Définition
Une attestation de logiciel (en anglais, Software Attestation) est une déclaration vérifiable et authentifiée, étayée par des preuves, selon laquelle un logiciel donné répond à des normes de sécurité et de qualité prédéfinies. Ce processus est essentiel pour confirmer que le logiciel est conforme aux politiques, normes ou réglementations requises avant qu’il ne soit déployé.
Aperçu de la gouvernance logicielle
Les attestations de logiciels instaurent une couche de confiance fondamentale en créant un registre vérifiable et auditable de l’historique d’un logiciel et de sa posture de sécurité. Elles sont essentielles pour instaurer la confiance dans la chaîne d’approvisionnement logicielle en donnant aux consommateurs l’assurance de l’intégrité et de l’origine des logiciels. Le processus d’attestation logicielle consiste à générer une déclaration signée contenant des informations sur l’origine du logiciel, son processus de build et les mesures de sécurité appliquées durant le développement – en somme, une garantie cryptographique de la provenance du logiciel et du respect des bonnes pratiques de développement sécurisé.
Les attestations sont un élément important de la Gouvernance, gestions des risques et conformité (GRC) car la réussite d’un plan de GRC dépend de la capacité d’une organisation à collecter des attestations et à agir en conséquence.
Importance des attestations logicielles dans le développement de logiciels sécurisés
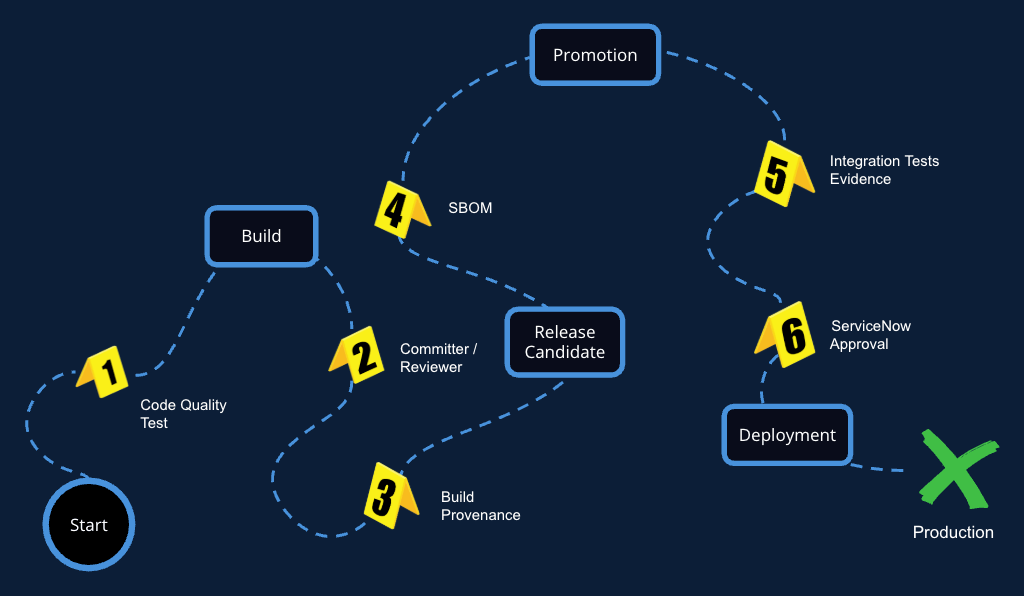
Les attestations logicielles sont un élément clé d’un cycle de vie de développement logiciel (SDLC) sécurisé, car elles offrent un mécanisme pour valider l’intégrité des composants à chaque étape. À l’heure où les logiciels sont de plus en plus constitués de composants tiers et open source, les attestations permettent de s’assurer que chaque morceau de code a été vérifié et qu’il provient d’une source fiable. Cette vérification est essentielle pour empêcher l’introduction de codes malveillants ou de vulnérabilités dans le produit final. En exigeant des attestations, les organisations peuvent faire appliquer leurs politiques de sécurité et s’assurer que tous les logiciels respectent un socle de sécurité homogène avant intégration ou déploiement, réduisant ainsi fortement le risque d’attaques sur la chaîne d’approvisionnement.
