Definition
Release management is the structured process of planning, coordinating, and overseeing software deployments. It helps ensure that new features, updates, and fixes are delivered safely, consistently, and with minimal disruption.
Overview of Release Management
Release management is a key discipline within the software development lifecycle. It defines how changes move from development through testing and into production. By aligning cross-functional teams around a repeatable process, release management helps reduce risk, improve quality, and deliver software more efficiently. It is especially important in agile and DevOps environments where frequent releases are common.
The Release Management Process
Release management governs how software changes progress from development through deployment in a structured, controlled, and repeatable manner. It provides a standardized approach for planning, building, testing, and releasing software, ensuring that every change is tracked and executed with minimal disruption. By following a defined process, organizations can reduce risk, improve software quality, and deliver value to users faster and more reliably. This approach also helps teams coordinate across functions, manage dependencies, and maintain stability, even when delivering frequent updates in agile or DevOps environments.
Phases of the Release Management Process
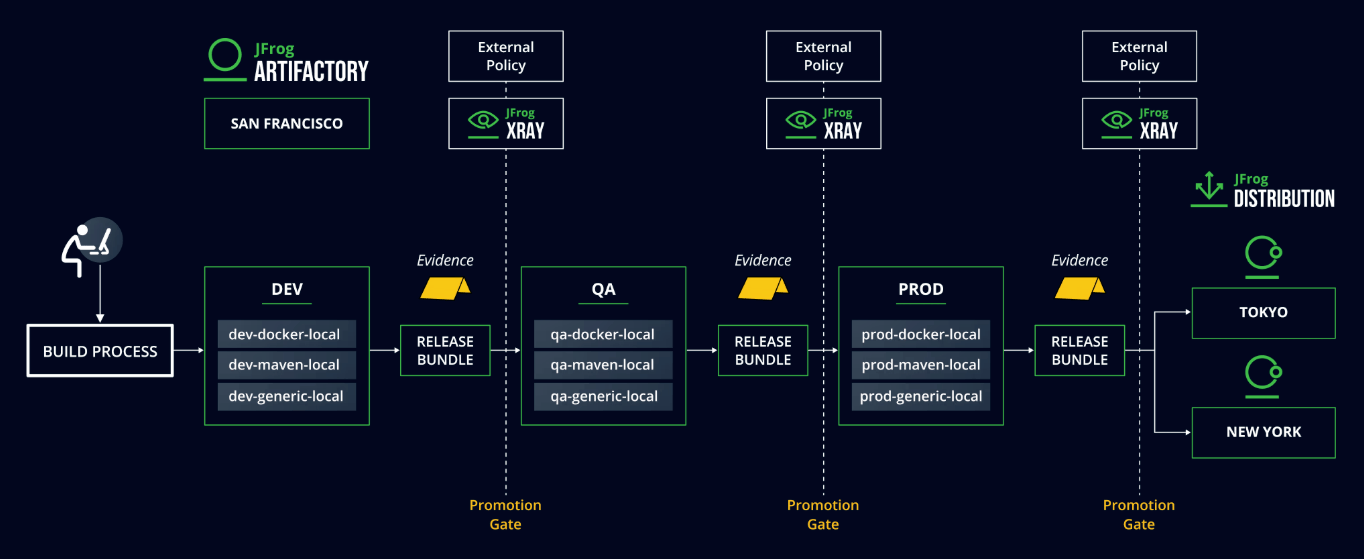
The process typically unfolds across five core phases: planning, build and integration, testing and validation, deployment, and post-deployment review. When moving your application between these stages, you can validate quality and mandatory steps by reviewing the evidence or attestations, and approve or reject based on your defined policy.
In the planning phase, teams define the scope of the release, set timelines, and identify resource needs. This stage involves outlining dependencies, estimating risks, and ensuring that both technical and business goals are aligned.
Once planning is complete, the build and integration phase begins. Here, developers compile code and integrate changes into a shared repository. Continuous integration tools often automate the generation of build artifacts, which are then versioned and stored for testing and deployment.
Next is the testing and validation phase, where releases are evaluated for functionality, performance, and security. Teams conduct regression tests, performance benchmarks, and compliance checks to ensure the release meets organizational standards. In many cases, user acceptance testing (UAT) is also included before the release is approved.
The deployment phase involves rolling out the release to production or staging environments. Techniques like canary deployments or blue-green releases may be used to minimize risk. Monitoring is crucial at this stage to detect issues early and ensure that the release performs as expected in a live environment.
Finally, the review and post-deployment phase provides an opportunity for reflection. Teams analyze metrics, gather stakeholder feedback, and document lessons learned. This retrospective step helps identify opportunities for process improvement and enhances the quality of future releases.
Key Activities in Each Phase
Each phase of the release management process comes with distinct activities. During planning, teams align on objectives, assess risk, and finalize a schedule. In the build and integration stage, source code is compiled, and automated tests are run to ensure quality from the start. Testing and validation involve multiple layers of checks—from automated unit tests to more extensive manual testing—to confirm the release is stable and compliant.
