
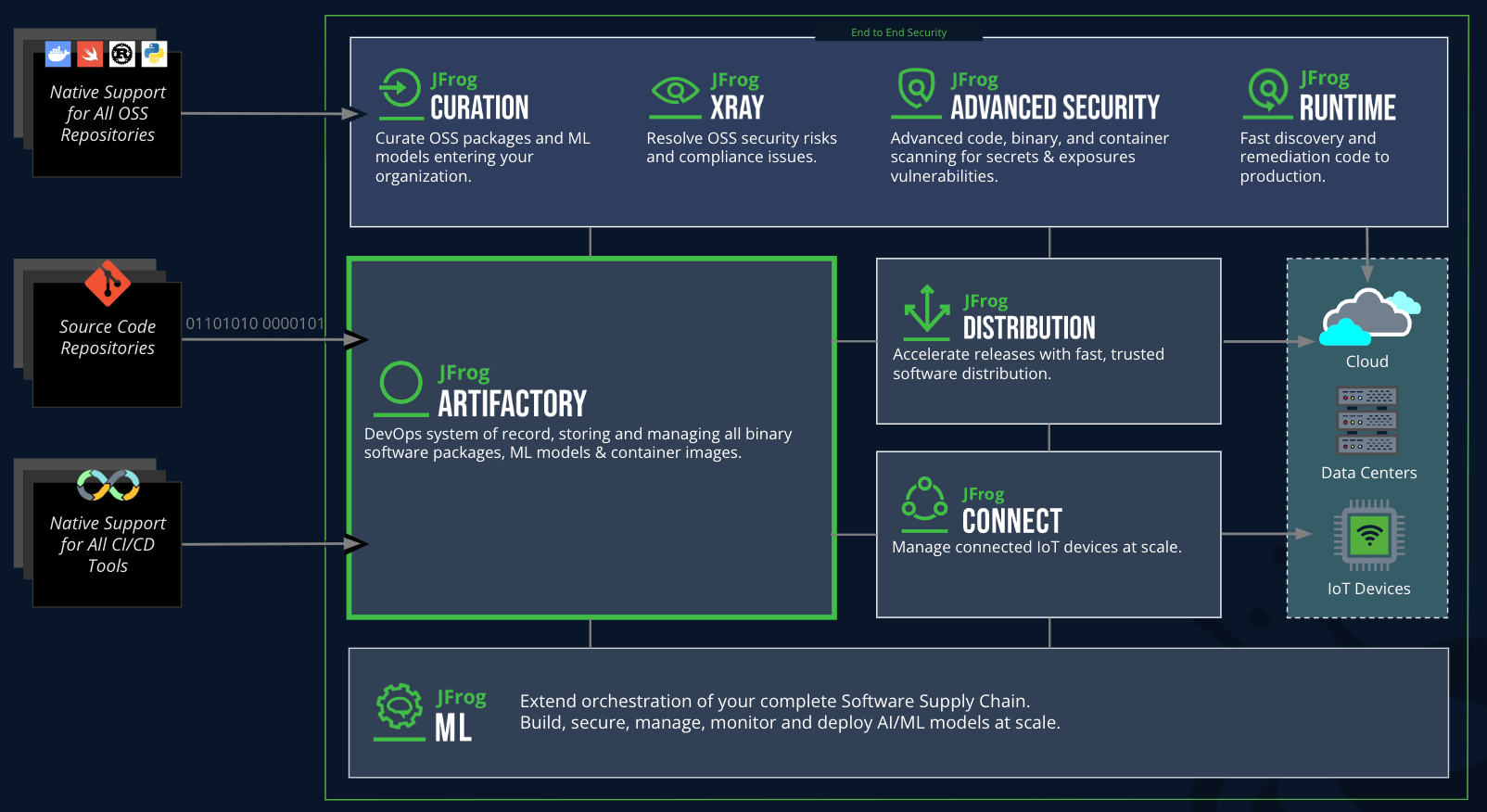
Integrating Apache Ivy with JFrog Artifactory provides a central repository to manage and resolve dependencies, both internal and external. Artifactory enhances security and traceability of artifacts, ensures better control over your build dependencies, and caches external libraries for faster builds. You can also manage permissions, promote builds, and automate CI/CD processes.
To configure Apache Ivy to use JFrog Artifactory:
Create an Ivy repository in JFrog Artifactory (usually a Maven-type repository).
In your ivysettings.xml, define the Artifactory repository URL, specifying the credentials and repository patterns for retrieving and publishing artifacts.
Example configuration:
Include the resolver in your build script to make Artifactory the source for dependencies.
To publish artifacts using Ivy, you need to configure a publish resolver in your ivysettings.xml. Example configuration:
After this setup, use the ant ivy:publish command to deploy artifacts to the configured Artifactory repository.
You can authenticate Ivy with JFrog Artifactory by providing credentials in your ivysettings.xml file or in a properties file. In ivysettings.xml, include authentication information in your resolver configuration like this:
/artifactory/”
username=”” password=”” />
Alternatively, you can store credentials in a separate properties file and reference it in the build script to avoid hardcoding sensitive data.
JFrog Artifactory supports dependency resolution for Ivy projects by acting as a proxy for both local and remote repositories. Artifactory retrieves dependencies from external sources (e.g., Maven Central) and caches them, optimizing build times and reducing external network requests. It allows you to create virtual repositories that aggregate multiple repositories, ensuring that both internal and external artifacts are resolved seamlessly. Dependency resolution also benefits from version control, caching, and audit logs that track all dependencies used in a project.