Acteurs clés du processus d’attestation
Collecte de preuves tout au long du SDLC
Le processus de Software Attestation mobilise plusieurs parties prenantes à différents stades du SDLC, chacune ayant des responsabilités distinctes :
- Les développeurs sont responsables d’appliquer des pratiques de codage sécurisé et de fournir les premières preuves et métadonnées relatives au code qu’ils écrivent.
- Les ingénieurs DevSecOps intègrent la génération et la vérification d’attestations dans les processus CI/CD et automatisent le processus afin de le rendre reproductible et évolutif.
- Les équipes de sécurité définissent les politiques et les normes de sécurité auxquelles le logiciel doit se conformer. Elles sont souvent chargées d’examiner et de valider les attestations afin d’en garantir la conformité.
- Les responsables release veillent à ce que seuls les logiciels dont les attestations sont valides et vérifiées soient approuvés en vue de leur déploiement.
- Les auditeurs, les régulateurs ou les responsables GRC sont les consommateurs finaux de l’attestation, qu’ils utilisent pour vérifier l’intégrité et la fiabilité du logiciel qu’ils reçoivent.
Le rôle de l’attestation logicielle dans la mise en conformité de la sécurité
L’attestation logicielle est un mécanisme puissant qui permet de démontrer le respect des obligations réglementaires et sectorielles en matière de sécurité. Elle fournit la preuve tangible qu’une organisation suit les pratiques de développement sécurisé prescrites.
Comment l’attestation logicielle favorise la conformité avec les normes de l’industrie
De nombreuses normes industrielles et réglementations gouvernementales, telles que le NIST (Secure Software Development Framework (SSDF)), exigent des organisations qu’elles fournissent des preuves de leurs pratiques de développement sécurisé. L’attestation logicielle soutient directement la conformité en générant des enregistrements immuables et vérifiables qui confirment le respect de ces normes. Par exemple, une attestation peut prouver qu’une analyse de vulnérabilité a été effectuée, que le code a été construit dans un environnement sécurisé ou que tous les composants inclus proviennent de sources fiables. Ces attestations peuvent être présentées aux auditeurs et aux organismes de réglementation comme des preuves concrètes de la conformité, ce qui simplifie le processus d’audit et réduit le risque de sanctions pour non-conformité.
La relation entre l’attestation logicielle et la gestion des risques
L’attestation logicielle est un élément clé d’une gestion des risques opérationnels. En fournissant une trace vérifiable de l’intégrité et de la provenance d’un logiciel, l’attestation aide les organisations à identifier et atténuer les risques liés à l’altération du code, aux modifications non autorisées et à l’intégration de composants vulnérables. Lorsqu’une organisation peut faire confiance aux logiciels qu’elle déploie, elle réduit le risque opérationnel lié aux failles de sécurité, aux pannes de système et aux dommages financiers et réputationnels qui en découlent. L’attestation fournit les données nécessaires à l’évaluation des risques, ce qui permet aux équipes chargées de la sécurité de prendre des décisions éclairées sur les logiciels dont l’utilisation est sûre et sur les faiblesses potentielles de la chaîne d’approvisionnement.
Études de cas démontrant la conformité grâce à l’attestation
Bien que les études de cas internes soient souvent confidentielles, l’impact de l’attestation logicielle est évident dans la façon dont les gouvernements et les industries hautement réglementées l’adoptent. À la suite d’attaques très médiatisées de la chaîne d’approvisionnement, le gouvernement américain a publié l’Executive Order 14028, qui oblige les agences fédérales à obtenir une nomenclature logicielle (SBOM) et une attestation pour les logiciels qu’ils achètent.
Les entreprises qui fournissent des logiciels au gouvernement fédéral américain utilisent désormais des attestations pour prouver que leurs produits répondent à ces nouvelles exigences strictes en matière de sécurité. Par exemple, un fournisseur de logiciels peut attester que son produit a été développé conformément au NIST SSDF, satisfaisant ainsi aux règles de passation des marchés publics fédéraux et démontrant un engagement en faveur de la sécurité qui renforce la confiance de ses clients gouvernementaux.
Bonnes pratiques pour l’attestation logicielle
La mise en œuvre d’un processus d’attestation logicielle efficace nécessite une combinaison d’outils automatisés, de directives procédurales claires et d’une culture de sensibilisation à la sécurité. Le respect des meilleures pratiques garantit que les attestations sont à la fois fiables et significatives.
