Definition
A semantic release is an automated workflow that strictly adheres to the principles of Semantic Versioning (SemVer) to manage software releases. Its primary goal is to eliminate the manual effort and human error involved in versioning and publishing software. The process works by analyzing the commit messages since the last release to automatically determine the correct next version number and generate changelogs.
Overview of Semantic Release Automation
The primary value of Semantic Release lies in its ability to automate the entire release process, from determining the next version to publishing release notes. By tying the release directly to the content and intent of a developer’s commit messages, it eliminates the need for manual and often inconsistent version bumps. This not only increases release velocity but also reduces the potential for human error.
Key principles of semantic release
Semantic Release is a tool, but also a method for release management with the goal of automating the software release workflow. Its key principles include deriving the next version number from a project’s commit messages and automating the generation of changelogs and release notes based on the same commit history. This ensures that every release is a consistent and predictable event.
How semantic differs from traditional software release management
Traditional release management often involves manual steps, such as human judgment to decide on the next version number and manually creating release notes. This can be time-consuming and prone to errors. In contrast, semantic release automates this process entirely by following a strict set of rules based on the commit history, making the process faster, more reliable, and consistent across the entire SDLC.
Benefits of using semantic release in software development
Automating releases with a semantic approach provides several benefits to a software development team. It removes the emotional and often inconsistent human element from the versioning process, ensuring releases are always predictable. It also automatically generates accurate and detailed release notes, which saves developers time and improves communication with users about new features and bug fixes. By integrating seamlessly into a CI/CD pipeline, it enables a continuous delivery model, a more secure software development lifecycle and faster time-to-market.
The Role of Semantic Versioning
Semantic versioning provides the foundation upon which semantic release operates. It is a formal set of rules that defines how version numbers are assigned and incremented, ensuring that every version includes meaningful information about the changes in that particular version.
Overview of semantic versioning principles
Semantic versioning (SemVer) uses a three-part numbering system: PATCH.MAJOR.MINOR. Each part of the version number conveys a specific type of change:
- PATCH: Incremented for backward-compatible bug fixes
- MAJOR: Incremented for backward-incompatible changes
- MINOR: Incremented for new, backward-compatible features
This system gives users and other developers clear expectations about the impact of a new release, allowing them to confidently manage their project dependencies.
How semantic versioning integrates with semantic release
Semantic Release directly consumes a project’s commit messages, which must follow a conventional format, such as the Conventional Commits specification. This format links specific keywords (e.g., feat: for a new feature, fix: for a bug fix) to the corresponding part of the SemVer scheme. This integration allows the automated tool to parse the commit history and determine precisely which version number needs to be incremented (patch, minor, or major), automating a task that would otherwise be manual.
Real-world examples of semantic versioning
Consider a project at version 1.0.0. If a developer commits a bug fix with the message: "fix: resolve login bug", the next release would automatically be 1.0.1. If they add a new feature with the message: "feat: add user profile page", the version would become 1.1.0. A breaking change, such as: "feat!: remove legacy API endpoint", would trigger a major version bump to 2.0.0. This strict, automated process provides transparency and predictability for any user relying on the project.
Setting Up Semantic Release
Implementing a semantic release workflow requires careful planning and precise configuration to integrate it successfully into your existing development and release workflow. Well defined prerequisites and setup steps ensure that the automation works reliably and consistently with your codebase and team’s practices.
Prerequisites for implementing semantic release
Before implementing semantic release, a few key prerequisites must be in place:
- First, your project must use a version control system like Git.
- Second, your team needs to adopt a standardized commit message convention. This convention is critical because the automated tool uses these messages to decide on version bumps.
- Third, you need a CI/CD pipeline to automatically run the semantic release process.
Step-by-step guide for configuration
Follow these steps to configure your semantic release parameters
- Install the Semantic Release CLI: Add the semantic-release package and relevant plugins to your project as dev dependencies.
- Configure Plugins: Define the plugins in a configuration file (e.g.,
.releaserc.json) to specify how the tool should behave. This includes plugins for your Git repository, changelog generation, and package management system (e.g., npm, Maven, etc.). - Set up CI/CD Integration: Add a step to your CI/CD pipeline that runs the
semantic-releasecommand. This step should execute after your tests and builds have passed, using a dedicated service account with the necessary permissions to publish releases. - Enforce Commit Message Convention: Use a tool like
commitlintwith a Git hook to validate commit messages, ensuring every commit adheres to the required format.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
One common pitfall is inconsistent commit messages. If developers don’t follow the Conventional Commits specification, the automation will fail. To prevent this, it is suggested to use pre-commit hooks that validate messages before they are pushed out.
Another issue is permission errors with the CI/CD pipeline. You must ensure the service account used by the pipeline has the correct permissions to write to your repository and publish packages. You can avoid conflicts and streamline workflows by also carefully managing dependencies in your project and its build.
Best Practices and Strategies for Semantic Release
Implementing a semantic release workflow is not just about tools; it’s about adopting best practices that foster a culture of discipline and collaboration. This section outlines strategies to ensure your semantic release process is effective and sustainable.
Establishing a workflow that incorporates semantic release
A successful workflow begins with clear communication and team-wide adoption of a well-defined and consistent commit message format. Developers must understand that their commit messages are now much more than just notes; they are the actual triggers for the release process. The workflow should be integrated into the CI/CD pipeline, starting with code changes and ending with a fully automated release to a binary repository manager. You should also ensure that your pipelines include automated tests and security scans, so that only high-quality code is ever released. This is a core part of the “Shift Left” security strategy, which emphasizes identifying and fixing problems as early as possible in the development lifecycle.
