentication and can be used instead of a user and password. Using access tokens opens up a whole range of capabilities.
Cross-Instance Authentication
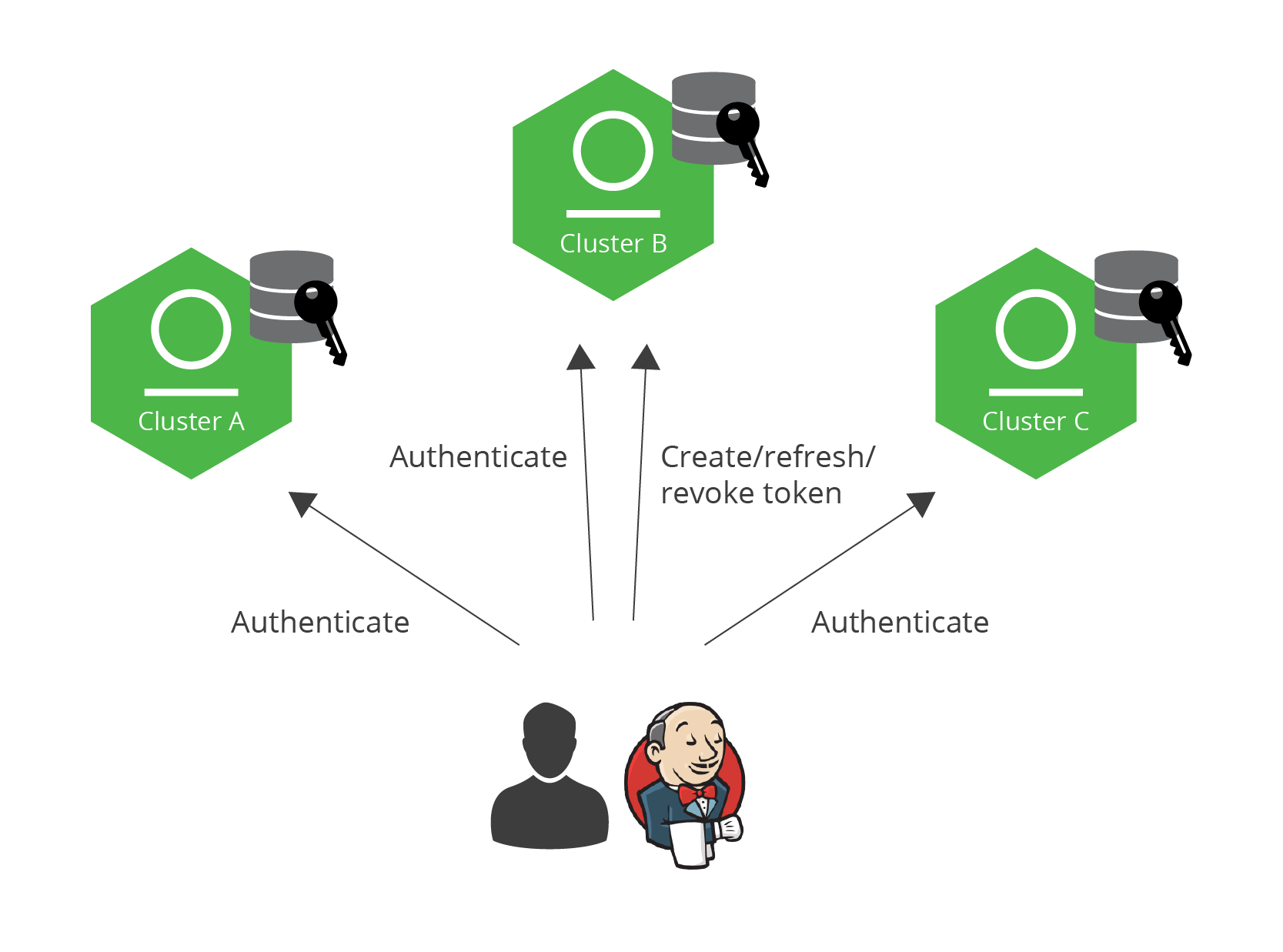
Imagine Jack, a developer, who needs to access more than one instance of Artifactory. For example, one instance may be used during development, and another instance used during QA or staging. When authenticating with user/password, you would need to create a user for Jack on both instances, however, using access tokens, authentication is simplified. By sharing public certificates between a set of Artifactory instances, you can establish a circle of trust in which an access token issued by any members in the circle, can be accepted by all other members. So if those two Artifactory instances are in a circle of trust, you only need to create an access token for Jack on either of those instances, and he can use that to access the other one.
But wait, there’s more. Since Artifactory is used as the authentication provider for the other JFrog services, then Jack can also use the same access token to access any Xray, Mission Control or Distribution services that are connected to any of the Artifactory instances within the circle of trust.
Non-User Authentication
But Jack isn’t the only one who needs access to Artifactory. Your CI/CD server does too. You can configure your CI/CD server with an access token it can use to access any Artifactory instance within the circle of trust. So, for example, your CI/CD server could pull dependencies from one Artifactory instance and upload builds to another.
Both end users and CI/CD servers can use a token to access any Artifactory service within the circle-of-trust.