Étapes de la mise en œuvre de processus efficaces d’attestation logicielle
Une mise en œuvre réussie de l’attestation logicielle suit une approche structurée :
- Définition de politiques : établir des politiques de sécurité et de conformité claires à l’échelle de l’organisation qui définissent ce qui doit être attesté. Il s’agit notamment de spécifier les analyses de sécurité requises, les bibliothèques approuvées et les environnements de build sécurisés.
- Intégration dans le SDLC : intégrer le processus d’attestation directement dans le pipeline CI/CD. Les attestations doivent être générées automatiquement à des étapes clés, par exemple après un build réussi ou des analyses de sécurité réussies.
- Automatisation de la collecte de preuves : utiliser des outils permettant de récolter les preuves nécessaires de manière automatique, tels que les résultats d’analyse, les journaux de builds et les certificats de signature de code. Cela minimise le travail manuel et réduit le risque d’erreur humaine.
- Génération et signature des attestations : créez un format standardisé pour vos attestations et signez-les par cryptographie pour garantir leur authenticité et leur intégrité.
- Remarque : vous pouvez décoder et vérifier les cadres SLSA, in-toto et Sigstore avec le décodeur en ligne d’attestation DSSE gratuit de JFrog.
- Stockage et vérification : stocker les attestations signées dans un endroit sûr et accessible, tel qu’un référentiel d’artefacts. Mettre en œuvre des contrôles automatisés pour vérifier la validité des attestations avant le déploiement de tout logiciel.
Outils et technologies pour rationaliser les efforts d’attestation
Plusieurs outils et technologies sont disponibles pour aider à automatiser et à rationaliser le processus d’attestation logicielle. Les outils de signature, tels que Sigstore sont en train de devenir des normes industrielles pour la signature cryptographique des artefacts logiciels et des attestations. Les plateformes CI/CD telles que Jenkins, CircleCI et GitHub Actions peuvent être configurées pour déclencher la génération d’attestations en tant que partie intégrale du pipeline. Des plateformes telles que la plateforme de chaîne d’approvisionnement logicielle de JFrog peuvent servir de référentiel central pour le stockage et la gestion des artefacts logiciels et des attestations correspondantes, fournissant ainsi une source unique de vérité pour la posture de sécurité de votre logiciel.
Défis et solutions courants en matière d’attestation logicielle
Les organisations sont souvent confrontées à plusieurs défis communs lors de la mise en œuvre d’attestations logicielles :
- Complexité et échelle : il n’est pas possible de générer et de gérer manuellement des attestations pour des milliers de composants logiciels. La solution : l’automatisation. En intégrant l’attestation dans le pipeline CI/CD, le processus peut être étendu sans surcharger les équipes de développement.
- Manque de normalisation : sans un format consistant, les attestations peuvent être difficiles à interpréter et à vérifier. La solution : L’adoption de normes industrielles, telles que les attestations in toto fournit un cadre commun qui simplifie le processus.
- Résistance des équipes de développement : certains développeurs considèrent l’attestation comme un fardeau additionnel. La solution : utiliser des outils conviviaux pour les développeurs et qui s’intègrent de manière transparente dans leurs workflows existants. Une documentation et une formation claires peuvent également contribuer à démontrer la valeur de l’attestation et à encourager son adoption.
Améliorer l’attestation logicielle avec JFrog
La mise en œuvre réussie de l’attestation logicielle nécessite une approche globale de la gestion de l’ensemble du cycle de vie de vos artefacts logiciels. Du stockage sécurisé à l’analyse des vulnérabilités et à la distribution, chaque étape doit être sécurisée pour garantir l’intégrité de votre chaîne d’approvisionnement logicielle.
Avec JFrog Evidence Collection, pilier de la plateforme JFrog, ce défi trouve une solution nette : l’attestation logicielle devient un accélérateur stratégique d’une livraison logicielle à la fois sécurisée et à grande vitesse.
Passez à l’étape suivante de la sécurisation de votre chaîne d’approvisionnement logicielle. Commencez un essai gratuit de la plateforme JFrog pour voir comment vous pouvez automatiser votre processus d’attestation logicielle.
En savoir plus sur JFrog Xray et ses capacités avancées de scan de sécurité.
Consultez les articles connexes sur la Sécurité de la chaîne d’approvisionnement logicielle et la création d’un la Nomenclature logicielle (SBOM).