Collaborating with teams for effective release management
Semantic release fosters better collaboration by making the release process transparent and predictable. Teams can rely on an automated system to handle versioning, freeing them to focus on development. For instance, a development team might leverage the semantic release workflow to update a microservice, and the operations team can rely on the automated changelogs to see precisely what has been updated without needing to manually parse through code changes. This shared understanding and automated process minimizes the friction traditionally associated with release coordination.
Monitoring and maintaining release quality over time
Monitoring is crucial for maintaining the quality of an automated release process. You should monitor your CI/CD pipeline for build failures, and your repository for any failed releases. Track the number of bug fixes and feature releases over time to ensure a healthy development cycle. Additionally, use tools that provide feedback loops on the quality of your releases, such as vulnerability scanners, to continuously improve security and reliability.
Implementing Semantic Release with the JFrog Platform
JFrog’s platform provides an ideal environment for a semantic release workflow, offering robust support for artifact management and CI/CD pipelines. This integration enhances the automation, security, and traceability of your release process.
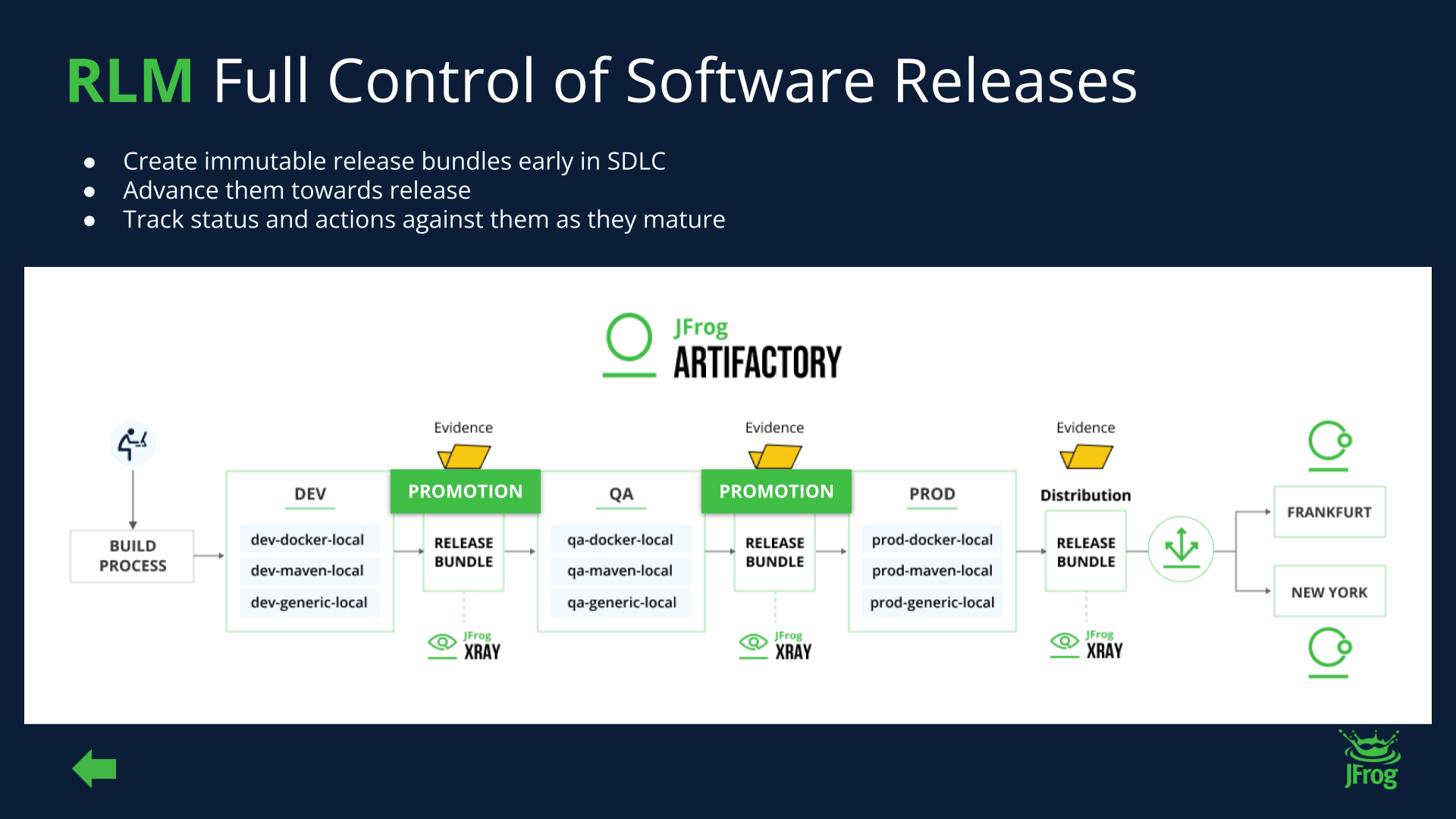
JFrog Artifactory acts as a centralized and universal repository for all software artifacts, including those generated by a semantic release process. It enables teams to manage, store, and secure versioned releases, ensuring that every component is traceable. Artifactory’s API and rich metadata capabilities are instrumental in providing the “single source of truth” necessary for a successful semantic release strategy.
When using JFrog with semantic release, it is strongly recommended to provide comprehensive application security by implementing vulnerability scanning at every stage of development, on every build. Solutions such as JFrog Xray and Advanced Security scan dependencies and packages for potential vulnerabilities, and determine remediation priorities based on the likelihood of an actual breach for each individual application. Additionally, use Artifactory’s promotion features to manage the lifecycle of your releases, moving them from a “staging” repository to a “production” repository only after they have passed all quality gates.
Want to see how JFrog streamlines your software releases and enhances your development workflows? Then feel free to take an online tour, to explore the platform for yourself, schedule a guided demo for a personalized walkthrough, or start a free trial at your convenience.