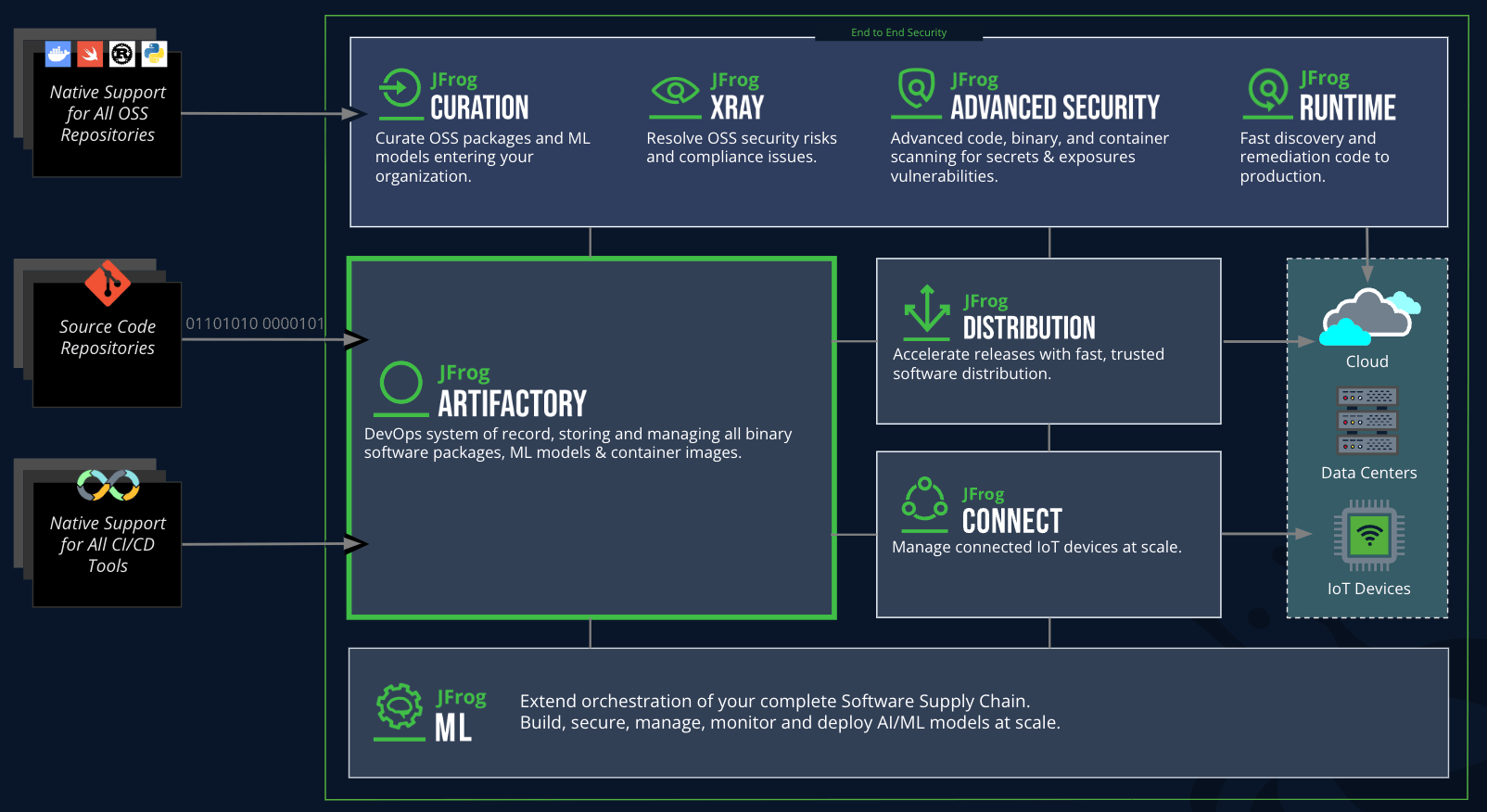
helping to deliver secure software updates from code to the edge.
You have been redirected to the JFrog website


Go-Registry - Wiki

So verwenden Sie JFrog Artifactory und GoCenter zusammen, um Go-Apps zu erstellen

Kurzanleitung: Go
JFrog Artifactory bietet ein zentralisiertes und sicheres Repository für Go-Module, mit dem Sie sowohl öffentliche als auch private Go-Abhängigkeiten verwalten können. Es verbessert die Kontrolle über Go-Module, verbessert die Sicherheit durch Berechtigungsverwaltung und gewährleistet die Rückverfolgbarkeit. Artifactory hilft auch beim Zwischenspeichern externer Go-Module und ermöglicht eine effiziente Abhängigkeitsauflösung in Ihren Entwicklungsteams.
Um Ihr Go-Projekt so zu konfigurieren, dass es JFrog Artifactory als Go-Registry verwendet, befolgen Sie diese Schritte:
Richten Sie ein Go-Repository in JFrog Artifactory ein.
Ändern Sie Ihre Go-Umgebung so, dass sie auf Artifactory verweist. Legen Sie die Umgebungsvariable GOPROXY auf Ihr Artifactory Go-Repository fest:
export GOPROXY=
So veröffentlichen Sie private Go-Module in JFrog Artifactory:
Konfigurieren Sie zunächst Ihren GOPROXY so, dass er auf das Artifactory Go-Repository verweist.
Verwenden Sie den Befehl go, um das Modul zu veröffentlichen:
go mod tidy
go mod vendor
go mod download
Nachdem Sie das Modul vorbereitet haben, stellen Sie es in Artifactory bereit, indem Sie die Go-Repository-Schnittstelle von Artifactory oder eine in Artifactory integrierte CI/CD-Pipeline verwenden.
Die Authentifizierung bei JFrog Artifactory kann mithilfe von API-Schlüsseln, Zugriffstoken oder der Basisauthentifizierung (Benutzername/Passwort) erfolgen. Sie können Ihre Authentifizierung mit netrc konfigurieren:
machine
login
passwort
Sobald dies eingestellt ist, kann Ihr Go-Client Module sicher zu und von Artifactory ziehen und pushen.
JFrog Artifactory bietet volle Unterstützung für die Versionierung von Go-Modulen, indem Module auf der Grundlage der semantischen Versionierung (v0, v1, v2 usw.) bereitgestellt werden. Artifactory fungiert als Go-Proxy und löst Abhängigkeiten auf, indem es Module sowohl aus lokalen als auch aus Remote-Repositories abruft. Die Lösung unterstützt das Caching von externen Abhängigkeiten (von proxy.golang.org, GitHub usw.), was eine schnellere Auflösung und bessere Stabilität durch die Reduzierung externer Netzwerkanfragen gewährleistet.