Deployment is typically executed according to a predefined strategy, with active monitoring to track success or identify rollbacks if necessary. After deployment, teams hold review meetings to evaluate performance, log any incidents, and refine future release workflows.
Stakeholder Involvement
Developers build and troubleshoot code, while QA validates quality. Operations and DevOps handle automation and infrastructure. Product managers align releases with business goals, and security teams ensure compliance. Involving the right stakeholders at each stage makes the release process more efficient and transparent.
Benefits of Effective Release Management
A consistent release management process supports software delivery by improving reliability, reducing risk, and helping teams scale their workflows efficiently. It provides a repeatable framework for planning, testing, and deploying changes, making it easier to coordinate across teams and environments. As development velocity increases, having a standardized process becomes essential for maintaining stability, meeting compliance requirements, and ensuring that updates are delivered with minimal disruption.
Improved Software Quality
Structured workflows and automated checks help identify issues early in the pipeline. By ensuring only validated code moves forward, release management reduces production defects and supports a more stable end-user experience.
Faster Time to Market
Clear handoffs and automation throughout the release process help eliminate delays and manual coordination. This enables teams to deliver updates and fixes more quickly while maintaining control and traceability.
Enhanced Collaboration Across Teams
Defined roles and responsibilities foster better communication between development, QA, operations, and product teams. This alignment improves coordination, reduces miscommunication, and streamlines release execution.
Key Roles in Release Management
Release management relies on defined roles and tight coordination across teams. At the center of this process is the release manager, who ensures each release is delivered smoothly and aligns with business goals. This role involves overseeing timelines, managing dependencies, and facilitating communication between development, QA, operations, and product stakeholders. By coordinating these efforts, the release manager helps minimize delays, reduce errors, and ensure that releases are executed according to plan and organizational standards.
Roles and Responsibilities of a Release Manager
The release manager oversees the full release lifecycle—scheduling, coordinating resources, tracking risks, and ensuring quality. They manage the release calendar, communicate timelines, and lead go/no-go decisions. Their role blends project management with a strong understanding of software delivery workflows.
Collaboration with Development and Operations Teams
Close collaboration with development and operations teams is essential. Release managers coordinate with developers on feature readiness and testing, while working with operations or DevOps teams to align on deployment plans and infrastructure needs. This helps ensure a seamless flow from code to production.
Importance of Communication and Coordination
Strong communication keeps stakeholders aligned. The release manager ensures everyone is informed about timelines, risks, and responsibilities. Clear coordination reduces surprises, speeds up issue resolution, and keeps releases on track.
Best Practices for Release Management
Effective release management depends on well-defined plans, automation, and ongoing performance measurement. These best practices help teams deliver software consistently and efficiently.
Establishing a Release Management Plan
A clear release plan outlines scope, timelines, responsibilities, and risk management strategies. It ensures coordination across teams and helps address compliance early. While structure is key, the plan should remain flexible enough to adapt to shifting priorities.
Continuous Integration and Delivery Practices
CI/CD is central to modern release workflows. Continuous integration enables frequent code merges and automated testing, while continuous delivery automates deployments to production-ready environments. These practices reduce manual errors, speed up releases, and provide rapid feedback for teams.
Metrics for Measuring Success
Tracking metrics like deployment frequency, lead time, change failure rate, and mean time to recovery (MTTR) helps teams assess performance and reliability. These indicators support continuous improvement and give stakeholders visibility into the health of the release process.
Tools for Release Management
Release management tools provide the structure and automation needed to deliver software efficiently and reliably. They support coordination, integration, and deployment across the development lifecycle.
Overview of Essential Release Management Tools
Core tools include version control systems, artifact repositories, deployment automation platforms, and release tracking solutions. Jira and Azure DevOps manage planning and issue tracking, while Git-based platforms like GitHub Actions or GitLab CI/CD support integration and testing. Tools like JFrog Artifactory manage artifacts, and deployment platforms such as Octopus Deploy or Spinnaker streamline releases across environments.
Integration with CI/CD Pipelines
Modern release tools integrate closely with CI/CD pipelines, enabling automated builds, tests, and deployments. This tight integration reduces manual steps, ensures consistency, and supports continuous delivery, helping teams release more frequently with fewer errors.
Evaluation Criteria for Selecting Tools
Key considerations when choosing tools include ease of integration, scalability, security, and visibility. The right tools should fit into existing workflows, offer access control and audit trails, and provide insights into release progress. Flexibility to support different architectures and environments is also essential for long-term value.
How JFrog Supports Release Management
JFrog supports release management by providing secure, traceable artifact storage and integrated tooling across the software delivery lifecycle. Artifactory maintains a reliable record of build outputs, making it easier to manage versioning, approvals, and environment promotion. Built-in scanning helps identify vulnerabilities and license issues early in the release process. Role-based access and policy controls limit who can promote or modify artifacts, helping teams meet compliance and security standards. JFrog also captures key metadata to support provenance, auditability, and consistency across releases—without slowing down development.
For more information, please visit our website, take a virtual tour, or set up a one-on-one demo.