Time-Based Access Control
So access tokens are a great way to provide users and machines with access to all the services within your circle of trust. Now, it’s difficult enough to manage and monitor an organization with a large number of users, but imagine trying manage all the access tokens you might issue to different users and machines. To prevent a maintenance nightmare, you can set an expiry period to an access token to limit the amount of time that user, or machine can use it. But, if you want to delegate control over the access token, you can also make it refreshable, so that trusted users will not have to request new tokens, every time their current token expires.
Assigning Group Scope
Finally, an access token doesn’t have to be “personal”. You can assign groups to an access token which will provide its user with group access privileges.
Access Federation: Complex Global User Management Made Easy
While access tokens are great to provide users (and build servers) with access to different JFrog services, they do not manage changes to the system. For example, new users added on one service could not automatically access another. A change in a user’s permissions on one service won’t be reflected in another parallel service. As enterprises scale up, and the number of users grows, managing the relationships between users, groups, access tokens and permissions across the company’s servers globally can become a complex and time-consuming exercise. Access federation makes managing these security entities simple and fully automated. You can think of it like the cross-instance authentication capabilities of access tokens extended to include all security entities within the circles-of-trust set up for the company’s global JFrog services. Fundamentally, what Access Federation provides is automatic synchronization of changes to security entities with the defined circles-of-trust.
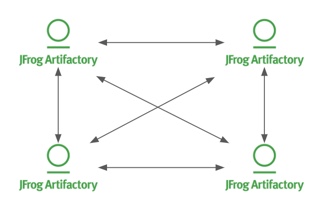
Using the Access YAML configuration file, you fully control which security are synchronized, and in which directions, enabling you to set up different topologies of synchronization for different use cases. Consider 4 separate teams working on a project, each using their own Artifactory service. To keep the teams synchronized, you want to provide equal access to all members on all servers. You could set this up as a full-mesh topology so that any change to one of the servers (e.g. a new user added to the team, a change in permissions, or formation of a new group) automatically gets synchronized to all the other servers, so everybody’s access to all servers remains the same.
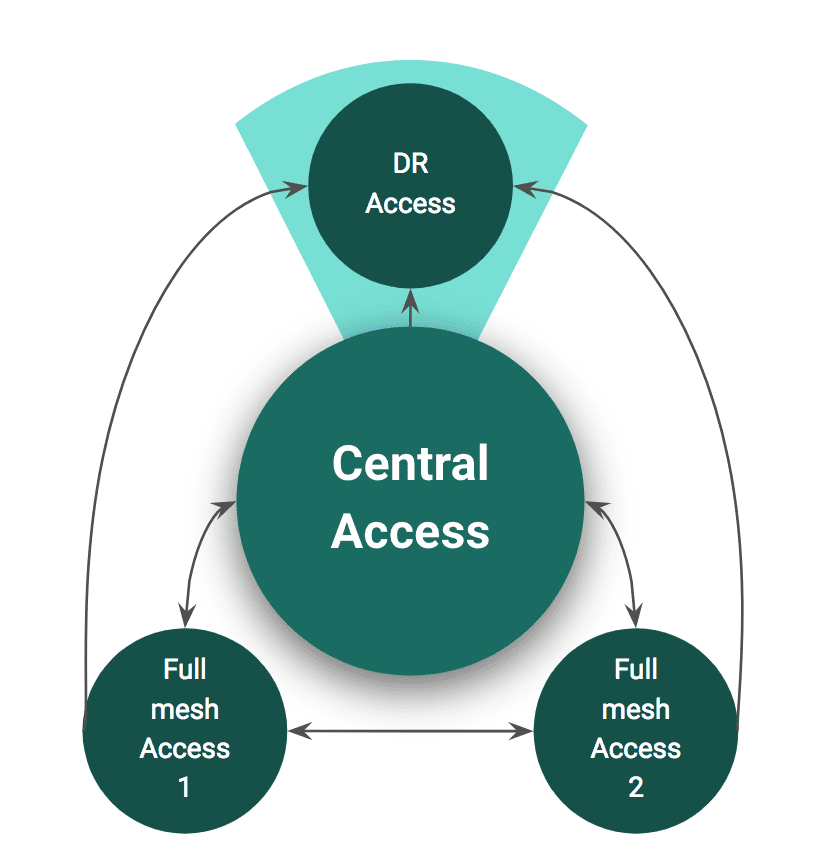
Another example could be maintenance of an Artifactory instance for Disaster Recovery. In the diagram below, Full mesh 1 and 2, and Central Access are setup in a full mesh topology, same as the one described above. But now, there is also a DR instance which can only receive changes made on any of the other services. If any of the other three servers goes down, the DR instance can be brought into full operation, and it will already be fully equipped with the complete and up-to-date security configuration of the remaining two instances.
Access Federation to support Disaster Recovery
Keeping your binaries secure, ensuring that all access to them is only by authenticated users with the right permissions is not something that starts in production systems. It’s the extreme end of the shift-left culture moving security into the heart of DevSecOps. JFrog Access gives you all the capabilities needed to ensure your binaries are safe, and only exposed according to your access policies, from the moment they are created until they are deployed to your production systems.